Overview
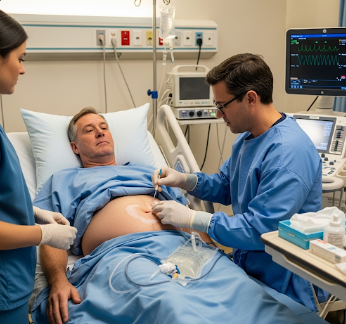
Paracentesis is a medical procedure in which fluid is removed from the abdominal cavity using a needle or catheter. It is primarily performed for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, such as relieving ascites caused by liver disease, heart failure, kidney disease, or cancer.
South Korea is recognized for advanced hospital facilities, experienced gastroenterologists, and minimally invasive techniques, making paracentesis safe, accurate, and effective.
What is Paracentesis?
Paracentesis involves inserting a sterile needle or catheter into the abdominal cavity to remove excess fluid. Key aspects include:
✔ Diagnostic paracentesis: Fluid is analyzed to identify infections, cancer cells, or other abnormalities.
➔ Therapeutic paracentesis: Removes large volumes of fluid to relieve abdominal pressure, pain, or breathing difficulty.
● Minimally invasive: Usually performed under local anesthesia.
★ Quick outpatient procedure: Typically completed in 20–60 minutes.
What are the Benefits?
Paracentesis provides several advantages:
✔ Immediate relief of abdominal distension and discomfort.
➔ Diagnostic clarity: Helps determine the cause of ascites.
● Minimally invasive: Less risk compared to surgical interventions.
★ Can be repeated if necessary to manage recurring fluid accumulation.
➤ Improves breathing, mobility, and overall comfort in patients with large fluid buildup.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Paracentesis?
Preparation ensures safety and accurate results:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound or CT) to locate fluid.
➔ Medication review: Inform your doctor about blood thinners or other medications.
● Fasting: Sometimes required for a few hours prior.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, benefits, risks, and post-procedure care.
➤ Informed consent: Ensure understanding of potential complications and expectations.
2) What happens during the procedure Paracentesis?
Paracentesis is usually performed under local anesthesia, often guided by ultrasound:
✔ Positioning: Patient typically lies on their back or slightly tilted to one side.
➔ Skin preparation: Area cleaned with antiseptic solution.
● Needle insertion: A needle or catheter is carefully inserted into the abdominal cavity.
★ Fluid removal: Fluid is aspirated for diagnostic testing or symptom relief.
➤ Monitoring: Vital signs observed during the procedure to ensure safety.
Korean hospitals often use ultrasound guidance and sterile techniques to improve precision and reduce complications.
3) What happens after Paracentesis?
Post-procedure care focuses on monitoring and recovery:
✔ Observation: Patient monitored for 1–2 hours for signs of bleeding or infection.
➔ Vital signs: Blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels checked.
● Fluid analysis: If diagnostic, lab results usually available within 24–48 hours.
★ Discomfort: Mild pain or tenderness at the puncture site may occur.
➤ Follow-up: Instructions on activity restrictions, wound care, and when to seek medical help.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Bleeding at puncture site
➔ Infection in the abdominal cavity (rare)
● Low blood pressure or electrolyte imbalance if large volumes removed
★ Injury to internal organs (rare)
➤ Persistent leakage from puncture site
Major Benefits:
✔ Relief of abdominal pressure and discomfort
➔ Diagnostic insight into cause of ascites
● Minimally invasive and outpatient-friendly
★ Can be repeated if fluid reaccumulates
➤ Improves mobility, breathing, and overall quality of life
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within a few hours.
➔ Mild discomfort: Pain or tenderness at puncture site is common.
● Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activity for 24 hours.
★ Long-term outcome: Repeated paracentesis may be needed for chronic conditions; underlying cause treatment is essential.
➤ Follow-up: Monitor for infection, electrolyte changes, or fluid reaccumulation.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Severe abdominal pain or swelling
➔ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
● Persistent bleeding from puncture site
★ Nausea, vomiting, or dizziness
➤ Shortness of breath or worsening abdominal distension
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert paracentesis care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced imaging guidance: Ultrasound or CT-assisted needle placement.
● Experienced gastroenterologists and interventional radiologists: Skilled in safe fluid removal.
★ Comprehensive care: Symptom relief, diagnostic testing, and follow-up monitoring.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Paracentesis removes excess abdominal fluid to relieve discomfort and improve breathing
➔ Diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, minimally invasive
● Quick outpatient procedure with short recovery time
★ Risks include bleeding, infection, or rare organ injury
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced imaging, skilled specialists, and thorough post-procedure monitoring