Overview
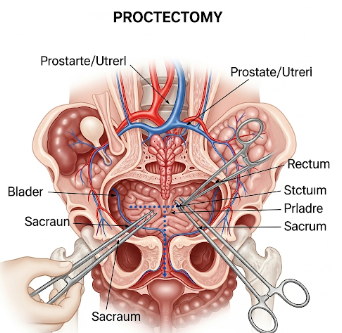
Proctectomy is a surgical procedure to remove all or part of the rectum, often indicated for rectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis, or severe rectal trauma. This procedure aims to eliminate disease, restore bowel function, and improve quality of life.
South Korea is renowned for advanced colorectal surgery, minimally invasive techniques, and excellent post-operative care, making it a leading destination for proctectomy procedures.
What is Proctectomy?
Proctectomy involves removal of diseased rectal tissue and may include:
✔ Partial proctectomy: Removing only the diseased section of the rectum.
➔ Total proctectomy: Complete removal of the rectum, often requiring a permanent or temporary stoma.
● Surgical approach: Open surgery, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted techniques.
★ Reconstruction options: Reconnection of the colon to the anus (anastomosis) or creation of an ileostomy/colostomy for fecal diversion.
The choice of approach depends on disease extent, patient anatomy, and surgeon expertise.
What are the Benefits?
Proctectomy provides several advantages:
✔ Removes cancerous or diseased tissue, reducing recurrence risk.
➔ Alleviates symptoms such as bleeding, pain, or obstruction.
● Improves bowel function in selected cases with restorative reconstruction.
★ Minimally invasive options reduce recovery time and surgical trauma.
➤ Enhances quality of life by controlling disease progression and symptoms.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Proctectomy?
Preparation is essential for safety and optimal outcomes:
✔ Comprehensive evaluation: Imaging, colonoscopy, labs, and cardiopulmonary assessment.
➔ Bowel preparation: Laxatives or enemas to clear the colon before surgery.
● Medication review: Adjust or stop blood thinners and certain medications as advised.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss surgical approach, risks, stoma care if needed, and recovery expectations.
➤ Lifestyle adjustments: Smoking cessation, nutrition optimization, and planning for post-operative care.
2) What happens during the procedure Proctectomy?
Proctectomy is performed under general anesthesia and can take 2–6 hours depending on complexity:
✔ Incision and access: Open, laparoscopic, or robotic approach to reach the rectum.
➔ Rectal tissue removal: Diseased portion of rectum is excised carefully.
● Lymph node removal: Performed in cancer cases for staging and disease control.
★ Reconstruction or diversion: Colon may be reconnected to the anus or a temporary/permanent stoma created.
➤ Closure and drainage: Surgical site closed and drains placed if needed to prevent fluid accumulation.
Korean surgeons often use advanced laparoscopic or robotic techniques for precise dissection, reduced trauma, and faster recovery.
3) What happens after Proctectomy?
Post-operative care focuses on healing, bowel function, and complication prevention:
✔ Hospital stay: Typically 5–10 days, depending on procedure and patient condition.
➔ Pain management: Medications, often via epidural or IV initially.
● Bowel function monitoring: Return of bowel movements, stoma care education if applicable.
★ Diet progression: Start with liquids, advance to soft foods, then regular diet.
➤ Follow-up: Wound care, stoma management, and monitoring for complications or recurrence.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection or abscess formation
➔ Bleeding or need for transfusion
● Anastomotic leak if reconnection performed
★ Bowel obstruction or adhesions
➤ Stoma complications if diversion is required (skin irritation, prolapse, or hernia)
Major Benefits:
✔ Definitive removal of diseased or cancerous tissue
➔ Symptom relief from bleeding, pain, or obstruction
● Potential restoration of bowel continuity (when feasible)
★ Minimally invasive approaches reduce recovery time and post-operative pain
➤ Enhanced quality of life by controlling disease progression
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: Hospital stay 5–10 days with close monitoring.
➔ Activity restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for several weeks.
● Diet progression: Gradual advancement from liquids to solid foods.
★ Long-term outcome: Many patients achieve good bowel function; stoma may be temporary or permanent depending on disease and reconstruction.
➤ Follow-up: Regular check-ups for wound healing, stoma care, and disease surveillance.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
➔ Persistent bleeding or abdominal pain
● Changes in stoma appearance, leakage, or severe irritation
★ Vomiting, severe constipation, or signs of bowel obstruction
➤ Unusual discharge from surgical site or sudden swelling
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert proctectomy care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced laparoscopic and robotic surgery: High precision, minimal invasiveness, and faster recovery.
● Expert colorectal surgeons: Skilled in cancer and inflammatory bowel disease surgery.
★ Comprehensive post-operative care: Pain management, stoma education, and follow-up monitoring.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Proctectomy removes diseased or cancerous rectal tissue
➔ Reduces symptoms and disease recurrence risk
● Minimally invasive approaches available for faster recovery
★ Risks include infection, bleeding, anastomotic leak, or stoma complications
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced surgery, expert surgeons, and comprehensive post-operative care