Overview
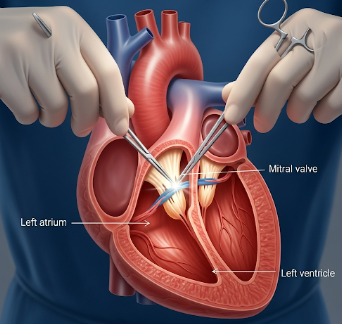
Mitral valve surgery is a cardiac procedure performed to repair or replace the mitral valve, which controls blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. This surgery is commonly required for mitral valve stenosis, mitral regurgitation, or congenital mitral valve defects.
In Korea, mitral valve surgery is performed by expert cardiothoracic surgeons using advanced techniques such as minimally invasive surgery, robotic-assisted surgery, or traditional open-heart approaches, ensuring precise correction and optimal heart function.
Highlights:
- ✅ Corrects mitral valve dysfunction
- ✅ Improves heart efficiency and reduces symptoms
- ✅ Can prevent complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, or stroke
- ✅ Advanced surgical options available including repair and replacement
What is Mitral Valve Surgery?
Mitral valve surgery is designed to restore normal function of the mitral valve by either:
- Repair: Fixing the patient’s existing valve using techniques like annuloplasty, leaflet repair, or chordal reconstruction
- Replacement: Replacing the valve with a mechanical or biological prosthesis if repair is not feasible
Indications include:
- Mitral regurgitation (leakage of the valve)
- Mitral stenosis (narrowing of the valve)
- Valve dysfunction due to infection (endocarditis) or degenerative disease
- Symptomatic patients with heart failure or arrhythmias
Important: Repair is usually preferred when feasible, as it preserves native tissue and improves long-term outcomes, but replacement may be necessary in severe cases.
What are the benefits?
- Improved cardiac function: Corrects blood flow, reducing symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations
- Prevents complications: Reduces risk of heart failure, stroke, or pulmonary hypertension
- Enhanced quality of life: Patients can return to normal activities with better exercise tolerance
- Long-term outcomes: Mitral valve repair often provides durable results, reducing the need for future interventions
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Relief from heart failure symptoms
- ⚡ Prevention of life-threatening complications
- ⚡ High success rates with experienced surgical teams
- ⚡ Options for minimally invasive or robotic-assisted approaches
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Mitral Valve Surgery?
- Preoperative evaluation: Echocardiography, cardiac catheterization, CT or MRI, blood tests, and chest imaging
- Medication review: Adjust anticoagulants, diabetes medications, and heart medications as instructed
- Fasting: Usually 8–12 hours before surgery
- Consent and counseling: Discuss procedure type (repair vs replacement), risks, recovery, and long-term care
- Lifestyle preparation: Arrange postoperative care, support, and plan for rehabilitation
2) What happens during Mitral Valve Surgery?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia administered
- Incision: Either a median sternotomy (traditional open-heart) or minimally invasive small chest incision
- Cardiopulmonary bypass: Blood is circulated via a heart-lung machine while the heart is stopped
- Valve repair or replacement:
- Repair: Techniques like annuloplasty rings, leaflet reconstruction, or chordal replacement
- Replacement: Implantation of mechanical or biological prosthetic valve
- Closure: Heart restarted, chest incision closed, and drains placed if necessary
Duration: Typically 3–6 hours depending on complexity
3) What happens after Mitral Valve Surgery?
- Recovery monitoring: ICU observation for 1–2 days, then step-down or general ward
- Pain management: Analgesics and monitoring for post-surgical discomfort
- Activity: Gradual mobilization; initially assisted walking, progressing to normal activities over weeks
- Follow-up care: Echocardiography and regular cardiology visits to monitor valve function and heart performance
Highlights for post-procedure care:
- ⚡ Monitor for signs of infection or bleeding
- ⚡ Follow strict anticoagulation regimen if mechanical valve implanted
- ⚡ Gradual cardiac rehabilitation improves recovery and fitness
- ⚡ Attend all follow-up visits to ensure valve function and heart health
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Bleeding or infection
- Stroke or heart attack during or after surgery
- Arrhythmias
- Valve dysfunction or prosthetic complications
- Rare anesthesia-related complications
Benefits:
- Corrects mitral valve dysfunction
- Improves heart efficiency and quality of life
- Prevents heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and stroke
- Long-lasting results, especially with repair procedures
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: 5–10 days, depending on surgery type and recovery
- Full recovery: 6–12 weeks for general activities; cardiac rehabilitation recommended
- Long-term outlook: Excellent for repaired or replaced valves, with regular follow-up
- Follow-up: Routine echocardiography, anticoagulation monitoring (if mechanical valve), and cardiology check-ups
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Follow cardiac rehabilitation and activity recommendations
- ✅ Adhere to medication and anticoagulation schedules
- ✅ Monitor for fever, swelling, or unusual symptoms
- ✅ Attend all follow-up appointments
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever or signs of infection
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations
- Excessive bleeding or fluid accumulation at incision site
- Signs of stroke or neurological changes
- Any unusual post-operative symptoms
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides advanced Mitral Valve Surgery care:
- Top hospitals: Specialized cardiac centers with experienced cardiothoracic surgeons
- Advanced surgical techniques: Open-heart, minimally invasive, and robotic-assisted valve repair/replacement
- Preoperative evaluation: Echocardiography, CT, MRI, and cardiology consultation
- Postoperative care: ICU monitoring, pain management, anticoagulation guidance, and cardiac rehabilitation
- International patient support: Online consultation, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Preoperative consultation, imaging, and evaluation
- Surgery performed under general anesthesia with cardiac support
- Postoperative ICU and ward care with monitoring
- Gradual recovery with cardiac rehabilitation and follow-up visits
- Long-term follow-up for valve function, anticoagulation, and cardiac health