Overview
Pyloromyotomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS), a condition most commonly seen in infants. HPS occurs when the muscle at the lower end of the stomach (pylorus) thickens, obstructing the passage of food into the small intestine, causing projectile vomiting, dehydration, and poor weight gain.
South Korea is recognized for expert pediatric surgeons, minimally invasive techniques, and comprehensive perioperative care, making pyloromyotomy safe, effective, and highly successful.
What is Pyloromyotomy?
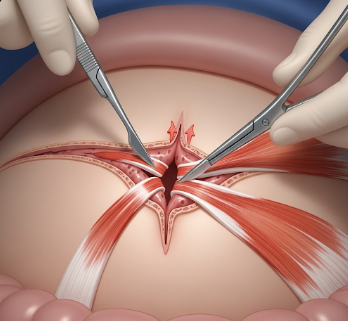
Pyloromyotomy involves splitting the thickened pyloric muscle without cutting through the inner lining of the stomach, which relieves obstruction while preserving normal anatomy. Key points include:
✔ Restores normal passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine.
➔ Relieves vomiting and allows proper nutrition and growth.
● Minimally invasive options available, including laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.
★ High success rate: Most infants experience complete resolution of symptoms.
This procedure is recommended for infants with confirmed hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, typically diagnosed via ultrasound and clinical symptoms.
What are the Benefits?
Pyloromyotomy provides several advantages:
✔ Rapid relief from vomiting and gastric outlet obstruction.
➔ Supports normal weight gain and hydration.
● Minimally invasive techniques allow shorter hospital stays.
★ Excellent long-term outcomes with minimal complications.
➤ Safe and standardized procedure with high surgical success rates in Korea.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Pyloromyotomy?
Preparation focuses on stabilizing the infant and optimizing surgical safety:
✔ Medical assessment: Blood tests, electrolyte correction, and ultrasound confirmation of pyloric stenosis.
➔ Hydration and electrolyte management: Infants are often dehydrated due to vomiting; IV fluids correct imbalances.
● Parental counseling: Explaining procedure, anesthesia, and recovery expectations.
★ Fasting: Typically, infants are kept nil per os (NPO) for several hours before surgery.
➤ Consent: Parents or guardians provide informed consent after understanding risks and benefits.
2) What happens during the procedure Pyloromyotomy?
Pyloromyotomy can be performed via open or laparoscopic approach under general anesthesia:
✔ Incision: Small upper abdominal incision (open) or several tiny ports (laparoscopic).
➔ Muscle splitting: Thickened pyloric muscle is carefully split longitudinally without perforating the inner lining.
● Verification: Surgeon ensures muscle separation allows unobstructed gastric emptying.
★ Closure: Incision or port sites closed with fine sutures; minimal scarring.
➤ Procedure duration: Usually 30–60 minutes depending on technique.
Korean pediatric surgeons emphasize precision and gentle tissue handling to minimize complications and support rapid recovery.
3) What happens after Pyloromyotomy?
Post-operative care focuses on hydration, feeding, and monitoring for complications:
✔ Recovery room monitoring: Vital signs and pain assessment.
➔ Feeding: Small, frequent feeds typically start within 12–24 hours post-surgery.
● Pain management: Mild analgesics; infants usually tolerate well.
★ Hospital stay: 1–2 days for laparoscopic approach; slightly longer for open surgery.
➤ Follow-up: Monitor weight gain, vomiting resolution, and incision healing.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at incision or port site
➔ Bleeding (rare)
● Perforation of stomach or duodenum (very rare)
★ Incomplete relief requiring reoperation (rare)
➤ Anesthesia-related complications
Major Benefits:
✔ Rapid resolution of vomiting and gastric obstruction
➔ Promotes normal growth and hydration
● Minimally invasive with short hospital stay
★ High long-term success and low complication rates
➤ Standardized procedure in Korea with excellent outcomes
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Infants are monitored for vital signs and feeding tolerance.
➔ Feeding: Gradual introduction of formula or breast milk within 12–24 hours.
● Activity: Normal infant activity resumed; mild discomfort may occur at incision site.
★ Hospital discharge: Usually 1–2 days for laparoscopic, slightly longer for open surgery.
➤ Long-term outcome: Complete resolution of vomiting, improved weight gain, and normal growth.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact the doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Persistent vomiting or inability to tolerate feeds
➔ Fever or signs of infection at the incision site
● Abdominal distension or severe pain
★ Lethargy or dehydration signs
➤ Unusual bleeding from incision or port sites
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert pyloromyotomy services with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital Pediatric Surgery.
➔ Minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques for rapid recovery and minimal scarring.
● Experienced pediatric surgeons: Skilled in both open and laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.
★ Comprehensive perioperative care: Pre-op stabilization, surgery, post-op monitoring, and follow-up growth tracking.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, appointment coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Pyloromyotomy treats hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants
➔ Minimally invasive and safe with high success rate
● Rapid relief of vomiting and improved growth
★ Risks are rare but include infection, bleeding, or very rare perforation
➤ Korean hospitals provide expert surgeons, advanced techniques, and comprehensive post-op care