Overview
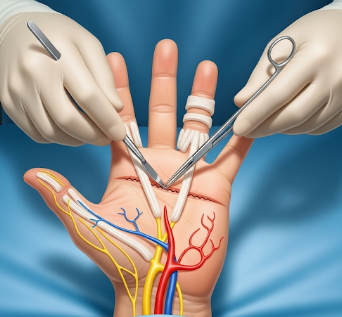
Dupuytren’s fasciectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting Dupuytren’s contracture, a condition where fibrous tissue in the palm thickens and tightens, causing fingers (usually the ring and little fingers) to curl inward. This condition can limit hand function and interfere with daily activities.
In South Korea, Dupuytren’s fasciectomy is performed in advanced hand surgery and orthopedic centers, using precise microsurgical techniques, ensuring effective correction, minimal complications, and faster recovery.
What is Dupuytren’s Fasciectomy?
Dupuytren’s fasciectomy involves surgically removing or releasing the thickened fibrous cords in the palm to restore finger extension and hand function.
Types of fasciectomy:
- Partial fasciectomy: Removal of only the diseased tissue, most common
- Total fasciectomy: Removal of the entire affected fascia, used in severe cases
- Needle aponeurotomy (percutaneous fasciectomy): Minimally invasive alternative using a needle to divide the cords
Purpose:
- Restore finger extension and hand mobility
- Relieve pain and stiffness
- Prevent progression of contracture
- Improve ability to perform daily tasks
What are the Benefits?
Dupuytren’s fasciectomy offers several functional and health benefits:
✔ Restores normal finger and hand function.
✔ Relieves discomfort and stiffness.
✔ Improves ability to perform daily activities, such as gripping and writing.
✔ Reduces the risk of progression to severe contracture.
✔ Provides long-term improvement compared to non-surgical treatments.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Dupuytren’s Fasciectomy?
- Preoperative evaluation: Comprehensive hand assessment, X-rays, and functional tests
- Medical review: Discuss medications, allergies, and existing conditions
- Consent and counseling: Understand procedure, risks, recovery, and expected outcomes
- Hand care preparation: Stop certain medications (blood thinners) if instructed; maintain hand hygiene
Korean hand surgery centers provide personalized pre-op planning and patient education for optimal outcomes.
2) What happens during Dupuytren’s Fasciectomy?
- Anesthesia: Local, regional, or general anesthesia depending on severity
- Incision and exposure: Surgeon makes precise incisions in the palm to access diseased fascia
- Tissue removal: Thickened cords are excised or released to allow finger extension
- Closure: Skin is closed carefully to minimize scarring; drains may be placed
- Duration: Usually 1–3 hours depending on extent of contracture
Advanced Korean centers utilize microsurgical techniques, magnification, and minimally invasive approaches to enhance precision and reduce complications.
3) What happens after Dupuytren’s Fasciectomy?
- Immediate: Hand is bandaged and immobilized; pain and swelling are managed
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to improve finger mobility and prevent recurrence
- Follow-up: Regular monitoring for wound healing, nerve function, and hand movement
- Recovery: Most patients regain significant function within 6–12 weeks, though complete recovery may take months
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Infection at the surgical site
- ➤ Bleeding or hematoma formation
- ➤ Nerve or tendon injury (rare)
- ➤ Scarring or stiffness
- ➤ Recurrence of contracture over time
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Restores hand and finger function
- ✔ Reduces pain and stiffness
- ✔ Improves grip strength and daily activity performance
- ✔ Long-term improvement in quality of life
- ✔ Effective correction for moderate to severe Dupuytren’s contracture
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Elevate hand to reduce swelling; pain management with medication
- 1–2 weeks: Stitches removed; gentle range-of-motion exercises begin
- 6–12 weeks: Progressive rehabilitation to restore strength, flexibility, and hand function
- Long-term: Recurrence is possible; follow-up care and exercises reduce risk
South Korean centers provide structured post-op physiotherapy, monitoring, and patient education to maximize recovery and functional outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your surgeon if you notice:
- ➤ Excessive pain, redness, or swelling
- ➤ Signs of infection, such as pus or fever
- ➤ Numbness, tingling, or reduced hand movement
- ➤ Unusual bleeding or hematoma
- ➤ Recurrence of finger contracture
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class Dupuytren’s fasciectomy services due to:
- Experienced hand surgeons and orthopedic specialists
- Advanced microsurgical and minimally invasive techniques
- Comprehensive preoperative assessment and patient counseling
- Structured post-op rehabilitation programs
- High success rates with low complication and recurrence rates
- International patient support including scheduling, translation, and follow-up
Top hospitals and clinics for Dupuytren’s Fasciectomy in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Hand Surgery & Orthopedic Center
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced Hand Surgery Clinic
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery
- Seoul National University Hospital – Orthopedic & Reconstructive Hand Surgery