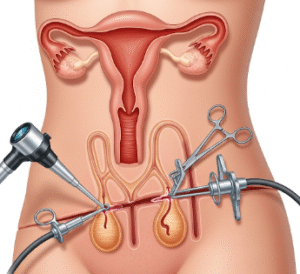
Overview
Blood in urine, medically known as hematuria, is a condition where red blood cells are present in the urine. It may appear as pink, red, or cola-colored urine, depending on the amount and source of bleeding. Hematuria can be visible (gross hematuria) or detectable only under a microscope (microscopic hematuria). While sometimes harmless, blood in urine can indicate serious urinary tract issues, kidney disease, or systemic conditions. In Korea, urology clinics and hospitals provide advanced diagnostic evaluations, treatment options, and preventive care for patients presenting with hematuria.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Can occur in individuals of all ages; more common in adults with urinary tract infections or kidney problems.
▶ Appearance: Pink, red, brown, or cola-colored urine.
▶ Causes: Urinary tract infections, kidney stones, trauma, tumors, or systemic diseases.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Pain during urination, frequent urination, abdominal or flank pain, and urinary urgency.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Antibiotics, minimally invasive surgeries, kidney stone removal, tumor management, and lifestyle adjustments.
What is Blood in Urine?
Hematuria refers to the presence of red blood cells in the urinary system, which can originate from any part of the urinary tract, including kidneys, ureters, bladder, prostate, or urethra.
▶ Gross Hematuria: Blood is visible to the naked eye; urine may appear pink, red, or brown.
▶ Microscopic Hematuria: Blood is present but detectable only through urine tests.
▶ Transient Hematuria: Temporary and often harmless, caused by exercise or minor trauma.
▶ Persistent Hematuria: Ongoing bleeding requiring medical investigation to identify the source.
Note: Hematuria is a symptom, not a disease; identifying the underlying cause is critical for effective treatment.
What Symptoms Are Related to Blood in Urine?
▶ Visible Blood in Urine: Pink, red, or cola-colored urine.
▶ Pain or Burning Sensation: During urination, often associated with infections or stones.
▶ Frequent Urination: Urgency and increased urinary frequency.
▶ Abdominal or Flank Pain: Often seen with kidney stones or urinary obstruction.
▶ Fever or Chills: May indicate a urinary tract infection.
▶ Back Pain: Kidney involvement or obstruction can cause lower back discomfort.
▶ Fatigue: Chronic blood loss can lead to anemia.
▶ Clots in Urine: Presence of blood clots in more severe cases.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Blood in urine can result from urinary tract, kidney, systemic, or traumatic causes:
▶ Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections causing inflammation and bleeding.
▶ Kidney Stones: Hard deposits damaging urinary tract tissues.
▶ Bladder or Kidney Tumors: Benign or malignant growths causing hematuria.
▶ Trauma: Injury to the kidneys, bladder, or urethra.
▶ Enlarged Prostate (BPH): Can lead to urinary tract obstruction and bleeding in men.
▶ Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of kidney filters affecting urine color.
▶ Medications: Blood thinners, anticoagulants, or chemotherapy agents.
▶ Strenuous Exercise: Temporary hematuria after intense physical activity.
▶ Inherited Disorders: Polycystic kidney disease or sickle cell disease affecting renal function.
Note: Determining the exact cause requires urinalysis, imaging, and sometimes cystoscopy or kidney evaluation.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Visible Blood in Urine: Any presence of blood should be evaluated promptly.
▶ Persistent Hematuria: Ongoing or recurrent episodes need medical assessment.
▶ Painful Urination or Abdominal Pain: Indicates infection, stones, or obstruction.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, or swelling.
▶ Family History: Kidney disease, cancer, or clotting disorders.
▶ Medication Concerns: If taking anticoagulants or other drugs affecting clotting.
▶ Sudden Severe Pain: Especially with kidney stones or trauma.
Tip: Early evaluation ensures accurate diagnosis, prevents complications, and addresses potentially serious underlying conditions.
Care and Treatment
Management depends on the cause, severity, and location of bleeding:
▶ Antibiotic Therapy: For urinary tract infections or bacterial causes.
▶ Kidney Stone Management: Lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or surgical removal.
▶ Tumor Treatment: Surgical removal, chemotherapy, or minimally invasive procedures for bladder or kidney tumors.
▶ Medication Review: Adjusting drugs that may cause bleeding.
▶ Hydration and Lifestyle: Adequate water intake, avoiding irritants, and monitoring urinary habits.
▶ Monitoring: Regular urine tests to track hematuria and response to treatment.
▶ Supportive Care: Pain management, anemia treatment, and dietary modifications if necessary.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
▶ Urology Consultation: Comprehensive assessment including history, physical exam, and risk evaluation.
▶ Laboratory Tests: Urinalysis, urine culture, blood tests for kidney function and coagulation.
▶ Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI for structural or obstructive causes.
▶ Cystoscopy: Endoscopic examination of the bladder to detect tumors, stones, or injury.
Advanced Therapies:
▶ Minimally Invasive Procedures: Lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or laser treatments for stones or tumors.
▶ Surgical Intervention: Rarely required for severe or persistent bleeding from tumors or structural issues.
▶ Medication Therapy: Tailored antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or medications to control underlying conditions.
▶ Supportive Care: Iron supplementation for anemia, hydration, and dietary guidance.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Patient Education: Guidance on recognizing symptoms, preventing recurrence, and maintaining urinary tract health.
▶ Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring with urinalysis and imaging to ensure resolution.
▶ Specialist Clinics: Korean hospitals offer integrated care combining urology, nephrology, imaging, and patient support services.
Outcome: With timely evaluation and comprehensive treatment in Korea, blood in urine is effectively addressed, underlying causes are treated, and urinary and renal health is preserved, preventing complications such as chronic kidney disease or malignancy progression.