Overview
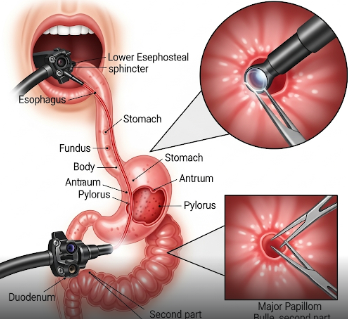
EGD (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy), also known as Upper Endoscopy, is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine (duodenum). It helps detect conditions like ulcers, inflammation, bleeding, tumors, and structural abnormalities.
In South Korea, EGD is performed in advanced gastroenterology centers and hospitals using high-resolution endoscopes, sedation, and precise imaging technology for accurate diagnosis, minimal discomfort, and effective treatment.
What is EGD (Upper Endoscopy)?
EGD is a minimally invasive procedure in which a flexible endoscope with a light and camera is inserted through the mouth to examine the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Purpose:
- Detect ulcers, gastritis, esophagitis, tumors, and polyps
- Evaluate unexplained abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or swallowing difficulties
- Perform biopsies or remove polyps
- Monitor conditions such as GERD or Barrett’s esophagus
Therapeutic uses include:
- Controlling bleeding
- Dilating strictures
- Removing small tumors or foreign bodies
What are the Benefits?
EGD offers several diagnostic and therapeutic benefits:
✔ Provides direct visualization of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
✔ Allows early detection of cancers or precancerous lesions.
✔ Enables biopsy or minor therapeutic interventions during the procedure.
✔ Minimally invasive with low complication risk.
✔ Quick recovery and outpatient feasibility in most cases.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for EGD?
- Fasting: Avoid food and drink for at least 6–8 hours before the procedure
- Medication review: Inform the doctor about blood thinners, diabetes medications, or other chronic treatments
- Medical history: Share any allergies, respiratory, or heart conditions
- Consent: Understand the procedure, sedation, risks, and recovery
- Arrangements: Arrange for a companion to drive you home if sedation is used
Korean gastroenterology centers provide detailed instructions, sedation options, and patient counseling to ensure comfort and safety.
2) What happens during EGD?
- Sedation: Administered intravenously to relax the patient
- Endoscope insertion: Flexible tube is gently passed through the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- Examination: High-definition images are captured; abnormalities can be biopsied or treated
- Duration: Usually 15–30 minutes, depending on the complexity and any therapeutic intervention
Advanced Korean centers use state-of-the-art endoscopes, high-resolution imaging, and minimally invasive techniques for precision and safety.
3) What happens after EGD?
- Immediate: Patient monitored until sedation wears off; may experience mild sore throat or bloating
- Diet: Gradual return to normal eating; avoid alcohol or heavy meals initially
- Results: Biopsy results may take a few days; the doctor discusses findings and follow-up
- Recovery: Most patients resume normal activities within 24 hours
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Sore throat, bloating, or minor discomfort
- ➤ Reaction to sedation (rare)
- ➤ Bleeding from biopsy or therapeutic procedures
- ➤ Perforation of the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum (very rare)
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Accurate diagnosis of upper gastrointestinal conditions
- ✔ Early detection of precancerous or cancerous lesions
- ✔ Enables treatment during the same procedure
- ✔ Minimally invasive and outpatient-friendly
- ✔ Reduces the need for more invasive surgeries
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Mild throat discomfort or bloating for a few hours
- Short-term: Follow doctor’s advice on diet, activity, and medications
- Long-term: Follow-up EGD may be recommended for chronic conditions or high-risk patients
- Lifestyle: Diet, hydration, and medication adherence improve outcomes
South Korean centers provide structured post-procedure guidance, sedation recovery monitoring, and patient education to ensure safety and comfort.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
- ➤ Severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or fever
- ➤ Persistent throat pain or difficulty swallowing
- ➤ Vomiting blood or black/tarry stools
- ➤ Signs of infection at sedation site or IV line
- ➤ Unexpected complications post-procedure
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class EGD services due to:
- Experienced gastroenterologists and endoscopy specialists
- Advanced high-definition endoscopes and imaging technology
- Sedation and anesthesia options for patient comfort
- Ability to perform diagnostic and therapeutic procedures simultaneously
- Structured pre- and post-procedure patient care
- International patient support for consultation, scheduling, and follow-up
Top hospitals for EGD in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Gastroenterology & Endoscopy
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced GI Endoscopy
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Endoscopy & Digestive Health
- Seoul National University Hospital – Gastroenterology & Endoscopic Surgery