Overview
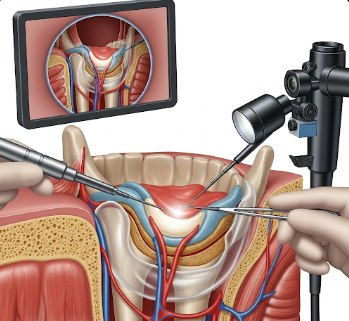
TMJ arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jawbone to the skull. TMJ disorders can cause jaw pain, difficulty chewing, clicking or popping sounds, headaches, and limited mouth opening.
In Korea, TMJ arthroscopy is performed in specialized maxillofacial and oral surgery centers, using advanced endoscopic technology. The procedure offers precise diagnosis, effective treatment, reduced recovery time, and minimal complications compared to open surgery.
What is Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Arthroscopy?
TMJ arthroscopy involves inserting a small endoscope (arthroscope) into the joint space to visualize and treat internal joint issues.
Common indications include:
- ✦ TMJ internal derangement (displaced disc, joint dysfunction).
- ➤ Chronic pain or inflammation not responsive to conservative therapy.
- ✦ Arthritis or degenerative joint disease affecting the TMJ.
- ➤ Adhesions or scar tissue removal to improve mobility.
The procedure may involve joint lavage (washing), debridement, removal of adhesions, or injection of medications to relieve pain and restore function.
What are the Benefits?
TMJ arthroscopy provides several advantages:
✅ Minimally invasive approach with tiny incisions.
➤ Reduces jaw pain, clicking, and popping.
✦ Restores normal jaw function and range of motion.
➤ Shorter recovery time compared to open joint surgery.
✅ Can diagnose and treat joint problems simultaneously.
✦ Low risk of complications with high success rates in experienced centers.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for TMJ Arthroscopy?
Preparation steps include:
- ✦ Medical evaluation: review medical history, allergies, medications, and prior jaw surgeries.
- ➤ Imaging studies: MRI or CT scans to assess joint anatomy and pathology.
- ✦ Laboratory tests: blood work as needed for anesthesia clearance.
- ➤ Medication adjustments: discontinue blood thinners if advised.
- ✦ Fasting instructions: usually required for several hours before general or local anesthesia.
- ➤ Consent and counseling: discuss procedure type, anesthesia, risks, benefits, and recovery expectations.
2) What happens during the procedure TMJ Arthroscopy?
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia:
➤ Step 1: Small incisions (2–3 mm) are made near the TMJ.
✦ Step 2: An arthroscope is inserted into the joint to visualize internal structures.
➤ Step 3: Saline may be injected to expand the joint and improve visibility (joint lavage).
✦ Step 4: Debridement of inflamed tissue, removal of adhesions, or repositioning of displaced discs may be performed.
➤ Step 5: Medications such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid may be injected into the joint.
✦ Step 6: Incisions are closed with sutures or steri-strips, and sterile dressing applied.
Korean TMJ centers prioritize precision, minimal trauma, and rapid recovery using advanced arthroscopic equipment.
3) What happens after TMJ Arthroscopy?
Postoperative care includes:
- ✦ Monitoring: vital signs, pain, and swelling.
- ➤ Pain management: prescribed oral analgesics or anti-inflammatories.
- ✦ Diet: soft diet for several days to reduce joint strain.
- ➤ Oral hygiene: careful cleaning around incision sites.
- ✦ Activity guidance: avoid wide jaw opening, heavy chewing, or strenuous activity for a few days.
- ➤ Follow-up: assessment of healing, jaw function, and symptom improvement.
Most patients experience significant pain relief and improved jaw mobility within a few days to weeks, with full recovery usually achieved in 2–4 weeks.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ✦ Mild swelling, bruising, or discomfort around the joint.
- ➤ Infection at incision sites (rare).
- ✦ Temporary numbness or tingling of facial nerves.
- ➤ Persistent pain or limited jaw movement in rare cases.
Benefits:
- ✅ Minimally invasive with small incisions.
- ✅ Reduces jaw pain, inflammation, and clicking.
- ✅ Restores normal range of motion.
- ✅ Short recovery and low complication rates.
- ✅ Accurate diagnosis and treatment in a single procedure.
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery after TMJ arthroscopy generally includes:
- ➤ Immediate care: mild swelling and discomfort managed with medication.
- ✦ Diet: soft foods for 1–2 weeks.
- ➤ Physical therapy: gentle jaw exercises may be recommended to restore mobility.
- ✦ Activity: avoid trauma or excessive jaw movement during initial recovery.
- ➤ Long-term outcome: most patients experience long-lasting pain relief, improved jaw function, and minimal recurrence of joint problems.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if you notice:
⚠ Severe or increasing jaw pain.
⚠ Swelling, redness, or discharge at incision sites.
⚠ Numbness, tingling, or weakness of facial muscles.
⚠ Difficulty opening or closing the mouth beyond expected recovery.
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides world-class TMJ arthroscopy with:
- ✦ Expert oral and maxillofacial surgeons experienced in arthroscopic techniques.
- ➤ Advanced imaging and endoscopic equipment for precise diagnosis and treatment.
- ✦ Minimally invasive procedures for rapid recovery and minimal scarring.
- ➤ Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care, including pain management, physiotherapy, and follow-up.
- ✦ Safe and effective procedures for both local and international patients.
- ➤ Multidisciplinary support to optimize joint health, comfort, and function.
Korea ensures patients receive safe, precise, and effective treatment for TMJ disorders with minimal complications and excellent long-term outcomes.
Highlights of TMJ Arthroscopy in Korea
- ✅ Minimally invasive procedure with small incisions.
- ➤ Accurate diagnosis and treatment in a single procedure.
- ✦ Reduces pain, inflammation, and jaw clicking.
- ➤ Short recovery and low complication rates.
- ✅ Comprehensive pre- and post-procedure care in advanced Korean centers.