Overview
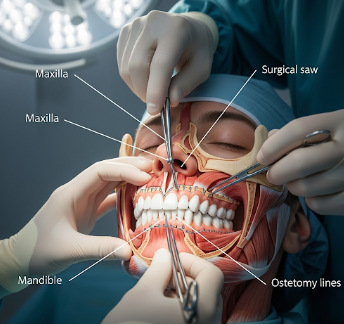
Maxillofacial surgery is a specialized surgical discipline focusing on the treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects of the mouth, jaw, face, and related structures. This includes both cosmetic and functional corrections, such as jaw realignment, facial trauma repair, congenital deformity correction, and tumor removal.
In Korea, maxillofacial surgery is performed by highly skilled oral and maxillofacial surgeons, using state-of-the-art technology, including 3D imaging, minimally invasive approaches, and robotic-assisted surgery, ensuring precise outcomes with optimal aesthetics and functionality.
Highlights:
- ✅ Corrects congenital and acquired facial deformities
- ✅ Treats jaw and facial fractures
- ✅ Improves oral function, speech, and chewing
- ✅ Advanced cosmetic reconstruction available
What is Maxillofacial Surgery?
Maxillofacial surgery encompasses surgical interventions on the facial bones, jaws, oral cavity, and surrounding soft tissues. Common procedures include:
- Orthognathic surgery (correcting jaw alignment)
- TMJ surgery (temporomandibular joint disorders)
- Facial trauma repair (fractures of jaw, cheek, or orbital bones)
- Cleft lip and palate repair
- Removal of tumors or cysts in the facial region
- Cosmetic surgeries like chin or cheekbone reshaping
Important: Maxillofacial surgery addresses both functional and aesthetic concerns, improving oral health, facial symmetry, and overall quality of life.
What are the benefits?
- Functional improvement: Corrects bite, chewing, and jaw alignment
- Cosmetic enhancement: Restores facial symmetry and appearance
- Pain relief: Treats TMJ disorders, facial nerve compression, and chronic jaw pain
- Trauma repair: Restores structure and function after injuries
- Long-term health: Prevents complications such as tooth wear, jaw misalignment, and breathing difficulties
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Improved oral and facial function
- ⚡ Enhanced facial aesthetics and symmetry
- ⚡ Relief from chronic jaw or facial pain
- ⚡ Reconstructive solutions for congenital or trauma-related deformities
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Maxillofacial Surgery?
- Preoperative evaluation: 3D imaging (CT or CBCT), dental models, medical history, and blood tests
- Medication review: Stop blood thinners or other medications as instructed
- Fasting: Required if general anesthesia is planned
- Consent and counseling: Discuss the type of surgery, expected outcomes, potential risks, and recovery plan
- Lifestyle preparation: Arrange transportation, post-surgery care, and dietary adjustments
2) What happens during Maxillofacial Surgery?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is most commonly used
- Surgical procedure: Varies depending on the type of surgery:
- Orthognathic surgery: Realignment of jaws with plates and screws
- TMJ surgery: Repair or replacement of joint structures
- Trauma repair: Reduction and fixation of fractures using plates, screws, or wires
- Tumor or cyst removal: Excision followed by reconstruction if needed
- Closure: Sutures, plates, or other fixation devices applied as needed
Duration: Typically 1–6 hours depending on the complexity of the surgery
3) What happens after Maxillofacial Surgery?
- Recovery monitoring: ICU or ward observation for pain, bleeding, and airway management
- Pain management: Analgesics and sometimes anti-inflammatory medications
- Activity: Soft diet, limited physical activity, and head elevation
- Follow-up care: Wound inspection, dental adjustments, physiotherapy, and imaging to monitor healing
Highlights for post-procedure care:
- ⚡ Swelling, bruising, and temporary numbness are common
- ⚡ Soft or liquid diet recommended initially
- ⚡ Oral hygiene and wound care crucial to prevent infection
- ⚡ Attend all follow-up visits for optimal outcomes
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Infection or delayed wound healing
- Nerve injury causing numbness or tingling
- Bleeding or hematoma formation
- Malocclusion or bite issues if alignment is not optimal
- Rare anesthesia-related complications
Benefits:
- Restores facial structure and function
- Improves oral health and bite alignment
- Corrects aesthetic or congenital deformities
- Provides long-term relief from pain or functional impairments
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: 1–5 days depending on procedure type
- Full recovery: 2–6 weeks for most activities; jaw exercises may continue for several months
- Long-term outlook: Excellent with proper follow-up, physiotherapy, and adherence to dietary restrictions
- Follow-up: Regular visits to monitor healing, jaw function, and oral health
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Follow dietary and oral hygiene instructions
- ✅ Perform recommended physiotherapy exercises
- ✅ Avoid strenuous activities and trauma to the face
- ✅ Attend all follow-up appointments for assessment and adjustments
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- Excessive swelling, bleeding, or unusual discharge
- Severe pain not relieved by medication
- Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing
- Numbness or sensory changes in the face
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides advanced Maxillofacial Surgery care:
- Top hospitals: Specialized craniofacial and oral-maxillofacial centers
- Advanced surgical techniques: 3D imaging, computer-assisted planning, minimally invasive, and robotic-assisted surgery
- Comprehensive care: Preoperative planning, surgery, postoperative monitoring, physiotherapy, and dental support
- Cosmetic and reconstructive options: Jaw realignment, facial contouring, and trauma repair
- International patient support: Online consultations, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Preoperative consultation and imaging assessment
- Surgical planning and patient counseling
- Surgery performed under general anesthesia with advanced techniques
- Postoperative monitoring, pain management, and diet modification
- Follow-up visits for wound healing, jaw function, and aesthetic outcomes