Overview
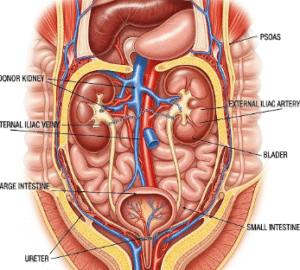
Paracentesis is a medical procedure used to remove excess fluid (ascites) from the abdominal cavity. This fluid accumulation can result from liver disease, cancer, heart failure, or infection.
South Korea offers advanced paracentesis services in hospitals and specialized clinics, ensuring safe, minimally invasive procedures with precise imaging guidance and post-procedure care.
What is Paracentesis?
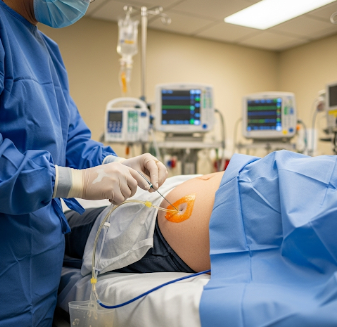
Paracentesis involves inserting a needle or catheter into the abdominal cavity to drain excess fluid. The procedure can be:
✔ Diagnostic: Fluid is collected for laboratory analysis to determine the underlying cause.
➔ Therapeutic: Fluid is removed to relieve symptoms such as abdominal swelling, discomfort, or breathing difficulty.
● Imaging-guided: Ultrasound or CT guidance improves safety and accuracy.
★ Minimally invasive: Usually performed at bedside or in an outpatient setting.
What are the Benefits?
Paracentesis offers several important benefits:
✔ Relieves abdominal pressure and discomfort caused by fluid accumulation.
➔ Improves breathing and mobility in patients with massive ascites.
● Allows accurate diagnosis by analyzing the collected fluid.
★ Can prevent complications such as infection or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
➤ Provides rapid symptomatic relief with minimal recovery time.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Paracentesis?
Proper preparation ensures safety and effectiveness:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound or CT), and review of medications.
➔ Medication management: Blood thinners may need to be paused to reduce bleeding risk.
● Empty bladder: Patient may be asked to void before the procedure.
★ Patient counseling: Explain procedure, potential risks, and post-procedure care.
➤ Positioning: Patient may be seated or lying down for optimal access to fluid.
2) What happens during the procedure Paracentesis?
The procedure is minimally invasive and usually takes 15–30 minutes:
✔ Local anesthesia: Numbs the insertion site on the abdominal wall.
➔ Needle or catheter insertion: Guided by imaging for precise fluid removal.
● Fluid aspiration: Fluid is collected for diagnostic testing or drained therapeutically.
★ Volume monitoring: Large-volume drainage is done gradually to prevent hypotension.
➤ Closure: Small dressing applied at insertion site; pressure may be applied to prevent bleeding.
Korean hospitals often use ultrasound-guided paracentesis to reduce complications and increase accuracy.
3) What happens after Paracentesis?
Post-procedure care focuses on monitoring, fluid balance, and infection prevention:
✔ Observation: Short period of monitoring for bleeding, hypotension, or discomfort.
➔ Activity restrictions: Usually minimal; patients may resume normal activities quickly.
● Fluid monitoring: In some cases, repeated paracentesis may be required for chronic conditions.
★ Wound care: Keep the insertion site clean and dry.
➤ Follow-up: Results of fluid analysis guide further treatment.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at the puncture site
➔ Bleeding or hematoma
● Abdominal pain or discomfort
★ Low blood pressure if large volumes are removed too quickly
➤ Rare complications: bowel perforation or leakage of ascitic fluid
Major Benefits:
✔ Relieves abdominal distension and discomfort
➔ Improves breathing and mobility in patients with ascites
● Provides diagnostic information for targeted treatment
★ Minimally invasive and safe with expert guidance
➤ Rapid symptom relief with short recovery time
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Most patients feel relief immediately after fluid removal.
➔ Short observation: Usually 1–2 hours post-procedure.
● Repeat procedures: May be needed in patients with recurrent ascites.
★ Long-term outcome: Symptom management, improved quality of life, and guidance for underlying disease treatment.
➤ Follow-up: Laboratory results of fluid analysis help guide treatment for liver disease, cancer, or infection.
When To Call the Doctor
Seek medical advice if experiencing:
✔ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
➔ Persistent abdominal pain or swelling
● Bleeding from the insertion site
★ Dizziness, fainting, or unusual weakness
➤ Re-accumulation of fluid causing severe discomfort
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert paracentesis care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced imaging guidance: Ultrasound or CT-assisted paracentesis for safety and precision.
● Experienced medical teams: Skilled in both diagnostic and therapeutic paracentesis.
★ Comprehensive post-procedure care: Observation, fluid management, and follow-up testing.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and post-procedure follow-up for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Paracentesis removes excess abdominal fluid safely
➔ Provides diagnostic and therapeutic benefits
● Relieves pressure, improves breathing, and enhances mobility
★ Risks include infection, bleeding, hypotension, or rare organ injury
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced imaging-guided techniques with excellent post-procedure care