Overview
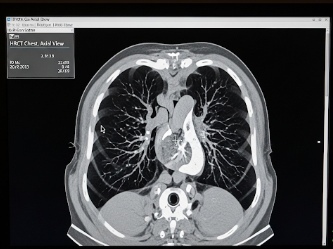
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) is an advanced form of radiation treatment used to precisely target tumors while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. By using real-time imaging before and during radiation delivery, IGRT enhances accuracy, safety, and effectiveness, making it particularly useful for cancers in areas prone to movement, such as the lungs, prostate, or abdomen.
South Korea is globally recognized for state-of-the-art radiotherapy technology, highly experienced oncologists, and precision-guided cancer care, making it a preferred destination for IGRT.
What is IGRT?
IGRT is a specialized radiation therapy technique that involves:
- Using imaging modalities (CT, X-ray, MRI, or cone-beam CT) to visualize the tumor immediately before or during radiation delivery
- Adjusting patient positioning and radiation beam direction based on tumor movement
- High-precision radiation targeting → Reduces exposure to surrounding healthy organs
- Integration with modern radiotherapy platforms such as linear accelerators and stereotactic systems
Indications include:
- Prostate, lung, head and neck, liver, and pancreatic cancers
- Tumors located near critical organs
- Moving tumors affected by breathing or organ motion
- Patients requiring precise dose escalation without increasing side effects
What are the Benefits?
- High precision and accuracy → Minimizes radiation exposure to healthy tissue
- Reduced side effects → Lower risk of gastrointestinal, urinary, or skin complications
- Enhanced tumor control → Allows higher radiation doses to tumors safely
- Adaptability → Adjusts for tumor movement and anatomical changes during treatment
- Shorter treatment courses in some cases due to precise targeting
- Expert care in Korea → IGRT delivered with cutting-edge technology and experienced oncology teams
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for IGRT?
- Pre-treatment consultation → Review medical history, imaging scans, and cancer stage
- Simulation session → CT or MRI scans to map tumor location and plan treatment
- Positioning and immobilization → Custom molds, masks, or cushions may be created for consistent positioning
- Dietary or medication guidance → Follow oncologist instructions if specific preparation is needed
- Fasting or bladder preparation → Required in some cases, e.g., pelvic cancers
2) What happens during IGRT?
- Patient positioning → Lie on treatment couch in the same position as simulation
- Imaging before treatment → Cone-beam CT, X-ray, or MRI confirms tumor location
- Adjustment of radiation beams → On-the-spot corrections made if the tumor has shifted
- Radiation delivery → High-precision beams administered to the tumor
- Duration → Each session usually 15–45 minutes depending on complexity
- Monitoring → Continuous observation to ensure safety and accuracy
3) What happens after IGRT?
- Immediate post-treatment → Resume normal activities; no recovery time needed for each session
- Follow-up schedule → Regular imaging and oncology consultations to assess response
- Side effect management → Mild fatigue, skin redness, or localized irritation may occur
- Long-term monitoring → Imaging and lab tests to track tumor response and manage complications
- Integration with other treatments → Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or surgery may be combined
Risks / Benefits
Risks
- ➤ Skin irritation or redness in the treated area
- ➤ Fatigue during the treatment course
- ➤ Temporary swelling or inflammation of nearby tissues
- ➤ Radiation-related organ damage (rare, minimized with IGRT)
- ➤ Potential nausea or urinary symptoms depending on tumor location
Benefits
- ➤ Precise tumor targeting with minimal damage to healthy tissue
- ➤ Reduced side effects compared to conventional radiation therapy
- ➤ Ability to treat moving tumors safely
- ➤ Shorter, more effective treatment courses
- ➤ Access to world-class oncology teams and technology in Korea
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery → Patients can resume daily activities after each session
- Treatment course → Usually several sessions over 1–6 weeks depending on cancer type
- Long-term outlook → High precision targeting improves tumor control rates and reduces recurrence risk
- Side effect management → Oncologists provide supportive care for fatigue, skin care, and minor complications
- Follow-up care → Imaging, lab tests, and oncology consultations ensure optimal outcomes
South Korea provides comprehensive cancer care, including IGRT, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and multidisciplinary follow-up, ensuring patients receive personalized, state-of-the-art treatment.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your oncologist if you notice:
- ⚠️ Severe skin reactions or blistering
- ⚠️ Intense fatigue affecting daily life
- ⚠️ Persistent nausea, vomiting, or urinary symptoms
- ⚠️ Shortness of breath or chest pain during or after treatment
- ⚠️ Signs of infection or unusual symptoms around the treatment site
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a leading destination for IGRT due to:
- Advanced radiation therapy technology, including linear accelerators, cone-beam CT, and MRI-guided systems
- Expert radiation oncologists and multidisciplinary teams
- Personalized treatment planning using simulation and image-guidance
- Integrated supportive care → Nutrition, physiotherapy, and symptom management
- International patient services → Appointment scheduling, translation, and follow-up support
Top Hospitals for IGRT in Korea:
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced image-guided radiotherapy for complex tumors
- Samsung Medical Center – Precision IGRT with multidisciplinary oncology support
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Comprehensive cancer care integrating IGRT and other therapies
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Personalized treatment planning and follow-up for international patients
👉 For patients with complex, moving, or hard-to-reach tumors, IGRT in Korea provides precise, safe, and effective radiation therapy with state-of-the-art technology and expert care.