Overview
Esophageal dilation is a medical procedure used to widen a narrowed (strictured) esophagus. This procedure helps relieve difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), improve nutrition, and restore normal esophageal function. It is commonly performed for patients with esophageal strictures, achalasia, or scarring from acid reflux or surgery.
In South Korea, esophageal dilation is carried out in advanced gastroenterology centers and hospitals, employing high-resolution endoscopy, precision dilation tools, and expert gastroenterologists to ensure safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment.
What is Esophageal Dilation?
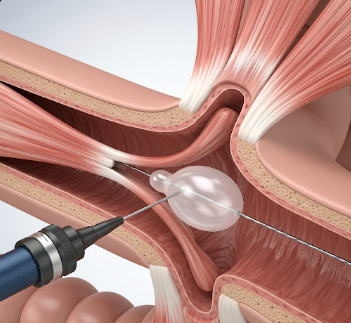
Esophageal dilation involves stretching or widening the esophagus using specialized instruments to treat strictures or narrowing that cause swallowing difficulties.
Purpose:
- Restore normal swallowing function
- Reduce risk of malnutrition or aspiration
- Treat benign or post-surgical esophageal strictures
- Improve quality of life by relieving pain and discomfort
Techniques:
- Bougie dilation: Using tapered rods to gradually widen the esophagus
- Balloon dilation: Inflating a balloon at the stricture site to expand the esophagus
- Endoscopic guidance: Ensures accurate placement and prevents complications
What are the Benefits?
Esophageal dilation offers multiple functional and therapeutic benefits:
✔ Immediate improvement in swallowing and nutrition.
✔ Minimally invasive with outpatient procedure option.
✔ Can be repeated if strictures recur.
✔ Reduces risk of complications associated with untreated esophageal narrowing.
✔ Enhances overall quality of life.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Esophageal Dilation?
- Fasting: No food or drink for 6–8 hours before the procedure
- Medical history: Inform your doctor about medications, allergies, or heart/lung conditions
- Consent and counseling: Understand procedure, risks, expected outcomes, and post-care
- Pre-procedure testing: May include blood tests, X-ray, or esophagram
Korean hospitals provide detailed pre-op instructions, sedation options, and personalized assessment to maximize safety.
2) What happens during Esophageal Dilation?
- Anesthesia or sedation: Local anesthesia with conscious sedation or general anesthesia depending on patient needs
- Endoscope insertion: Flexible endoscope is passed through the mouth to the esophagus
- Dilation:
- Balloon or bougie dilators gently expand the narrowed area
- Pressure and size are carefully monitored
- Duration: Usually 15–45 minutes, depending on the location and severity of stricture
Advanced Korean centers use high-resolution endoscopes, fluoroscopy guidance, and precise dilation instruments for safety and accuracy.
3) What happens after Esophageal Dilation?
- Immediate: Mild throat discomfort or chest pressure may occur
- Diet: Start with liquids, then gradually return to soft and regular foods
- Follow-up: Monitor for complications, recurrence, or additional dilations if needed
- Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within 24–48 hours
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Sore throat, chest discomfort, or mild pain
- ➤ Bleeding at the dilation site
- ➤ Esophageal perforation (rare but serious)
- ➤ Infection (rare)
- ➤ Recurrence of stricture requiring repeat dilation
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Rapid relief of swallowing difficulties
- ✔ Minimally invasive with short procedure time
- ✔ Can prevent malnutrition and aspiration
- ✔ Allows accurate diagnosis and treatment in the same session
- ✔ Can be repeated safely if needed
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Mild discomfort, usually resolves within a few hours
- Short-term: Resume soft foods first, avoid hard or sharp foods for several days
- Follow-up: Endoscopic check or repeat dilation may be scheduled based on response
- Long-term: Most patients experience significant improvement in swallowing; recurrence rates vary depending on underlying condition
South Korean gastroenterology centers provide structured post-procedure care, dietary guidance, and follow-up plans to optimize outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
- ➤ Severe chest pain or difficulty swallowing
- ➤ Vomiting blood or black/tarry stools
- ➤ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- ➤ Shortness of breath or severe discomfort
- ➤ Persistent or worsening symptoms after the procedure
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class esophageal dilation services due to:
- Expert gastroenterologists and endoscopy specialists
- Advanced high-resolution endoscopy and precision dilation tools
- Minimally invasive techniques with sedation options
- Comprehensive pre- and post-procedure care
- High patient safety and success rates
- International patient support including consultation, scheduling, and follow-up
Top hospitals for Esophageal Dilation in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Gastroenterology & Endoscopy
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced GI Endoscopy
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Digestive Health & Endoscopy
- Seoul National University Hospital – Gastroenterology & Therapeutic Endoscopy