Overview
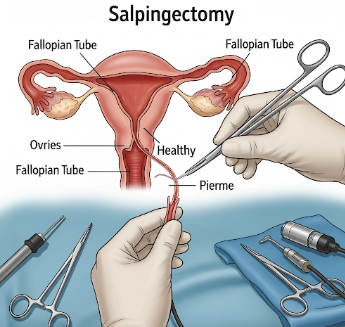
Salpingectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of one or both fallopian tubes. It is commonly performed for conditions such as ectopic pregnancy, hydrosalpinx, chronic infection, or as a preventative measure for ovarian cancer in high-risk patients.
In Korea, salpingectomy is offered in advanced gynecology and minimally invasive surgery centers, using laparoscopic or robotic-assisted techniques. Patients benefit from precise surgery, minimal scarring, rapid recovery, and expert post-operative care.
What is Salpingectomy?
Salpingectomy involves removing part or all of the fallopian tube to treat disease, prevent complications, or reduce cancer risk.
Types include:
- ✦ Unilateral salpingectomy – removal of one fallopian tube.
- ➤ Bilateral salpingectomy – removal of both tubes, often for cancer prevention or bilateral disease.
- ✦ Laparoscopic salpingectomy – minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and cameras.
- ➤ Open salpingectomy (laparotomy) – larger incision, typically used in complicated cases.
The procedure may be performed alone or as part of hysterectomy or infertility treatment.
What are the Benefits?
Salpingectomy offers several important benefits:
✅ Treats ectopic pregnancy – prevents rupture and serious complications.
➤ Reduces risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk women (BRCA mutation carriers).
✦ Eliminates diseased fallopian tubes caused by infection or blockage.
➤ Minimally invasive options – faster recovery and minimal scarring.
✅ Can improve fertility outcomes in certain cases, such as hydrosalpinx.
✦ Short hospital stay and rapid return to daily activities.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Salpingectomy?
Preparation steps include:
- ✦ Medical evaluation – pelvic ultrasound, blood tests, and assessment of reproductive health.
- ➤ Medication adjustments – stopping blood thinners or other contraindicated medications.
- ✦ Pre-operative discussion – procedure type, risks, fertility implications, and recovery plan.
- ➤ Fasting – usually 6–8 hours before surgery.
- ✦ Consent and counseling – particularly regarding fertility, contraception, and hormone management if bilateral tubes are removed.
- ➤ Pre-anesthesia assessment – ensuring fitness for general anesthesia.
2) What happens during the procedure Salpingectomy?
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and takes 30–90 minutes depending on complexity:
➤ Step 1: Small incisions are made in the abdomen for laparoscopic instruments (or a larger incision for open surgery).
✦ Step 2: The fallopian tube(s) are identified and carefully dissected from surrounding structures.
➤ Step 3: Blood vessels supplying the tube are sealed using clips, cautery, or sutures.
✦ Step 4: The tube(s) are removed completely, and the surgical area is inspected.
➤ Step 5: Incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted approaches reduce tissue trauma, shorten recovery, and minimize post-operative pain.
3) What happens after a Salpingectomy?
Post-operative care includes:
- ✦ Hospital stay: usually 1 day for laparoscopic surgery, longer if complications occur.
- ➤ Pain management – mild analgesics for discomfort.
- ✦ Wound care – keeping incision sites clean and dry.
- ➤ Gradual return to normal activities within 1–2 weeks.
- ✦ Follow-up visits – to monitor healing, infection, and overall recovery.
- ➤ Fertility and hormone counseling if both tubes are removed or if combined with other procedures.
Most patients experience rapid symptom relief and can resume normal activities shortly after recovery.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ✦ Infection at the incision or pelvic site.
- ➤ Bleeding or injury to nearby organs.
- ✦ Adhesion formation affecting future fertility.
- ➤ Anesthesia-related complications.
- ✦ Rare complications: damage to ovaries or surrounding tissues.
Benefits:
- ✅ Eliminates diseased or damaged fallopian tubes.
- ✅ Treats or prevents ectopic pregnancy.
- ✅ Reduces ovarian cancer risk in high-risk women.
- ✅ Minimally invasive with rapid recovery and minimal scarring.
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery after salpingectomy is usually smooth:
- ➤ Hospital stay: 1 day for laparoscopic, 2–3 days for open surgery.
- ✦ Pain management: mild discomfort, managed with standard analgesics.
- ➤ Return to normal activities: 1–2 weeks.
- ✦ Fertility outlook: unilateral salpingectomy usually preserves fertility; bilateral salpingectomy eliminates natural conception potential.
- ➤ Long-term outlook: excellent, especially when performed for ectopic pregnancy, hydrosalpinx, or prophylactic reasons.
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they notice:
⚠ Severe abdominal pain or swelling.
⚠ Fever, chills, or signs of infection.
⚠ Heavy vaginal bleeding or unusual discharge.
⚠ Nausea, vomiting, or inability to tolerate food.
⚠ Persistent incision pain, redness, or drainage.
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides world-class salpingectomy care with:
- ✦ Experienced gynecologic surgeons specializing in minimally invasive and robotic-assisted techniques.
- ➤ Advanced laparoscopic and robotic equipment for precise surgery.
- ✦ Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care, including fertility counseling and monitoring.
- ➤ Short hospital stay and rapid recovery protocols.
- ✦ Affordable treatment packages compared to Western countries.
- ➤ Multilingual support for international patients, including pre-surgery coordination and post-operative follow-up.
Korea is a top destination for salpingectomy, offering safe, precise, and effective treatment with excellent recovery outcomes.
Highlights of Salpingectomy in Korea
- ✅ Treats ectopic pregnancy and removes diseased fallopian tubes.
- ➤ Minimally invasive laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
- ✦ Reduces risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk patients.
- ➤ Rapid recovery with short hospital stay.
- ✅ Performed by top Korean gynecologic surgeons with expert post-operative care.