Overview
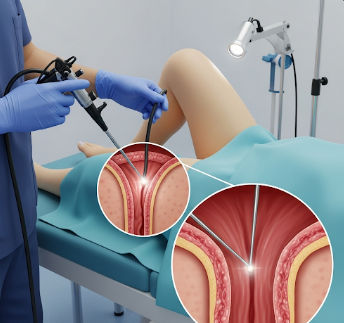
Proctoscopy, also called rigid sigmoidoscopy, is a diagnostic procedure to examine the rectum and lower part of the colon. It allows doctors to detect abnormalities such as polyps, hemorrhoids, inflammation, or early-stage cancer.
South Korea is known for advanced endoscopy centers, skilled gastroenterologists, and state-of-the-art imaging technology, making it a safe and accurate destination for proctoscopy procedures.
What is Proctoscopy (Rigid Sigmoidoscopy)?
Rigid sigmoidoscopy uses a short, rigid tube called a proctoscope equipped with a light source to visually inspect the rectum and distal sigmoid colon. Key aspects include:
✔ Direct visualization of rectal mucosa.
➔ Detection and biopsy of abnormal tissue if necessary.
● Minimally invasive: Outpatient procedure with quick recovery.
★ Short procedure time: Usually completed in 5–15 minutes.
It is commonly used for screening, diagnosis, and follow-up of colorectal conditions.
What are the Benefits?
Proctoscopy offers several advantages:
✔ Early detection of rectal abnormalities, including cancer and polyps.
➔ Quick and minimally invasive with limited discomfort.
● Allows tissue sampling for biopsy during the same procedure.
★ Can guide treatment decisions for hemorrhoids, inflammation, or tumors.
➤ Outpatient procedure: No hospital stay required.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Proctoscopy?
Preparation ensures accurate results:
✔ Bowel preparation: Mild enema to clear the lower rectum.
➔ Medication review: Inform doctor about anticoagulants or other relevant medications.
● Dietary instructions: Usually light diet before the procedure; fasting not always required.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, benefits, and possible discomfort.
➤ Personal hygiene: Cleanliness of anal area recommended.
2) What happens during the procedure Proctoscopy?
Proctoscopy is generally performed without anesthesia or with mild sedation:
✔ Positioning: Patient lies on their side with knees drawn up (Sims’ position).
➔ Insertion of proctoscope: Gently inserted into rectum.
● Examination: Doctor inspects rectal walls for lesions, bleeding, or abnormal tissue.
★ Biopsy or minor intervention: Polyps may be sampled or small hemorrhoids treated.
➤ Completion: Proctoscope removed; procedure typically lasts 5–15 minutes.
Korean gastroenterologists use high-definition scopes and advanced imaging for accurate visualization and diagnosis.
3) What happens after Proctoscopy?
Post-procedure care focuses on monitoring and resuming normal activity:
✔ Immediate recovery: Usually outpatient with minimal downtime.
➔ Discomfort: Mild cramping or bloating may occur briefly.
● Bleeding: Small bleeding may happen if biopsy performed.
★ Follow-up: Results of biopsy or findings discussed within days.
➤ Activity: Resume normal activities immediately unless advised otherwise.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Mild rectal discomfort or cramping
➔ Minimal bleeding, especially after biopsy
● Rare infection
★ Rare rectal perforation or injury
➤ Allergic reaction to lubrication or topical anesthetic (if used)
Major Benefits:
✔ Rapid and minimally invasive diagnostic procedure
➔ Early detection of polyps, cancer, and other abnormalities
● Allows biopsy during the same procedure
★ Outpatient procedure with short recovery
➤ Guides treatment decisions for rectal and lower colon diseases
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Most patients return to normal activity immediately.
➔ Mild discomfort or cramping: Usually resolves within a few hours.
● Diet: Resume normal diet unless instructed otherwise.
★ Follow-up: Review of biopsy results and treatment planning if needed.
➤ Long-term outlook: Enables early detection and effective management of rectal diseases.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
✔ Severe rectal pain or persistent cramping
➔ Significant bleeding or blood clots
● Fever or signs of infection
★ Severe or prolonged bloating
➤ Unusual symptoms not explained by the procedure
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert proctoscopy services with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced endoscopy equipment: High-definition rigid scopes for precise visualization.
● Experienced gastroenterologists: Skilled in diagnostic and minor therapeutic interventions.
★ Comprehensive care: Biopsy, pathology analysis, and follow-up care.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Proctoscopy (Rigid Sigmoidoscopy) is a quick, minimally invasive diagnostic procedure
➔ Detects early rectal abnormalities including cancer and polyps
● Can include biopsy or minor treatment during the procedure
★ Risks are minimal: mild discomfort, minor bleeding, rare perforation
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced equipment, expert physicians, and comprehensive follow-up care