Overview
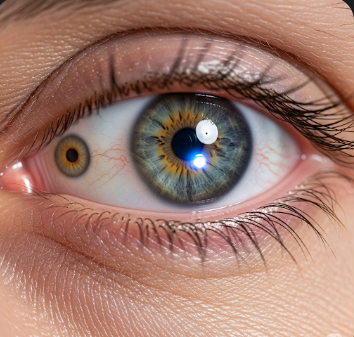
Argyll Robertson Pupil is a rare ophthalmologic sign characterized by small, irregular pupils that constrict when focusing on near objects (accommodation) but do not constrict in response to bright light (light-near dissociation). It is most commonly associated with neurosyphilis, particularly in its tertiary stage, but can also occur in other neurological conditions.
In South Korea, ophthalmology and neurology clinics provide diagnostic evaluation, including detailed eye examinations, neurological assessment, and laboratory testing for syphilis and other systemic conditions. Early recognition of Argyll Robertson pupil is crucial for timely intervention, as it often signals underlying neurological disease requiring comprehensive management.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Argyll Robertson pupil shows constriction during accommodation but not in response to light.
➡️ It is most commonly associated with tertiary neurosyphilis, but can be seen in diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or other central nervous system disorders.
➡️ Usually bilateral and small in size.
➡️ Serves as a clinical marker for neurological involvement in systemic diseases.
➡️ Early diagnosis aids in the treatment of underlying infections or neurological conditions.
What is Argyll Robertson Pupil?
Argyll Robertson pupil is defined by its light-near dissociation:
- Accommodation Response: Pupils constrict normally when focusing on a close object.
- Light Response: Pupils fail to constrict adequately in response to direct bright light.
The pupils are typically small, irregular, and bilateral, often described as “prostitute’s pupils” in historical medical literature, reflecting their selective response. This phenomenon is usually a sign of midbrain or pretectal area involvement in the central nervous system.
What Symptoms are Related to Argyll Robertson Pupil?
While the pupil abnormality itself may not cause noticeable visual symptoms, associated features often relate to the underlying neurological or systemic condition:
- Difficulty with visual adaptation to light and darkness
- Diplopia (double vision) in some cases
- Signs of neurosyphilis: cognitive changes, gait disturbances, or sensory deficits
- Other neurological deficits depending on central nervous system involvement
- Occasionally mild photophobia
- May coexist with other ocular signs such as optic atrophy or retinal changes
What Causes / Possible Causes of Argyll Robertson Pupil?
Highlights:
➡️ Neurosyphilis: The classic cause, resulting from syphilitic infection affecting the midbrain.
➡️ Diabetes Mellitus: Chronic diabetes can cause autonomic neuropathy affecting pupillary reflexes.
➡️ Multiple Sclerosis: Demyelinating lesions in the midbrain may produce light-near dissociation.
➡️ Other Neurological Disorders: Brainstem lesions, tumors, or trauma involving pretectal or midbrain areas.
➡️ Congenital Causes: Rarely, some individuals may have similar pupillary characteristics from birth.
➡️ Medication Effects: Certain drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system may mimic pupillary abnormalities.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If you notice abnormal pupil size, shape, or response to light.
➡️ If there is difficulty adapting to changes in lighting or experiencing unusual visual symptoms.
➡️ For evaluation of potential underlying infections, such as syphilis, or neurological disorders.
➡️ If accompanied by neurological symptoms such as gait changes, numbness, weakness, or cognitive difficulties.
➡️ For early diagnosis to prevent progression of underlying systemic or neurological disease.
➡️ To differentiate pupillary abnormalities caused by medication, trauma, or congenital conditions.
Care and Treatment
Management of Argyll Robertson pupil focuses on treating the underlying cause and monitoring neurological function.
Highlights:
➡️ Infection Management: Prompt treatment of neurosyphilis with intravenous penicillin or appropriate antibiotics.
➡️ Neurological Monitoring: Evaluation for central nervous system involvement using imaging and neurological exams.
➡️ Chronic Disease Management: Control of diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or other contributing systemic conditions.
➡️ Ophthalmologic Follow-Up: Monitoring visual function, pupillary responses, and detecting complications.
➡️ Symptom Support: Visual aids, environmental adaptations, or counseling for light sensitivity.
➡️ Education and Awareness: Understanding the significance of pupillary changes and adherence to treatment plans.
➡️ Regular Screening: Periodic check-ups to assess progression or improvement following therapy.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced diagnostic and treatment options for Argyll Robertson pupil and associated conditions:
Highlights:
➡️ Ophthalmology Clinics: Comprehensive eye examinations, pupillometry, and visual function testing.
➡️ Neurology Centers: Evaluation and management of central nervous system conditions causing light-near dissociation.
➡️ Infectious Disease Clinics: Diagnosis and treatment of neurosyphilis with intravenous antibiotics and follow-up testing.
➡️ Integrated Multidisciplinary Care: Collaboration among ophthalmologists, neurologists, and infectious disease specialists.
➡️ Chronic Disease Management Programs: Support for diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and other systemic contributors.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Multilingual services, structured evaluation and treatment plans, and follow-up care for international patients.
➡️ Patient Education: Guidance on pupillary abnormalities, visual adaptation, and prevention of complications from underlying diseases.