Overview
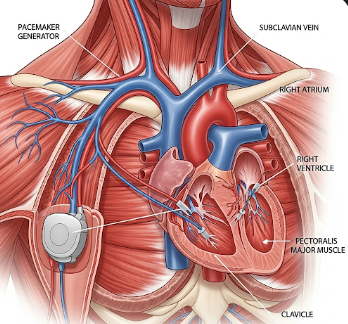
Pacemaker insertion is a medical procedure to implant a small electronic device that helps regulate abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias). The pacemaker monitors the heart’s electrical activity and delivers electrical impulses to maintain a regular heartbeat, ensuring adequate blood flow throughout the body.
South Korea is known for advanced cardiac care, highly skilled cardiologists, and cutting-edge pacemaker technology, making it a preferred destination for patients seeking safe, effective, and long-term arrhythmia management.
What is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin near the collarbone with leads (wires) threaded into the heart chambers. It functions to:
- Monitor heart rate and rhythm continuously
- Deliver electrical impulses when the heart beats too slowly (bradycardia)
- Ensure proper coordination of atrial and ventricular contractions
- Provide long-term protection against heart rhythm disorders
Indications for pacemaker insertion include:
- Symptomatic bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Heart block or conduction system abnormalities
- Syncope (fainting) due to arrhythmias
- Heart failure patients with electrical dyssynchrony
What are the Benefits?
- Restores normal heart rhythm → Improves blood circulation and energy levels
- Reduces risk of fainting or sudden cardiac events
- Improves quality of life → Reduces fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath
- Minimally invasive procedure → Small incision with quick recovery
- Continuous heart monitoring → Data recorded for follow-up and device adjustment
- Expert cardiac care in Korea → High procedural success and advanced device programming
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for pacemaker insertion?
- Preoperative evaluation → ECG, echocardiogram, blood tests, chest X-ray
- Medication review → Adjust blood thinners or heart medications as advised
- Fasting → Typically 6–8 hours before the procedure
- Pre-procedure consultation → Discuss device type (single-chamber, dual-chamber, or biventricular), anesthesia, and risks
- Lifestyle preparation → Avoid smoking, maintain hydration, and follow cardiologist instructions
2) What happens during the procedure?
- Anesthesia → Local anesthesia with mild sedation
- Patient positioning → Supine on procedure table with upper chest exposed
- Surgical steps →
- Small incision made near the collarbone
- Leads inserted through a vein into heart chambers
- Leads tested for proper sensing and pacing
- Pacemaker connected to leads and implanted under the skin
- Incision closed with sutures or adhesive
- Duration → Approximately 1–2 hours depending on device type and complexity
- Monitoring → Continuous ECG, oxygen saturation, and vital signs
3) What happens after pacemaker insertion?
- Immediate post-operative care → Observation in recovery for a few hours to overnight
- Pain management → Mild analgesics prescribed for comfort
- Activity restrictions → Avoid lifting the arm on the implantation side above shoulder level for 4–6 weeks
- Device programming → Pacemaker settings adjusted to individual heart rhythm needs
- Follow-up visits → Device checks, incision healing assessment, and cardiac monitoring
Risks / Benefits
Risks
- ➤ Infection at the implantation site
- ➤ Bleeding, bruising, or hematoma
- ➤ Lead displacement or malfunction
- ➤ Rare heart perforation or arrhythmia induction
- ➤ Allergic reaction to local anesthesia or device materials
Benefits
- ➤ Restores and maintains normal heart rhythm
- ➤ Reduces risk of fainting or sudden cardiac events
- ➤ Minimally invasive with short recovery time
- ➤ Continuous monitoring and programmable device
- ➤ High success rate under expert cardiac care in Korea
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery → Mild soreness at incision site; monitored in hospital
- Short-term follow-up → Device check and ECG within 1–2 weeks
- Return to normal activity → Light activity after a few days; full activity after 4–6 weeks
- Long-term outcomes → Improved survival, reduced symptoms of bradycardia, and enhanced quality of life
- Post-procedure care → Regular device checks, medication adherence, and avoiding strong electromagnetic interference
- Lifestyle guidance → Maintain heart-healthy habits, avoid heavy lifting on the implantation side, and attend follow-ups
South Korea provides comprehensive cardiac care, device monitoring, and patient education to ensure safe and effective long-term outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your cardiologist immediately if you notice:
- ⚠️ Redness, swelling, or discharge at the incision site
- ⚠️ Fever or signs of infection
- ⚠️ Severe chest pain or shortness of breath
- ⚠️ Dizziness, fainting, or unusual palpitations
- ⚠️ Device alarms or unexpected shocks (if combined with ICD)
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a leading destination for pacemaker implantation due to:
- Expert cardiologists and electrophysiologists
- State-of-the-art cardiac catheterization labs
- Comprehensive pre- and post-procedure care
- Minimally invasive implantation with high success and low complication rates
- International patient support → Consultation, translation, scheduling, and follow-up coordination
Top Hospitals for Pacemaker Insertion in Korea:
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced pacemaker and cardiac device implantation
- Samsung Medical Center – Expertise in complex arrhythmias and device management
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Comprehensive cardiac care and monitoring
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Multidisciplinary cardiac management and device follow-up
👉 For patients with abnormal heart rhythms, pacemaker implantation in Korea provides a safe, effective, and expertly managed solution with long-term cardiac protection.