Overview
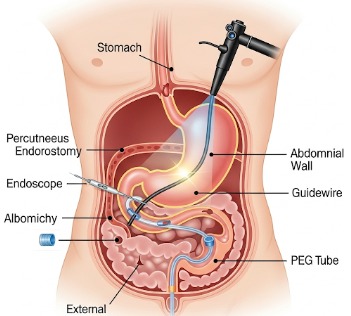
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement is a procedure in which a feeding tube is inserted directly into the stomach through the abdominal wall, allowing for long-term nutritional support. PEG is commonly indicated for patients who cannot swallow safely due to neurological disorders, stroke, cancer, or other chronic conditions.
South Korea is renowned for advanced gastroenterology centers, experienced endoscopists, and modern minimally invasive techniques, making PEG tube placement safe, effective, and reliable.
What is PEG Tube Placement?
PEG tube placement is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure designed to provide direct access to the stomach for nutritional support. Key features include:
✔ Direct stomach access: Ensures delivery of nutrition, fluids, and medications.
➔ Endoscopic guidance: Allows precise tube placement while minimizing complications.
● Long-term solution: Suitable for patients needing extended enteral feeding.
★ Outpatient or short-stay procedure: Usually performed under sedation with minimal recovery time.
PEG is preferred when oral intake is unsafe or insufficient, avoiding the discomfort and complications of nasogastric feeding tubes.
What are the Benefits?
PEG tube placement offers multiple advantages:
✔ Ensures adequate nutrition in patients unable to eat orally.
➔ Minimally invasive: Less risk than open surgical gastrostomy.
● Supports hydration, medications, and supplements safely.
★ Improves quality of life by enabling consistent feeding.
➤ Long-term feeding option: Durable and reliable for chronic conditions.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for PEG Tube Placement?
Preparation ensures safety and success:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging, and endoscopy assessment.
➔ Medication review: Adjust blood thinners or anticoagulants as instructed.
● Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours before the procedure.
★ Patient counseling: Explain procedure, benefits, potential complications, and aftercare.
➤ Consent and support: Ensure patient and caregiver understand tube care and feeding procedures.
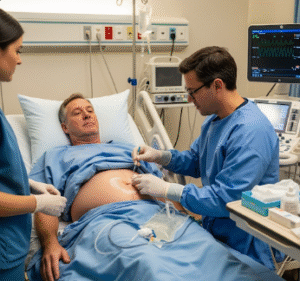
2) What happens during the procedure PEG Tube Placement?
PEG tube placement is performed using endoscopic guidance under local anesthesia and sedation:
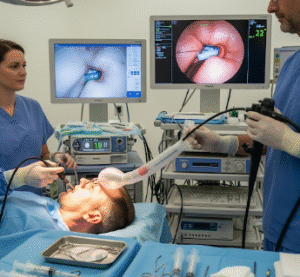
✔ Endoscope insertion: A flexible endoscope is passed into the stomach via the mouth.
➔ Site selection: Abdominal wall is identified and sterilized for tube placement.
● Needle and guidewire insertion: A needle punctures the abdominal wall; guidewire passed into the stomach.
★ Tube placement: PEG tube is threaded over the guidewire into the stomach; internal bumper ensures secure positioning.
➤ Verification: Endoscopic visualization confirms correct placement.
Korean hospitals often use high-definition endoscopes and sterile techniques to reduce complications and ensure accurate placement.
3) What happens after PEG Tube Placement?
Post-procedure care focuses on healing, feeding initiation, and monitoring for complications:
✔ Immediate observation: Monitor vital signs and procedure site for bleeding or infection.
➔ Tube care: Clean skin around the tube; prevent irritation or infection.
● Feeding initiation: Often started 4–24 hours after placement, depending on patient condition.
★ Monitoring: Watch for leakage, blockage, or displacement.
➤ Follow-up: Regular assessment by gastroenterology and nutrition teams to adjust feeding plan.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at the tube insertion site
➔ Bleeding or bruising
● Tube blockage or displacement
★ Perforation or injury to surrounding organs (rare)
➤ Aspiration if feeding technique is improper
Major Benefits:
✔ Reliable long-term nutritional support
➔ Minimally invasive with shorter recovery than surgical gastrostomy
● Allows hydration, medication administration, and nutrient delivery
★ Improves quality of life in patients unable to swallow
➤ Can be maintained at home with proper caregiver training
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Most patients can resume normal activity within 24 hours.
➔ Pain management: Mild discomfort or soreness at the insertion site is common.
● Tube maintenance: Daily cleaning and monitoring prevent infection.
★ Feeding adaptation: Gradual introduction of formula to minimize complications.
➤ Long-term outcome: PEG tubes provide safe, effective, and durable nutritional support for chronic conditions.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Severe abdominal pain or swelling at tube site
➔ Persistent bleeding or pus
● Tube dislodgement or blockage
★ Fever or signs of infection
➤ Difficulty feeding, nausea, or vomiting
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert PEG tube placement care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced endoscopic technology for precise and safe placement.
● Experienced gastroenterologists and nutrition teams: Skilled in long-term care and tube management.
★ Comprehensive care: Placement, feeding plan development, caregiver training, and follow-up.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and post-procedure continuity for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ PEG tube provides safe, long-term nutritional support for patients unable to swallow
➔ Minimally invasive procedure performed under endoscopic guidance
● Supports hydration, medications, and feeding at home
★ Risks include infection, bleeding, or tube displacement
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced technology, skilled specialists, and comprehensive post-placement care