Overview
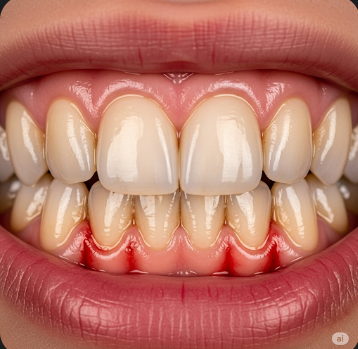
Bleeding gums, medically referred to as gingival bleeding, occur when the gum tissue becomes inflamed, sensitive, or damaged, causing blood to appear during brushing, flossing, or even spontaneously. While occasional minor bleeding may result from aggressive brushing or trauma, persistent or recurrent bleeding can indicate underlying gum disease, nutritional deficiencies, systemic conditions, or medication side effects. In Korea, dental clinics and hospitals provide comprehensive oral care, advanced diagnostic tools, and preventive therapies to manage bleeding gums effectively and maintain overall oral health.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Common among adults and children, particularly those with poor oral hygiene.
▶ Appearance: Blood may be visible on toothbrushes, floss, or in the mouth.
▶ Causes: Gingivitis, periodontitis, vitamin deficiencies, hormonal changes, medications, or systemic conditions.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Swollen or tender gums, bad breath, loose teeth, or gum recession.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Professional dental cleaning, periodontal therapy, medications, laser treatments, and oral hygiene education.
What are Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums occur when the gum tissue becomes inflamed or compromised, making it susceptible to bleeding during minor trauma or spontaneously.
▶ Gingivitis: Mild gum inflammation without bone loss, often reversible with proper care.
▶ Periodontitis: Advanced gum disease affecting the supporting structures of teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss.
▶ Medication-Induced Bleeding: Some medications, such as anticoagulants, can increase gum bleeding risk.
▶ Hormonal or Systemic Factors: Pregnancy, menopause, diabetes, or blood disorders can contribute.
Note: Bleeding gums are a warning sign that oral health requires attention, and early intervention prevents more serious complications.
What Symptoms Are Related to Bleeding Gums?
▶ Red, Swollen Gums: Inflammation visible along the gum line.
▶ Tenderness or Pain: Discomfort while brushing or eating.
▶ Persistent Bleeding: Gums that bleed easily, even with light pressure.
▶ Bad Breath (Halitosis): Caused by bacterial buildup in inflamed gums.
▶ Receding Gums: Exposure of tooth roots due to tissue loss.
▶ Loose Teeth: In advanced periodontitis, teeth may become unstable.
▶ Discoloration of Gums: Dark red or purplish hue indicating inflammation or infection.
▶ Pus or Infection Signs: Rare, but may occur in severe gum disease.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Bleeding gums can result from local, systemic, or lifestyle-related factors:
▶ Poor Oral Hygiene: Plaque accumulation leads to gingival inflammation.
▶ Gingivitis: Early-stage gum disease caused by bacterial infection.
▶ Periodontitis: Advanced gum disease with tissue and bone damage.
▶ Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of vitamin C (scurvy) or vitamin K can impair clotting.
▶ Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, puberty, or menopause increase gum sensitivity.
▶ Medications: Blood thinners, certain antihypertensives, or chemotherapy drugs.
▶ Medical Conditions: Diabetes, leukemia, clotting disorders, or immune deficiencies.
▶ Trauma: Brushing too hard, flossing aggressively, or dental appliances causing injury.
Note: Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further complications.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Persistent or Recurrent Bleeding: Even with proper oral care.
▶ Swollen or Painful Gums: Significant discomfort or inflammation.
▶ Loose Teeth or Gum Recession: Signs of advanced periodontal disease.
▶ Systemic Symptoms: Fatigue, unexplained bruising, or prolonged bleeding elsewhere.
▶ Medication Concerns: If taking anticoagulants or other medications that increase bleeding risk.
▶ Signs of Infection: Pus, fever, or severe pain in the gums.
▶ Difficulty Eating or Speaking: Due to oral discomfort.
Tip: Early dental evaluation ensures proper diagnosis, prevents disease progression, and supports overall oral and systemic health.
Care and Treatment
Management of bleeding gums focuses on reducing inflammation, improving oral hygiene, and treating underlying causes:
▶ Professional Cleaning: Removal of plaque and tartar to reduce bacterial infection.
▶ Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning for patients with periodontitis.
▶ Medication Therapy: Antimicrobial mouth rinses, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory drugs as prescribed.
▶ Nutritional Support: Adequate intake of vitamin C, vitamin K, and other essential nutrients.
▶ Improved Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing, and rinsing.
▶ Lifestyle Modifications: Smoking cessation, balanced diet, and stress management.
▶ Regular Monitoring: Follow-up dental visits to track gum health and prevent recurrence.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
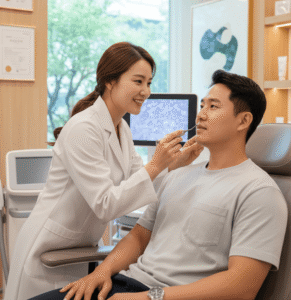
▶ Dental Consultation: Comprehensive oral exam including gum probing and X-rays.
▶ Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to detect vitamin deficiencies or clotting disorders.
▶ Periodontal Assessment: Determination of gum disease severity and treatment planning.
Advanced Therapies:
▶ Laser Gum Treatment: Minimally invasive procedures to remove infected tissue and promote healing.
▶ Surgical Intervention: Flap surgery or bone grafts for severe periodontitis.
▶ Prescription Medications: Antimicrobial gels, mouth rinses, or systemic antibiotics for infections.
▶ Preventive Programs: Dental clinics in Korea provide structured programs combining cleaning, education, and monitoring.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Patient Education: Proper brushing, flossing techniques, and gum care routines.
▶ Follow-Up Care: Monitoring for signs of recurrence or progression.
▶ Specialist Clinics: Korean dental hospitals offer integrated care combining preventive, medical, and surgical treatments for gum health.
Outcome: With early intervention and proper management in Korea, bleeding gums are effectively treated, inflammation is reduced, and long-term oral health is maintained, preventing tooth loss and systemic complications.