Overview
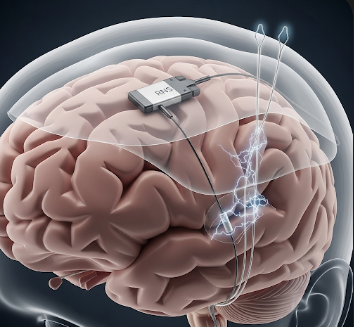
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS) is an advanced therapy for drug-resistant epilepsy that involves implanting a device to detect abnormal brain activity and deliver targeted electrical stimulation to prevent seizures. RNS is designed for patients who continue to have seizures despite optimal medication therapy.
South Korea is known for highly skilled neurosurgeons, cutting-edge implantable devices, and advanced neuro-monitoring technology, making RNS implantation safe and effective.
What is Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS)?
RNS involves placing electrodes in the brain at seizure focus areas and connecting them to a small neurostimulator implanted in the skull. Key points include:
✔ Detects abnormal electrical activity in real time.
➔ Delivers responsive electrical pulses to prevent or reduce seizures.
● Minimally invasive implantable therapy performed under general anesthesia.
★ Customizable and reversible: device programming can be adjusted or the device removed if needed.
This therapy is indicated for patients with focal epilepsy not adequately controlled with anti-seizure medications and who are not candidates for resective surgery.
What are the Benefits?
RNS provides multiple advantages:
✔ Reduces seizure frequency and severity.
➔ Improves quality of life and daily functioning.
● Minimally invasive with relatively short recovery.
★ Continuous brain monitoring allows precise therapy adjustment over time.
➤ Potentially reduces need for multiple medications.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Responsive Neurostimulation?
Preparation focuses on medical optimization and safety:
✔ Neurological assessment: EEG, MRI, and seizure mapping to identify seizure foci.
➔ Medication review: Adjust anti-seizure medications as advised.
● Medical clearance: Blood tests, cardiac evaluation, and anesthesia assessment.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, expected outcomes, and device management.
➤ Family education: Caregivers should understand device operation, follow-ups, and seizure logging.
2) What happens during the Responsive Neurostimulation procedure?
The procedure is performed in a surgical suite under general anesthesia:
✔ Electrode placement: Electrodes inserted into brain areas identified as seizure foci.
➔ Device implantation: Electrodes connected to a neurostimulator implanted in the skull.
● Intraoperative testing: Device tested to ensure accurate detection and stimulation.
★ Closure: Incision closed; small dressing applied.
➤ Procedure duration: Typically 2–4 hours depending on seizure focus number and complexity.
Korean neurosurgeons emphasize precision in electrode placement and device programming to optimize seizure control and minimize complications.
3) What happens after Responsive Neurostimulation?
Post-operative care focuses on monitoring, device programming, and gradual seizure management:
✔ Immediate recovery: Patient observed in hospital; mild headache or scalp soreness common.
➔ Device activation: Programmed weeks after implantation once surgical site heals.
● Follow-up: Regular adjustments based on seizure patterns and device data.
★ Medication management: Anti-seizure medications may be tapered gradually if seizures improve.
➤ Long-term monitoring: Device records seizure activity, aiding ongoing therapy optimization.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at surgical site
➔ Bleeding or hematoma
● Device malfunction or lead displacement
★ Seizure worsening (rare)
➤ Rare neurological deficits or allergic reaction to device materials
Major Benefits:
✔ Reduces seizure frequency and severity
➔ Continuous, responsive seizure management
● Minimally invasive with outpatient or short hospital stay
★ Device programming customizable for optimal therapy
➤ Improves quality of life and functional independence
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Mild headache, swelling, or soreness at incision site.
➔ Hospital stay: Typically 1–2 days for monitoring.
● Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activity for 2–4 weeks; normal daily activity gradually resumed.
★ Long-term outcome: Many patients experience a 50–70% reduction in seizure frequency over several months.
➤ Follow-up: Device interrogation, programming adjustments, and regular neurological evaluations.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Fever, redness, or swelling at incision site
➔ Persistent headache, nausea, or neurological changes
● Device malfunction or unusual stimulation sensations
★ Seizure worsening or new neurological symptoms
➤ Uncontrolled bleeding or signs of infection
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert Responsive Neurostimulation services with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital Neurosurgery & Epilepsy Centers.
➔ Experienced neurosurgeons and epileptologists skilled in implantable neurostimulation therapy.
● Advanced technology: State-of-the-art RNS devices and programming systems.
★ Comprehensive care: Pre-op evaluation, implantation, post-op monitoring, and long-term device management.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, appointment coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ RNS detects and responds to abnormal brain activity to reduce seizures
➔ Minimally invasive implantable therapy with customizable programming
● Continuous monitoring aids long-term seizure control
★ Risks include infection, device malfunction, bleeding, or neurological changes
➤ Korean hospitals provide expert surgeons, advanced devices, and comprehensive post-op care