Overview
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that combines endoscopy and high-frequency ultrasound to examine the digestive tract and surrounding organs. It is primarily used to evaluate pancreatic diseases, gastrointestinal tumors, bile ducts, and lymph nodes.
In South Korea, EUS is performed in advanced gastroenterology centers using high-definition endoscopes and expert endoscopists, ensuring accurate diagnosis, minimal discomfort, and safe management. Korea is recognized globally for its cutting-edge endoscopic technology and skilled specialists, making it a top destination for EUS.
What is Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
EUS involves inserting a flexible endoscope equipped with an ultrasound probe through the mouth or rectum. The device captures detailed images of the digestive tract walls and surrounding tissues, allowing doctors to detect abnormalities that conventional imaging may miss.
EUS is commonly used to:
- Detect tumors in the pancreas, stomach, esophagus, or rectum
- Evaluate gastrointestinal tract diseases
- Examine bile ducts and gallbladder
- Guide fine-needle aspiration (FNA) for tissue sampling
- Assess lymph nodes and nearby organs for cancer staging
This procedure is minimally invasive, precise, and safer than traditional surgical biopsies, offering both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits.
What are the benefits?
Endoscopic Ultrasound provides multiple advantages:
- High-resolution imaging → detailed view of digestive tract walls and surrounding organs
- ➤ Early detection of tumors and lesions → crucial for timely treatment
- ➤ Guided tissue sampling → EUS-FNA allows accurate biopsy without surgery
- ➤ Minimally invasive → avoids external incisions, reducing recovery time
- ➤ Assists in treatment planning and staging → especially in gastrointestinal cancers
- ➤ Widely available in Korea with modern equipment and highly trained endoscopists
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
Proper preparation ensures safety and accurate results:
- Fasting → typically no food or drink for 6–8 hours prior to the procedure
- Medication review → inform your doctor of blood thinners, diabetes medications, or other relevant drugs
- Allergy information → inform the doctor about allergies to anesthesia or sedation
- Pre-procedure instructions → patients may be asked to arrange transportation due to sedation
- Medical history review → previous gastrointestinal conditions or surgeries are discussed
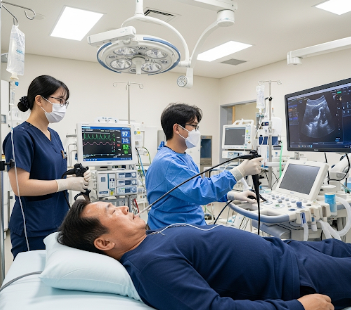
2) What happens during the procedure Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
The procedure usually takes 30–60 minutes depending on complexity:
- Sedation → mild to moderate sedation or general anesthesia is administered for comfort
- Endoscope insertion → a flexible tube with a high-frequency ultrasound probe is gently inserted through the mouth (upper GI) or rectum (lower GI)
- Ultrasound imaging → real-time images of the gastrointestinal tract and nearby organs are captured
- Tissue sampling (if needed) → fine-needle aspiration (FNA) may be performed to collect tissue for biopsy
- Completion → the endoscope is withdrawn, and the patient is monitored until sedation wears off
In Korea, EUS is performed with state-of-the-art endoscopes, allowing precise visualization and biopsy of lesions that might be difficult to detect otherwise.
3) What happens after an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
- Recovery from sedation → patients are monitored for 1–2 hours until fully alert
- Mild throat discomfort or bloating → common for a few hours
- Diet → light meals can usually be resumed after a few hours
- Follow-up → biopsy results are typically available in a few days
- Post-procedure instructions → avoid alcohol and heavy activity on the day of the procedure
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- Sore throat or minor discomfort after the procedure
- Mild bloating or cramping
- Rare complications → bleeding, infection, or perforation at the biopsy site
- Sedation-related risks (rare)
Key Benefits:
- Accurate diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic diseases
- ➤ Minimally invasive alternative to surgical biopsy
- ➤ Early detection and staging of tumors
- ➤ Guides treatment planning, improving outcomes
- ➤ High success rates in Korea with expert endoscopists and modern equipment
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery → most patients can return to normal activities within a few hours to a day, depending on sedation
- Biopsy follow-up → tissue analysis informs diagnosis and treatment decisions
- Long-term outlook → EUS helps detect diseases early, improving prognosis and enabling precise treatment
- In Korea, follow-up care includes multidisciplinary evaluation, ensuring comprehensive management of gastrointestinal and pancreatic disorders
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain or persistent bloating
- ➤ Fever or signs of infection
- ➤ Excessive bleeding from biopsy site
- ➤ Difficulty swallowing or persistent throat pain
- ➤ Any unusual symptoms after sedation
Prompt evaluation prevents complications and ensures safe recovery.
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is among the leading countries for advanced endoscopic procedures:
- High-definition endoscopic ultrasound machines → precise imaging and biopsy
- Expert gastroenterologists and endoscopists with experience in complex EUS procedures
- Comprehensive care packages → pre-procedure imaging, EUS, tissue analysis, and follow-up
- Minimally invasive approach → outpatient or short hospital stay, fast recovery
- International patient support → multilingual staff and streamlined scheduling
Patients choosing Korea for Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) can expect accurate diagnostics, safe procedures, and excellent follow-up care, making it one of the top destinations globally for gastrointestinal evaluation.