Overview
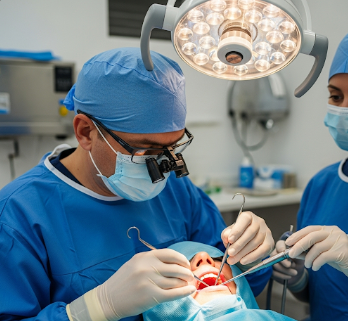
Oral surgery is a branch of dentistry that involves surgical treatment of the teeth, gums, jaws, and related structures. It addresses conditions that cannot be resolved with standard dental treatments, such as impacted teeth, jaw misalignment, oral tumors, or facial trauma.
In South Korea, oral surgery is performed at highly specialized dental and maxillofacial centers, using advanced imaging, 3D-guided surgery, and minimally invasive techniques to ensure precision, safety, and faster recovery.
What is Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery encompasses a variety of procedures aimed at restoring oral function, aesthetics, and health:
✔ Tooth extraction: Removal of impacted or damaged teeth.
➔ Jaw surgery (orthognathic surgery): Corrects misaligned jaws or bite issues.
● Dental implant placement: Provides permanent tooth replacement.
★ Treatment of cysts, tumors, or facial trauma.
Commonly treated conditions:
- Impacted wisdom teeth
- Malocclusion (misaligned bite)
- Cleft lip and palate
- Oral cysts or tumors
- Facial fractures
What are the Benefits?
Oral surgery offers several key advantages:
✔ Restores oral function, allowing proper chewing and speech.
➔ Corrects jaw misalignment for aesthetic and functional improvement.
● Prevents infection by removing impacted or diseased teeth.
★ Supports long-term dental health through implant placement.
➤ Reduces pain and discomfort associated with dental or jaw issues.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Oral Surgery?
Preparation depends on the specific procedure:
✔ Comprehensive evaluation: Dental X-rays, 3D CT scans, and oral exams.
➔ Medical history review: To identify allergies, medications, or chronic conditions.
● Fasting: Required for procedures under general anesthesia.
★ Medication adjustments: Blood thinners may need to be paused.
➤ Patient counseling: Surgeons explain procedure, risks, recovery, and oral care instructions.
2) What happens during the procedure Oral Surgery?
The procedure varies based on the type of oral surgery:
✔ Anesthesia: Local, sedation, or general anesthesia depending on complexity.
➔ Tooth extraction: Surgical exposure and removal of impacted teeth.
● Jaw surgery: Surgical cuts and repositioning of jaw bones, sometimes with plates and screws.
★ Implant placement: Titanium posts inserted into the jawbone for tooth replacement.
➤ Soft tissue procedures: Removal of cysts, tumors, or repair of trauma as needed.
Modern Korean clinics use minimally invasive techniques and computer-guided surgery to enhance precision and reduce complications.
3) What happens after Oral Surgery?
Recovery involves careful post-operative care:
✔ Immediate recovery: Observation for bleeding, swelling, and pain control.
➔ Diet: Soft foods recommended initially; avoid hard or chewy foods.
● Oral hygiene: Gentle rinsing and cleaning to prevent infection.
★ Pain management: Medications prescribed as needed.
➤ Follow-up: Regular check-ups to ensure proper healing and integration of implants or surgical repairs.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at surgical site
➔ Bleeding or swelling
● Nerve damage causing temporary or permanent numbness
★ Sinus complications (for upper jaw surgery)
➤ Implant failure or improper healing
Major Benefits:
✔ Resolves dental pain and prevents further complications
➔ Restores chewing, speaking, and aesthetic function
● Corrects jaw alignment and bite issues
★ Long-lasting dental implants provide permanent solutions
➤ Minimally invasive techniques in Korea enhance safety and recovery
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: 1–2 weeks for simple procedures; 4–6 weeks for jaw surgery.
➔ Oral hygiene: Gentle brushing and antiseptic rinses are crucial.
● Diet: Soft foods initially; gradually return to normal diet.
★ Long-term outlook: Most patients experience improved oral function and aesthetics.
➤ Follow-up care: Periodic visits for implants, jaw alignment, or trauma repair ensure lasting results.
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their doctor if they notice:
✔ Excessive bleeding or swelling
➔ Fever or signs of infection
● Numbness or tingling that does not improve
★ Difficulty opening the mouth or persistent pain
➤ Displacement of dental implants or surgical hardware
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is internationally recognized for oral and maxillofacial surgery:
✔ Top hospitals and clinics: Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center.
➔ Advanced imaging: 3D CT scans and computer-guided surgery for precision.
● Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted procedures reduce recovery time.
★ Multidisciplinary teams: Oral surgeons, orthodontists, prosthodontists, and anesthesiologists.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation services, travel assistance, and customized care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Oral surgery treats teeth, jaw, and facial issues surgically
➔ Includes extractions, implants, jaw realignment, and tumor removal
● Minimally invasive and computer-guided techniques enhance safety
★ Risks include infection, nerve injury, or implant failure
➤ Korean hospitals provide world-class outcomes with rapid recovery