Overview
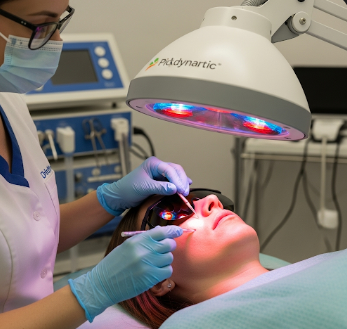
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive treatment that uses light-sensitive drugs and specific wavelengths of light to destroy abnormal or cancerous cells. PDT is commonly used for skin cancers, precancerous lesions, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, and certain eye conditions.
South Korea is recognized for advanced photodynamic therapy facilities, expert oncologists, and precise imaging-guided procedures, making it a leading destination for PDT with high success and safety rates.
What is Photodynamic Therapy?
PDT is a two-step process:
✔ Photosensitizing drug administration: The drug selectively accumulates in abnormal or cancerous cells.
➔ Activation with specific light wavelength: Light exposure triggers a reaction that destroys targeted cells.
● Minimally invasive: Usually outpatient with limited recovery time.
★ Selective targeting: Healthy surrounding tissue is mostly spared, reducing side effects.
PDT can be curative for early-stage cancers or palliative to reduce tumor burden and alleviate symptoms in advanced disease.
What are the Benefits?
Photodynamic Therapy offers several advantages:
✔ Minimally invasive with no large surgical incisions.
➔ Precise targeting of abnormal or cancerous cells while sparing healthy tissue.
● Reduced recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
★ Can be repeated multiple times if necessary without cumulative damage.
➤ Cosmetic benefits: Minimal scarring, especially for skin lesions.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Photodynamic Therapy?
Proper preparation ensures effectiveness and safety:
✔ Medical evaluation: Physical exam, imaging, and biopsy if needed.
➔ Medication review: Certain drugs or supplements may affect photosensitivity.
● Fasting or diet restrictions: Usually minimal unless treating internal organs.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, light avoidance afterward, potential side effects, and recovery.
➤ Skin or treatment site preparation: Cleaning and marking of target area if applicable.
2) What happens during the procedure Photodynamic Therapy?
The procedure depends on the treated organ and usually lasts 30–90 minutes:
✔ Drug administration: Photosensitizer given orally, intravenously, or topically.
➔ Incubation period: Allows drug to accumulate selectively in target cells (can range from hours to days).
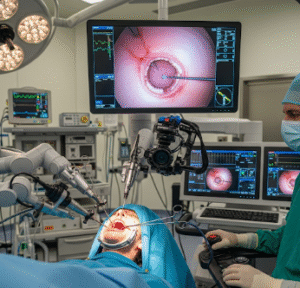
● Light activation: Target area is exposed to laser, LED, or fiber optic light of a specific wavelength.
★ Reactive oxygen species generation: Destroys abnormal or cancerous cells.
➤ Monitoring: Patient is observed for immediate reactions and comfort.
Korean hospitals often use image-guided PDT and advanced light delivery systems for precision and safety.
3) What happens after Photodynamic Therapy?
Post-procedure care focuses on healing, monitoring, and minimizing light exposure:
✔ Light sensitivity precautions: Avoid direct sunlight and strong indoor lighting for several days.
➔ Observation: Monitor for swelling, redness, or discomfort at treatment site.
● Pain or discomfort management: Mild analgesics if needed.
★ Follow-up imaging or biopsy: Ensures lesion response and checks for residual disease.
➤ Lifestyle guidance: Avoid strenuous activity and follow all dermatological or organ-specific care instructions.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Localized pain, redness, or swelling at treatment site
➔ Photosensitivity reactions (skin burns or rash if exposed to light)
● Temporary discoloration or scarring
★ Rare allergic reactions to photosensitizing agent
➤ Internal organ-specific risks: esophageal irritation, respiratory discomfort, or eye sensitivity
Major Benefits:
✔ Minimally invasive treatment with limited recovery
➔ Selective targeting of abnormal or cancerous cells
● Can be repeated safely for residual or recurrent lesions
★ Reduced scarring and excellent cosmetic outcomes
➤ Effective for early-stage cancers, precancerous lesions, and symptom management in advanced disease
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Usually outpatient with mild discomfort.
➔ Light precautions: Avoid sunlight and bright light for several days.
● Follow-up: Regular monitoring for lesion response and repeat treatment if necessary.
★ Long-term outcome: Effective tumor control, symptom relief, and high cosmetic satisfaction.
➤ Lifestyle: Resume normal daily activities with careful light protection and adherence to follow-up schedule.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
✔ Severe pain, swelling, or redness at treatment site
➔ Blistering or ulceration
● Signs of infection such as fever or discharge
★ Persistent photosensitivity or rash
➤ Unexpected complications related to treated organs (difficulty swallowing, vision changes, or respiratory issues)
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert photodynamic therapy care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced PDT equipment: Lasers, LEDs, and image-guided systems.
● Expert oncologists and dermatologists: Skilled in organ-specific PDT techniques.
★ Comprehensive post-procedure care: Monitoring, light precautions, and follow-up imaging.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Photodynamic Therapy treats abnormal or cancerous cells selectively
➔ Minimally invasive with short recovery
● Can be repeated safely and provides excellent cosmetic outcomes
★ Risks include photosensitivity, local irritation, pain, or rare allergic reactions
➤ Korean hospitals offer advanced equipment, precision techniques, and expert follow-up care