Overview
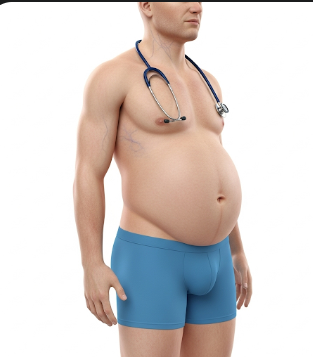
Abdominal distension, also known as a distended abdomen or bloating, is a common condition where the stomach area feels swollen or enlarged. It can be caused by gas, fluid retention, overeating, or underlying medical conditions. The sensation is often accompanied by discomfort, fullness, or visible swelling in the abdominal region.
While occasional bloating is generally harmless, persistent or severe distension may indicate gastrointestinal, liver, or systemic health issues. In South Korea, specialized gastroenterology and hepatology centers provide accurate diagnosis and advanced treatment options for abdominal distension, ensuring effective management of both minor and serious causes.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Abdominal distension is characterized by visible swelling or a feeling of fullness in the stomach area.
➡️ It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (lasting weeks or months).
➡️ Common causes include gas accumulation, constipation, fluid retention, or digestive disorders.
➡️ Persistent distension may signal underlying conditions such as liver disease, IBS, or gastrointestinal obstruction.
➡️ Korean hospitals offer state-of-the-art diagnostics and treatment options for effective management.
What is Abdominal Distension?
Abdominal distension refers to an enlargement of the abdominal area that is noticeable either visibly or as a sensation of fullness. It may be temporary, such as after eating a large meal, or chronic due to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), liver disease, or ascites (fluid buildup). The degree of distension may vary from mild bloating to significant swelling that affects daily activities.
What Symptoms are Related to Abdominal Distension?
Symptoms often associated with abdominal distension include:
- Swelling or visible enlargement of the abdomen
- Feeling of fullness or tightness
- Pain or discomfort in the stomach area
- Excessive burping or flatulence
- Nausea or decreased appetite
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath in severe cases
- Fatigue or malaise if associated with systemic disease
What Causes / Possible Causes of Abdominal Distension?
Highlights:
➡️ Digestive Disorders: Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, gastroparesis, or constipation.
➡️ Dietary Factors: Overeating, high-fiber foods, carbonated beverages, or food intolerances (e.g., lactose intolerance).
➡️ Fluid Retention: Ascites caused by liver disease, kidney disease, or heart failure.
➡️ Gastrointestinal Obstruction: Partial or complete blockage in the intestines.
➡️ Hormonal Causes: Menstruation, pregnancy, or hormonal imbalances.
➡️ Infections: Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections causing gastrointestinal upset.
➡️ Medical Conditions: Liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, or tumors affecting abdominal organs.
➡️ Medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants or steroids, may contribute.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If abdominal swelling is sudden, severe, or persistent.
➡️ If accompanied by severe pain, vomiting, or inability to pass gas or stool.
➡️ If there is unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or fever.
➡️ If the abdomen feels hard, tender, or shows signs of fluid buildup.
➡️ If nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin/eyes), or breathing difficulties occur.
➡️ For chronic or recurring distension that affects quality of life.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the distension. Common approaches include:
Highlights:
➡️ Dietary Adjustments: Avoiding gas-producing foods, carbonated drinks, and managing portion sizes.
➡️ Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, proper hydration, and stress management.
➡️ Medications: Laxatives for constipation, antacids, or medications for IBS or acid reflux.
➡️ Fluid Management: For cases involving fluid retention, diuretics or specific medical therapies may be prescribed.
➡️ Procedures: In severe ascites, fluid may be drained through paracentesis under medical supervision.
➡️ Surgical Intervention: Required in cases of gastrointestinal obstruction, tumors, or structural abnormalities.
➡️ Monitoring: Tracking symptoms, weight, and abdominal girth to assess treatment effectiveness.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced care for abdominal distension through specialized gastroenterology and hepatology departments.
Highlights:
➡️ Comprehensive Diagnostics: Ultrasound, CT scans, endoscopy, and blood tests to identify the underlying cause.
➡️ Specialized Gastroenterology Clinics: Provide tailored treatment plans for IBS, food intolerances, and other digestive disorders.
➡️ Liver and Kidney Care: Management of fluid retention from cirrhosis or renal issues with advanced therapies.
➡️ Minimally Invasive Procedures: Paracentesis, endoscopic procedures, or laparoscopic surgery for obstruction or tumors.
➡️ Dietary and Lifestyle Counseling: Nutritionists and dietitians design personalized plans to reduce bloating and distension.
➡️ Medical Tourism Services: Multilingual support, structured treatment packages, and follow-up care for international patients.
➡️ Follow-Up Programs: Regular monitoring to ensure long-term management and prevention of recurrence.