Overview
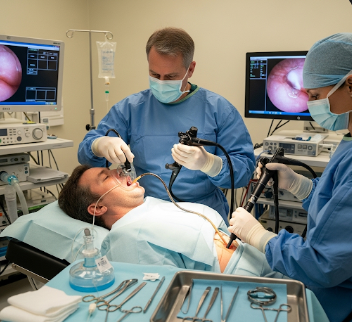
Upper GI endoscopy and colonoscopy are two essential diagnostic procedures used to examine the gastrointestinal tract. Upper GI endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy, EGD) evaluates the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, while colonoscopy examines the large intestine (colon) and rectum.
These procedures are commonly recommended for persistent abdominal pain, unexplained bleeding, chronic constipation, diarrhea, reflux symptoms, or screening for polyps and cancers.
South Korea is a global leader in gastrointestinal endoscopy, offering state-of-the-art equipment, minimally invasive techniques, sedation safety, and highly experienced gastroenterologists. Patients benefit from quick diagnosis, same-day discharge, and fast recovery.
What are Upper GI Endoscopy and Colonoscopy?
Upper GI Endoscopy (EGD):
- ➤ Uses a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) inserted through the mouth
- ➤ Visualizes the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- ➤ Can perform biopsies, polyp removal, or minor treatments during the procedure
Colonoscopy:
- ➤ Uses a longer flexible endoscope inserted through the rectum
- ➤ Examines the entire colon and rectum
- ➤ Can detect polyps, inflammation, tumors, or bleeding sites
- ➤ Allows biopsy or polyp removal during the same session
Both procedures can be performed separately or combined for comprehensive evaluation of the digestive tract.
What are the Benefits?
✔ Early detection of GI diseases, including ulcers, polyps, tumors, and inflammation
✔ Minimally invasive with low complication risk
✔ Real-time diagnosis and ability to perform treatment simultaneously
✔ Safe for adults and children with appropriate sedation
✔ Quick recovery, often same-day discharge
✔ Korean hospitals provide high-definition imaging and expert care
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for Upper GI Endoscopy and Colonoscopy?
- ● Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours before upper GI endoscopy
- ● Bowel preparation: Colonoscopy requires a clear liquid diet and laxatives 1–2 days prior
- ● Medication review: Certain medications (blood thinners, diabetes meds) may need adjustments
- ● Sedation planning: Korean hospitals provide adult and pediatric sedation protocols for comfort and safety
- ● Pre-procedure counseling: Parents or patients receive clear instructions and reassurance
2) What happens during the procedures?
- ➤ Upper GI Endoscopy:
- Sedation or anesthesia is administered
- Endoscope inserted through the mouth
- Gastroenterologist examines esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- Biopsies or minor treatments performed if needed
- ➤ Colonoscopy:
- Sedation ensures patient comfort
- Colonoscope inserted through the rectum
- Entire colon is visualized and cleansed using air/water
- Polyps removed or tissue biopsied as necessary
- ➤ Duration: Typically 15–45 minutes per procedure; both can be performed sequentially under sedation in one session
- ➤ Korean advantage: High-definition scopes and advanced monitoring reduce risk and improve diagnostic accuracy
3) What happens after the procedures?
- ● Recovery: Patients monitored until sedation wears off, usually 1–2 hours
- ● Diet: Resume light meals for adults; children follow pediatric guidance
- ● Observation: Watch for bleeding, pain, or discomfort
- ● Results: Biopsy or polyp reports available in a few days
- ● Korean hospitals: Provide multilingual explanations and follow-up care instructions
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Accurate detection and diagnosis of upper and lower GI issues
- ✦ Minimally invasive and safe
- ✦ Can perform biopsies and remove polyps during the same session
- ✦ Quick recovery and outpatient-friendly
⚠ Risks (rare):
- ➔ Mild sore throat after upper GI endoscopy
- ➔ Cramping, bloating, or minor bleeding after colonoscopy
- ➔ Reaction to sedation
- ➔ Rare perforation or infection
- ➔ Post-polyp removal bleeding (usually minor and manageable)
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Immediate recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within a few hours
- ➤ Full recovery: Usually within 24 hours; mild cramping may occur after colonoscopy
- ➤ Follow-up: Required if biopsies are taken or polyps removed
- ➤ Korean hospitals: Offer structured follow-up, multilingual reports, and expert consultations to ensure patient safety and comfort
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their doctor if they notice:
- ⚠ Persistent bleeding from the mouth or rectum
- ⚠ Severe abdominal pain, swelling, or cramping
- ⚠ Fever or chills after the procedure
- ⚠ Difficulty swallowing or persistent vomiting after upper GI endoscopy
- ⚠ Unusual weakness or dizziness
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a top destination for endoscopic gastrointestinal procedures due to:
- 🌟 Expert gastroenterologists trained in pediatric and adult endoscopy
- 🌟 Advanced equipment including high-definition and 4K scopes
- 🌟 Minimally invasive, outpatient-friendly procedures
- 🌟 Multilingual support for international patients
- 🌟 Integrated care, allowing biopsy analysis, polyp removal, and follow-up in one visit
Top Korean Hospitals for Upper GI Endoscopy and Colonoscopy:
- ✅ Seoul National University Hospital
- ✅ Asan Medical Center
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center
- ✅ Severance Hospital (Yonsei University)
- ✅ Bundang CHA Hospital (specialized GI center)
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Upper GI endoscopy examines esophagus, stomach, and duodenum; colonoscopy examines colon and rectum
- ➤ Safe, minimally invasive procedures with sedation
- ➤ Can perform biopsies or polyp removal in the same session
- ➤ Quick recovery — usually same day discharge
- ➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced imaging, expert care, and comprehensive follow-up