Overview
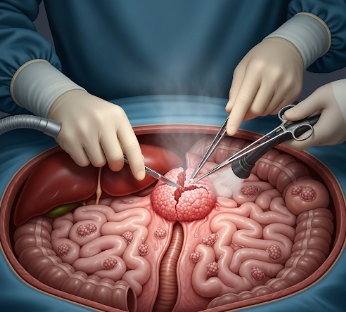
Debulking surgery, also known as cytoreduction surgery, is a specialized surgical procedure aimed at removing as much tumor mass as possible when complete excision is not feasible. It is commonly used for advanced ovarian, abdominal, or pelvic cancers, as well as certain solid tumors that cannot be fully removed due to proximity to vital organs.
In South Korea, debulking surgery is performed in highly specialized oncology centers and hospitals, using modern surgical techniques and multidisciplinary teams, ensuring maximal tumor removal while preserving organ function and minimizing complications.
What is Debulking Surgery (Cytoreduction Surgery)?
Debulking surgery is a therapeutic procedure that reduces tumor volume to enhance the effectiveness of chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapy. The procedure does not always remove the entire tumor but aims to leave behind minimal residual disease, which improves prognosis and treatment response.
Indications include:
- Advanced ovarian, abdominal, or pelvic cancers
- Tumors causing obstruction, pain, or functional compromise
- Preoperative tumors requiring reduction for subsequent therapies
- Selected cases of metastatic solid tumors
Purpose:
- Reduce tumor burden to improve survival and treatment outcomes
- Relieve symptoms caused by large tumors (pain, obstruction, or bleeding)
- Facilitate effectiveness of chemotherapy or radiation
- Enhance patient quality of life
What are the Benefits?
Debulking surgery provides several clinical and therapeutic benefits:
✔ Reduces tumor mass and pressure symptoms.
✔ Enhances response to chemotherapy or other systemic treatments.
✔ Can relieve pain, bowel or urinary obstruction, and bleeding.
✔ Improves overall survival in select cancers (especially ovarian).
✔ Allows tissue sampling for histopathology and molecular testing.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Debulking Surgery?
- Medical evaluation: Comprehensive blood tests, imaging (CT, MRI, PET-CT), cardiac and pulmonary assessment
- Medication review: Adjustments for anticoagulants, blood pressure, or diabetes medications
- Preoperative counseling: Discuss surgical approach (open, minimally invasive, or combined), risks, benefits, and expected recovery
- Nutritional optimization: Ensuring adequate nutrition to improve healing and recovery
- Consent: Understand the extent of surgery, potential complications, and postoperative care requirements
South Korean oncology centers provide detailed preoperative assessments and multidisciplinary planning to optimize outcomes.
2) What happens during Debulking Surgery?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is standard
- Surgical approach:
- Open laparotomy: Large abdominal incision for maximal access to tumor sites
- Minimally invasive/laparoscopic techniques: Selected patients with limited tumor burden
- Tumor removal: Surgeons excise as much tumor tissue as safely possible, sometimes including portions of ovaries, uterus, intestines, or peritoneum
- Adjunct procedures: Stent placement, organ resection, or lymph node removal if indicated
- Duration: Typically 3–8 hours, depending on tumor complexity and surgical extent
South Korean surgeons use advanced imaging, intraoperative navigation, and teamwork between oncology, gynecology, and surgical specialists to maximize safe tumor removal.
3) What happens after Debulking Surgery?
- Immediate post-op: Intensive monitoring in ICU or recovery unit, pain management, fluid and electrolyte monitoring
- Wound care: Incisions monitored and maintained under sterile conditions
- Medication: Pain relievers, antibiotics, anticoagulation, and anti-nausea medications as required
- Follow-up treatment: Chemotherapy or targeted therapy often initiated after recovery
- Activity: Gradual mobilization and rehabilitation; diet progression as tolerated
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Bleeding requiring transfusion
- ➤ Infection or sepsis
- ➤ Organ injury (bladder, bowel, or ureters)
- ➤ Postoperative adhesions or bowel obstruction
- ➤ Delayed wound healing, especially in complex or extensive surgeries
- ➤ Prolonged hospital stay and recovery
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Maximizes tumor reduction to improve survival
- ✔ Alleviates symptoms caused by large tumors
- ✔ Enhances chemotherapy or targeted therapy effectiveness
- ✔ Provides tissue for diagnostic and molecular analysis
- ✔ Can significantly improve quality of life and prognosis
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: ICU or high-dependency monitoring; pain, fatigue, and fluid imbalance are common
- 1–2 weeks: Stabilization of vital signs; gradual resumption of light activity
- 4–6 weeks: Recovery of strength and functional capacity; initiation or continuation of adjuvant therapy
- Long-term: Outcomes depend on cancer type, tumor burden, and residual disease; close oncological follow-up is essential
South Korean hospitals provide comprehensive rehabilitation, nutritional support, and follow-up programs for optimal post-surgical recovery.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your surgical or oncology team if:
- ➤ Persistent fever, chills, or signs of infection
- ➤ Excessive bleeding or drainage from the surgical site
- ➤ Severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or bowel obstruction symptoms
- ➤ Difficulty urinating or other organ-specific complications
- ➤ Any concerning post-operative symptoms beyond expected recovery
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class debulking surgery services due to:
- Experienced multidisciplinary oncology teams including surgical oncologists, gynecologists, and anesthesiologists
- Advanced surgical technology and intraoperative imaging
- Comprehensive perioperative care and ICU support
- Integration with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation
- International patient support with scheduling, translation, and follow-up
- High safety standards and excellent post-surgical outcomes
Top hospitals for Debulking Surgery in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Oncology & Surgical Services
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Gynecologic Oncology
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Cytoreduction Program
- Seoul National University Hospital – Advanced Cancer Surgery Division