Overview
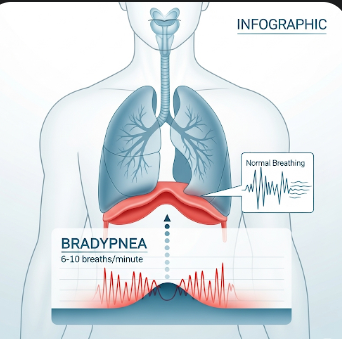
Bradypnea is a medical condition characterized by abnormally slow breathing, typically defined as fewer than 12 breaths per minute in adults. It can affect oxygen delivery to the body and may indicate underlying respiratory, neurological, or metabolic disorders. While some athletes or healthy individuals may exhibit slow breathing at rest, persistent bradypnea often requires clinical evaluation to prevent complications such as hypoxia or respiratory failure.
In South Korea, pulmonary and critical care centers provide advanced diagnosis and management for bradypnea, ensuring timely interventions for both acute and chronic causes.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Bradypnea is slower than normal breathing and may be accompanied by shallow or irregular respirations.
➡️ Causes can range from benign (e.g., athletic conditioning) to serious medical conditions such as drug overdose or brain injury.
➡️ Early detection is critical, as severe bradypnea can compromise oxygen supply to vital organs.
➡️ Monitoring and treatment depend on the underlying cause, patient age, and severity of symptoms.
➡️ South Korea provides specialized respiratory care, including advanced ventilatory support and monitoring.
What is Bradypnea?
Bradypnea is a respiratory condition characterized by an abnormally low rate of breathing.
Characteristics include:
- Respiratory rate slower than 12 breaths per minute in adults
- Shallow or irregular breathing may accompany slow respiratory rate
- May cause dizziness, fatigue, or fainting due to reduced oxygen levels
- Can be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying cause
- Often observed in hospitalized patients, those with respiratory or neurological disorders, or those taking certain medications
Bradypnea differs from other breathing abnormalities, such as tachypnea (rapid breathing) or apnea (absence of breathing).
What Symptoms are Related to Bradypnea?
Symptoms can vary depending on severity and cause:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or confusion due to hypoxia
- Fatigue or lethargy
- Bluish discoloration of lips or fingertips (cyanosis) in severe cases
- Headache or drowsiness due to elevated carbon dioxide (hypercapnia)
- Reduced exercise tolerance
Highlights:
➡️ Bradypnea may be asymptomatic in mild cases, especially in athletes or during sleep.
➡️ Severe or sudden bradypnea is a medical emergency and requires prompt intervention.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Bradypnea?
Highlights:
➡️ Central Nervous System Disorders: Brain injury, stroke, or tumors affecting respiratory centers in the brainstem.
➡️ Medications and Drugs:
- Opioids or sedatives can suppress the respiratory drive
- Certain anesthetics and muscle relaxants
➡️ Metabolic Disorders:
- Hypothyroidism or severe electrolyte imbalances
- Metabolic encephalopathy affecting breathing patterns
➡️ Respiratory Conditions: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or severe pneumonia in some cases
➡️ Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Slow or irregular breathing during sleep phases
➡️ Heart Conditions: Severe heart failure can reduce oxygen delivery and contribute to slow breathing
➡️ Normal Variants: Athletes or individuals with high cardiovascular efficiency may exhibit mild bradypnea at rest
➡️ Mechanism: Bradypnea occurs when the respiratory drive from the brain or feedback from oxygen/carbon dioxide sensors is impaired, reducing the rate or depth of breathing.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If you experience persistent slow breathing accompanied by dizziness, confusion, or fatigue.
➡️ If bradypnea occurs suddenly or worsens rapidly, particularly in combination with bluish lips, fainting, or severe shortness of breath.
➡️ If taking medications known to affect breathing, such as opioids or sedatives.
➡️ For children or elderly patients, even mild bradypnea warrants evaluation due to higher risk of complications.
➡️ Early medical assessment ensures timely management, preventing hypoxia, organ damage, or respiratory failure.
Care and Treatment
Management focuses on treating the underlying cause and ensuring adequate oxygenation:
Highlights:
➡️ Monitoring: Continuous pulse oximetry, respiratory rate checks, and arterial blood gas analysis.
➡️ Medication Adjustment: Reducing or discontinuing drugs that suppress breathing under medical supervision.
➡️ Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen for hypoxemia or low oxygen saturation.
➡️ Mechanical Ventilation: In severe or acute cases, ventilatory support may be required.
➡️ Treatment of Underlying Disorders:
- CNS disorders: neurosurgical or neurological interventions
- Metabolic disorders: correcting electrolyte or hormonal imbalances
- Respiratory infections: antibiotics, antivirals, or supportive care
➡️ Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding sedatives, managing sleep apnea, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
➡️ Patient Education: Recognizing early warning signs and when to seek urgent care.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced respiratory and critical care services for patients with bradypnea:
Highlights:
➡️ Pulmonology and Critical Care Clinics: Specialized assessment and monitoring of breathing disorders.
➡️ Advanced Ventilatory Support: Non-invasive ventilation (CPAP/BiPAP) and ICU-level mechanical ventilation.
➡️ Neurology and Endocrinology Services: Management of CNS or metabolic causes.
➡️ Sleep Medicine Centers: Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea contributing to bradypnea.
➡️ Medication Management Programs: Optimized drug therapy to reduce respiratory depression risk.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Approach: Pulmonologists, neurologists, endocrinologists, and critical care specialists collaborate for comprehensive care.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Structured evaluation, multilingual consultation, and follow-up care for international patients seeking treatment in Korea.