Overview
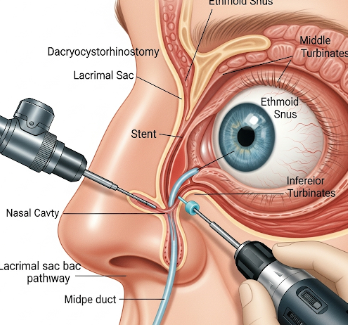
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical procedure designed to treat blocked tear ducts (nasolacrimal duct obstruction). Blocked tear ducts can cause excessive tearing (epiphora), recurrent eye infections, or chronic inflammation.
In South Korea, DCR is performed in ophthalmology and ENT specialty centers using modern endoscopic and minimally invasive techniques, ensuring high success rates, minimal scarring, and rapid recovery.
What is Dacryocystorhinostomy?
Dacryocystorhinostomy involves creating a new drainage pathway between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity, bypassing the blocked nasolacrimal duct. There are two primary approaches:
- External DCR: Traditional method involving a small incision on the side of the nose to access the lacrimal sac.
- Endoscopic DCR: Minimally invasive approach using a nasal endoscope to create the drainage pathway without external incision.
Indications include:
- Chronic tearing due to nasolacrimal duct obstruction
- Recurrent eye infections (dacryocystitis)
- Congenital or acquired blockage of the tear duct
- Failed conservative treatments such as massage or stenting
Purpose:
- Restore proper tear drainage
- Reduce recurrent eye infections
- Alleviate discomfort and excessive tearing
- Improve eye health and vision comfort
What are the Benefits?
DCR provides several functional and cosmetic advantages:
✔ Relieves chronic tearing and associated discomfort.
✔ Reduces recurrent eye infections and inflammation.
✔ High success rate, especially with endoscopic techniques.
✔ Minimal visible scarring with endoscopic approach.
✔ Improves quality of life and daily activities.
✔ Short recovery period compared to traditional surgical interventions.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Dacryocystorhinostomy?
- Medical evaluation: Eye examination, nasal endoscopy, and imaging (dacryocystography or CT scan)
- Medication guidance: Avoid blood-thinning medications if instructed
- Preoperative counseling: Discuss anesthesia options, procedure type (external vs endoscopic), and expected outcomes
- Hygiene: Nasal and facial cleaning; follow surgeon instructions
- Consent: Understand potential risks, benefits, and recovery expectations
South Korean ophthalmology clinics provide personalized preparation plans to ensure patient safety and optimal results.
2) What happens during Dacryocystorhinostomy?
- Anesthesia: Local with sedation or general anesthesia depending on patient preference and complexity
- External DCR:
- Small incision on the side of the nose
- Lacrimal sac exposed and a new drainage channel created into the nasal cavity
- Stent may be inserted to maintain patency
- Incision closed with fine sutures
- Endoscopic DCR:
- Nasal endoscope inserted through the nostril
- Bone and tissue are carefully removed to create a drainage pathway
- Stent may be placed to ensure tear flow
- Duration: Typically 60–90 minutes, depending on complexity
South Korean surgeons use advanced endoscopic equipment, microsurgical techniques, and precise stenting to maximize success and reduce complications.
3) What happens after Dacryocystorhinostomy?
- Immediate post-op: Mild swelling, bruising, or nasal discomfort may occur
- Medications: Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drops may be prescribed
- Stent care: If a stent is placed, follow-up visits are needed for removal or adjustment
- Follow-up: Regular monitoring to ensure patency of the new tear duct
- Activity: Avoid strenuous activity and nasal trauma; maintain nasal hygiene as instructed
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Infection at surgical site
- ➤ Bleeding or nasal crusting
- ➤ Swelling, bruising, or mild discomfort
- ➤ Scarring (minimal with endoscopic approach)
- ➤ Failure or recurrence requiring revision surgery
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Restores tear drainage and alleviates chronic tearing
- ✔ Reduces recurrent eye infections
- ✔ Minimally invasive with endoscopic approach
- ✔ High success rate with modern surgical techniques
- ✔ Improves quality of life and eye comfort
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Mild swelling, bruising, or watery eyes may occur
- 1–2 weeks: Healing progresses; most patients return to normal activities
- 4–6 weeks: Full recovery with stable tear drainage; stents removed if placed
- Long-term: Proper tear drainage maintained, reduced infection risk, and improved comfort
Korean ophthalmology centers provide structured post-operative care, follow-up examinations, and patient education for optimal outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your surgeon if you notice:
- ➤ Severe pain, redness, or swelling
- ➤ Persistent bleeding or nasal obstruction
- ➤ Signs of infection (fever, discharge)
- ➤ Stent displacement or tearing recurrence
- ➤ Unusual visual changes or discomfort
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers state-of-the-art DCR services due to:
- Experienced ophthalmologists and ENT specialists
- Advanced endoscopic and microsurgical equipment
- High success rates with minimal complications
- Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care
- International patient support including scheduling, translation, and follow-up
Top hospitals for Dacryocystorhinostomy in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Ophthalmology & ENT
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Oculoplastic Surgery
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Tear Duct Clinic
- Seoul National University Hospital – Ophthalmology & Oculoplastic Division