Overview
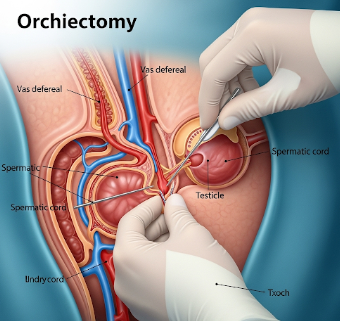
Orchiectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of one or both testicles. It is most commonly performed to treat testicular cancer, prostate cancer (as part of hormone therapy), or severe trauma/injury. In some cases, it may also be performed for gender-affirming surgery.
In South Korea, orchiectomy is conducted at leading urology and oncology centers, with minimally invasive techniques, precise surgical methods, and comprehensive post-operative care. Patients benefit from highly trained surgeons and a supportive recovery environment.
What is Orchiectomy?
Orchiectomy can be classified based on the purpose and technique:
✔ Radical orchiectomy: Entire testicle removed, usually for cancer treatment.
➔ Simple orchiectomy: Removal of the testicle for non-cancer reasons (injury, infection).
● Bilateral orchiectomy: Removal of both testicles, sometimes as part of prostate cancer hormone therapy or gender-affirming procedures.
★ Partial orchiectomy: Rare, preserves part of the testicle if feasible.
The procedure may also involve removal of the spermatic cord in cases of cancer to prevent spread.
What are the Benefits?
Orchiectomy offers several medical and therapeutic benefits:
✔ Curative treatment for testicular cancer.
➔ Hormone reduction in advanced prostate cancer to slow tumor growth.
● Pain relief in cases of severe trauma or infection.
★ Prevents metastasis when performed early for testicular malignancy.
➤ Part of gender-affirming surgery, aligning physical anatomy with identity.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Orchiectomy?
Preparation ensures a smooth procedure and recovery:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT), and cancer markers.
➔ Medication review: Blood thinners may need to be paused.
● Fasting: Usually 6–8 hours prior if general anesthesia is planned.
★ Counseling: Discuss surgical method, potential hormone changes, fertility implications, and recovery expectations.
➤ Fertility considerations: Sperm banking may be recommended for patients planning future fatherhood.
2) What happens during the procedure Orchiectomy?
Orchiectomy is performed under general or regional anesthesia:
✔ Incision: Typically in the groin (inguinal) or scrotum.
➔ Testicle removal: The surgeon carefully detaches the testicle from surrounding tissue.
● Spermatic cord management: In radical orchiectomy, the cord is removed to reduce cancer spread risk.
★ Closure: Incision is sutured, and a sterile dressing applied.
➤ Duration: Usually 30–60 minutes for a single testicle; bilateral orchiectomy may take slightly longer.
Korean hospitals use minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery and reduced scarring.
3) What happens after Orchiectomy?
Post-operative care focuses on healing and monitoring:
✔ Hospital stay: Often outpatient or 1–2 days depending on complexity.
➔ Pain management: Mild to moderate pain controlled with medications.
● Activity restrictions: Avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting for 2–4 weeks.
★ Hormonal changes: May require testosterone replacement therapy if both testicles are removed.
➤ Follow-up: Wound checks, monitoring for infection, and counseling on fertility or hormone therapy.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at the incision site
➔ Bleeding or hematoma formation
● Swelling or bruising of the scrotum
★ Hormonal imbalance or reduced libido (especially with bilateral orchiectomy)
➤ Psychological impact or emotional distress
Major Benefits:
✔ Effective treatment for testicular and prostate cancers
➔ Hormone regulation in prostate cancer therapy
● Pain relief in traumatic or diseased testicles
★ Prevents cancer spread when performed early
➤ Minimally invasive techniques in Korea improve safety and recovery
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: 1–2 weeks for incision healing; 4–6 weeks for full activity.
➔ Pain management: Most patients experience mild discomfort that resolves with medication.
● Hormone management: Testosterone replacement may be needed if both testicles are removed.
★ Fertility considerations: Sperm banking prior to surgery preserves reproductive options.
➤ Long-term outlook: Excellent for cancer treatment with high survival rates when diagnosed early.
When To Call the Doctor
Seek medical advice if experiencing:
✔ Excessive swelling, redness, or bleeding
➔ Fever or signs of infection
● Severe pain unrelieved by medication
★ Wound opening or discharge
➤ Hormonal imbalance symptoms such as fatigue, mood changes, or hot flashes
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class orchiectomy treatment, featuring:
✔ Leading hospitals: Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center.
➔ Advanced surgical techniques: Minimally invasive inguinal orchiectomy.
● Multidisciplinary teams: Urologists, oncologists, endocrinologists, and fertility specialists.
★ Comprehensive aftercare: Wound care, hormone therapy, and psychological support.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation services, travel coordination, and post-op follow-up for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Surgical removal of one or both testicles
➔ Treats testicular cancer, prostate cancer, trauma, or part of gender-affirming surgery
● Minimally invasive options reduce recovery time and scarring
★ Risks include infection, hormonal changes, or psychological impact
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced care, post-operative support, and excellent outcomes