Overview
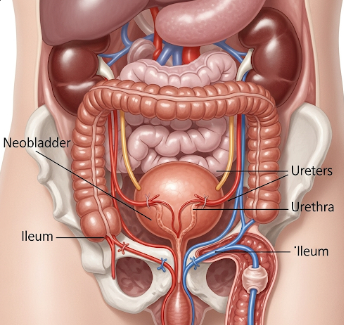
Neobladder reconstruction is a complex surgical procedure that creates a new bladder from a section of the intestine after the removal of the original bladder (cystectomy). It is most often performed in patients who have had their bladder removed due to bladder cancer, but it may also be used in severe trauma or congenital abnormalities. The new bladder (called a neobladder) is connected to the urethra, allowing patients to urinate in a more natural way without needing an external bag.
In South Korea, neobladder reconstruction is performed at leading urology and oncology centers using cutting-edge surgical techniques, including robot-assisted surgery. Korean hospitals emphasize not only cancer control but also quality of life, with excellent rehabilitation and long-term patient care.
What is Neobladder Reconstruction?
Neobladder reconstruction involves using a segment of the small intestine (commonly the ileum) to build a reservoir that functions like the natural bladder. The neobladder is then attached to the ureters (carrying urine from the kidneys) and the urethra (through which urine exits the body).
✔ Purpose: To restore natural urination after bladder removal.
➤ Alternative to urostomy: Unlike external urinary diversion (urostomy bag), a neobladder allows urine to pass through the urethra.
★ Patient suitability: Typically offered to younger, healthier patients who can manage the care and training needed for the new bladder.
What are the Benefits?
Neobladder reconstruction provides many quality-of-life advantages:
✔ Natural urination without needing an external urine bag.
➔ Improved body image and self-confidence.
● Better social comfort compared to an external pouch.
★ Long-term durability, functioning for decades with proper care.
➤ Maintains kidney function by ensuring proper drainage.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Neobladder Reconstruction?
Preparation is critical since this is a major surgery:
✔ Comprehensive evaluation: Imaging scans, cystoscopy, and lab tests confirm candidacy.
➔ Nutrition and fitness optimization: Patients may be asked to increase protein intake and exercise to support healing.
● Medication adjustments: Blood thinners and certain drugs may need to be stopped.
★ Bowel preparation: Since intestine is used, cleansing of the bowel is required before surgery.
➤ Counseling: Doctors explain the risks, benefits, and lifestyle changes, ensuring patients are mentally and emotionally prepared.
2) What happens during the procedure Neobladder Reconstruction?
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and can take 4–7 hours:
✔ Bladder removal (cystectomy): If not already done, the diseased bladder is removed.
➔ Intestine selection: A section of small intestine (usually 40–60 cm) is isolated.
● Neobladder creation: The intestinal segment is reshaped into a spherical reservoir.
★ Connection: The neobladder is attached to the ureters and urethra.
➤ Closure: The surgical site is closed, and drainage tubes/catheters are placed.
Modern Korean hospitals often use robot-assisted surgery, which provides:
- Smaller incisions
- Less blood loss
- Faster recovery
- Better cosmetic results
3) What happens after a Neobladder Reconstruction?
Post-surgical care is essential for recovery and function:
✔ Hospital stay: Usually 10–14 days for monitoring.
➔ Catheter use: A catheter remains in place for 2–3 weeks to allow healing.
● Urine training: Patients learn to empty the neobladder on schedule, as the sensation of fullness may differ from a natural bladder.
★ Rehabilitation: Pelvic floor exercises strengthen control and reduce leakage.
➤ Follow-up care: Regular imaging, lab tests, and check-ups ensure kidney and neobladder health.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
➔ Urinary leakage or incontinence (especially at night in early months)
✔ Urinary retention, requiring catheterization
● Infection in urinary tract or kidneys
★ Electrolyte imbalance due to intestine absorption properties
➤ Strictures (narrowing at the connection sites)
Major Benefits:
✔ More natural urination compared to external bags
➔ Improved quality of life
● No visible appliance on the body
★ Preserves dignity and independence
➤ Safe long-term solution for suitable patients
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: Patients may need 6–8 weeks before returning to normal daily activities.
➔ Continence improvement: Continence gradually improves, with most patients achieving daytime control in 6 months.
● Long-term function: With proper training, most patients urinate 4–6 times daily like normal.
★ Lifestyle adjustments: Patients need to set urination schedules, especially at night.
➤ Outlook: Many patients live full, active lives with a neobladder, and Korean hospitals provide continuous follow-up for cancer monitoring.
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their doctor immediately if they experience:
✔ Severe abdominal pain or fever (possible infection)
➔ Excessive leakage not improving with time
● Blood in urine after recovery
★ Difficulty emptying the neobladder
➤ Swelling in legs or abdomen (possible obstruction or kidney issue)
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is one of the leading destinations for bladder cancer surgery and urinary reconstruction. Patients benefit from:
✔ Highly trained urologists skilled in advanced and robot-assisted procedures.
➔ Top hospitals such as Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital.
● Integrated care teams including oncologists, urologists, rehabilitation specialists, and nutritionists.
★ Cutting-edge technology for precise surgery and faster recovery.
➤ Medical tourism support, including interpreters, recovery planning, and accommodation.
Korean hospitals focus on restoring both health and quality of life, making neobladder reconstruction a preferred choice for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Creates a new bladder from intestine after bladder removal
➔ Allows urination through the urethra, no external bag required
● Robot-assisted surgery in Korea offers faster recovery
★ Risks include leakage, infection, or strictures, but long-term outcomes are excellent
➤ Top Korean hospitals provide advanced surgery and comprehensive aftercare