Overview
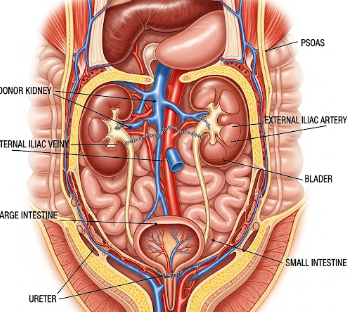
A kidney transplant is a surgical procedure to replace a non-functioning or diseased kidney with a healthy donor kidney. This procedure is the treatment of choice for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and provides better long-term outcomes than dialysis.
South Korea is recognized for advanced transplant programs, highly skilled surgeons, and comprehensive post-transplant care, making it a leading destination for patients seeking safe, effective, and long-term kidney replacement therapy.
What is a Kidney Transplant?
A kidney transplant involves:
- Removal of the non-functioning kidney (if necessary)
- Transplantation of a healthy donor kidney
- Restoration of kidney function to maintain waste filtration, fluid balance, and overall metabolism
Types of Kidney Transplant:
- Living donor transplant → Kidney from a healthy living donor (relative or compatible volunteer)
- Deceased donor transplant → Kidney from a recently deceased donor with prior consent
Purpose:
- Restore normal kidney function
- Eliminate or reduce dependence on dialysis
- Improve survival rates and quality of life
What are the Benefits?
- Restored kidney function → Eliminates or reduces dialysis dependency
- Improved quality of life → Better energy, diet, and overall health
- Long-term survival advantage → Transplants from living donors often have higher graft survival
- Reduced complications of kidney failure → Lower risk of cardiovascular issues, bone disease, and anemia
- Expert care in Korea → High success rates and comprehensive follow-up programs
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for a Kidney Transplant?
- Pre-transplant evaluation → Blood tests, imaging, cardiac assessment, and infection screening
- Donor compatibility testing → Blood type, HLA matching, and crossmatching
- Medication review → Adjust anticoagulants, immunosuppressants, and other medications
- Pre-procedure consultation → Discuss surgical plan, anesthesia, post-operative care, and potential complications
- Lifestyle preparation → Nutrition optimization, cessation of smoking, and general fitness
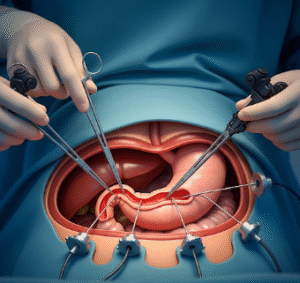
2) What happens during the procedure?
- Anesthesia → General anesthesia for complete sedation
- Patient positioning → Supine, sterile abdominal preparation
- Surgical steps →
- Donor kidney implanted in the lower abdomen
- Vascular connections established to iliac artery and vein
- Ureter connected to the bladder for urine drainage
- Verification of blood flow and urine production
- Closure of incisions with sutures
- Duration → Typically 3–5 hours
- Monitoring → Vital signs, urine output, and intraoperative imaging
3) What happens after surgery?
- Immediate post-operative care → ICU or high-dependency monitoring for 24–48 hours
- Immunosuppressive therapy → Prevent organ rejection
- Kidney function monitoring → Blood tests for creatinine, BUN, and electrolytes
- Activity restrictions → Gradual mobilization under supervision
- Follow-up visits → Frequent labs and consultations to ensure graft health
Risks / Benefits
Risks
- ➤ Organ rejection despite immunosuppressive therapy
- ➤ Infection due to immunosuppression
- ➤ Bleeding or vascular complications
- ➤ Surgical complications (wound infection, urine leakage)
- ➤ Long-term side effects of immunosuppressive drugs
Benefits
- ➤ Restores kidney function and reduces dialysis dependency
- ➤ Improves quality of life and life expectancy
- ➤ Better long-term survival compared to dialysis
- ➤ Reduces complications associated with kidney failure
- ➤ Expert multidisciplinary care in Korea ensures high success rates
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery → ICU stay for 1–2 days; hospital stay 5–10 days
- Short-term follow-up → Monitor kidney function, immunosuppressive therapy adjustment, and lab tests
- Return to daily activity → Light activity within a few weeks; full recovery within 2–3 months
- Long-term follow-up → Regular lab tests, kidney function monitoring, and lifestyle management
- Expected results → Functional kidney, improved energy, elimination of dialysis, and improved life quality
South Korea provides state-of-the-art transplant centers, continuous monitoring, and comprehensive patient education, ensuring safe and effective kidney transplantation outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your transplant team immediately if you notice:
- ⚠️ Decreased urine output or swelling
- ⚠️ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- ⚠️ Pain, redness, or discharge at the incision site
- ⚠️ Symptoms of organ rejection (fatigue, nausea, unusual pain, or jaundice)
- ⚠️ Any sudden changes in blood pressure or general health
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a leading destination for kidney transplantation due to:
- Expert transplant surgeons and nephrologists
- Advanced donor matching and immunosuppressive protocols
- Comprehensive multidisciplinary care → Nephrology, surgery, nutrition, and ICU
- Post-transplant monitoring and patient support services
- International patient services → Consultation, scheduling, translation, and follow-up
Top Hospitals for Kidney Transplant in Korea:
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Leading transplant program with high success rates
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced surgical techniques and post-op care
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Comprehensive multidisciplinary care
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Safe and expert kidney transplantation services
👉 For patients with end-stage renal disease, kidney transplant in Korea offers life-saving surgery, restored organ function, and significantly improved quality of life.