Overview
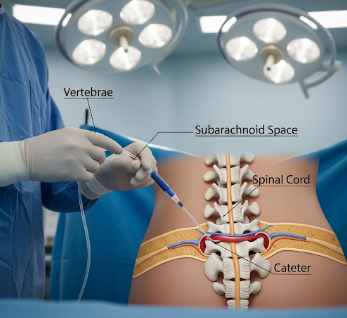
A Lumbar Drain is a medical procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the lower back (lumbar region) to drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is commonly used to reduce intracranial pressure, prevent CSF leakage, or assist in post-surgical recovery.
In Korea, lumbar drains are performed by experienced neurosurgeons and anesthesiologists using sterile techniques and imaging guidance to ensure precision and minimize complications.
Highlights:
- ✅ Helps manage cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure
- ✅ Prevents or treats CSF leakage
- ✅ Used in neurosurgery and spinal procedures
What is a Lumbar Drain?
A Lumbar Drain involves placing a thin catheter into the lumbar subarachnoid space of the spine to allow controlled drainage of CSF. This is often temporary and may be connected to a collection system for monitoring output.
Indications include:
- Prevention or treatment of CSF leaks after surgery
- Management of hydrocephalus or elevated intracranial pressure
- Adjunct in complex neurosurgical procedures
- Diagnostic purposes such as measuring CSF pressure
Important: Proper monitoring of drainage volume is critical to avoid complications such as low CSF pressure headaches or infection.
What are the benefits?
- Reduces intracranial pressure: Protects the brain and spinal cord
- Prevents CSF leakage: Especially post-neurosurgery
- Assists recovery: Improves outcomes after spinal or cranial procedures
- Diagnostic use: Helps evaluate CSF characteristics for medical decision-making
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Controlled and precise CSF drainage
- ⚡ Minimally invasive with short procedure time
- ⚡ Monitored drainage reduces risk of complications
- ⚡ Facilitates faster recovery in neurosurgical patients
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for a Lumbar Drain?
- Pre-procedure consultation: Review medical history, medications, and allergies
- Medication adjustments: Blood thinners may need to be paused
- Consent and education: Discuss risks, benefits, and duration of drainage
- Positioning: Patients may be asked to lie on their side or sit upright for catheter placement
- Infection prevention: Clean and sterile environment, possible prophylactic antibiotics
2) What happens during a Lumbar Drain?
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia at insertion site; sedation may be used if necessary
- Insertion: Needle inserted into the lumbar subarachnoid space between L3-L4 or L4-L5 vertebrae
- Catheter placement: Thin drain catheter advanced into the subarachnoid space
- Connection: Catheter connected to a closed collection system to monitor CSF output
- Verification: CSF flow observed to confirm correct placement
Duration: Typically 20–60 minutes
3) What happens after a Lumbar Drain?
- Monitoring: CSF output, neurological status, and vital signs closely monitored
- Positioning: Patients may need to remain flat or in specific positions to optimize drainage
- Pain management: Mild discomfort at insertion site may be treated with analgesics
- Follow-up care: Catheter removed after prescribed drainage period, usually several days
Highlights for post-procedure care:
- ⚡ Monitor for headache, nausea, or back pain
- ⚡ Keep insertion site clean and dry
- ⚡ Report fever, drainage changes, or neurological symptoms immediately
- ⚡ Follow all medical instructions for catheter care and removal
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Infection at insertion site or meningitis
- Headache due to low CSF pressure
- Bleeding or hematoma in the lumbar region
- Catheter blockage or displacement
Benefits:
- Controlled reduction of intracranial pressure
- Prevention or treatment of CSF leaks
- Supports recovery after neurosurgery
- Provides diagnostic information when needed
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Typically inpatient due to need for monitoring
- Full recovery: Catheter usually removed after several days; headaches or mild discomfort resolve soon after
- Long-term outlook: Safe with proper monitoring; most patients recover without complications
- Follow-up: Monitoring neurological function and ensuring no CSF leakage post-catheter removal
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Avoid sudden movements that may dislodge the catheter
- ✅ Maintain strict hygiene at the insertion site
- ✅ Report any unusual pain, drainage, or neurological changes
- ✅ Follow-up visits for neurological assessment
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- Severe headache, neck stiffness, or neurological changes
- Increased or unusual CSF leakage
- Catheter displacement or blockage
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides advanced lumbar drain care:
- Top hospitals: Experienced neurosurgeons and anesthesiologists
- Advanced monitoring: Continuous observation of CSF output and neurological status
- Minimally invasive placement: Sterile techniques and imaging guidance
- Postoperative care: Pain management, infection prevention, and safe catheter removal
- International patient support: Online consultation, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Online consultation and review of medical history
- Pre-procedure evaluation and preparation
- Lumbar drain insertion performed by expert neurosurgeon
- Monitoring and drainage management during hospital stay
- Safe removal of catheter and follow-up to ensure no complications