Overview
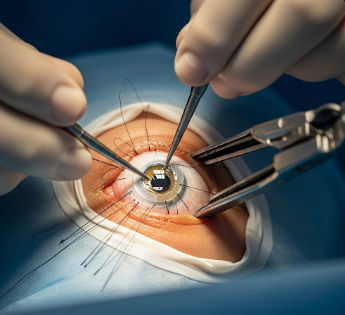
Corneal transplant surgery, also known as keratoplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea. The cornea is the transparent, dome-shaped front layer of the eye that focuses light onto the retina, and damage can significantly impair vision.
In South Korea, corneal transplant surgery is performed in advanced ophthalmology centers using state-of-the-art microsurgical techniques, including penetrating keratoplasty and lamellar keratoplasty. Korean hospitals provide comprehensive preoperative evaluation, precise surgical intervention, and structured post-operative care, ensuring optimal visual outcomes and minimal complications.
What is Corneal Transplant Surgery?
A corneal transplant replaces a diseased or scarred cornea with a donor cornea, restoring clarity and vision.
Types of corneal transplant include:
- Penetrating keratoplasty (PK): Full-thickness corneal transplant
- Anterior lamellar keratoplasty (ALK): Replaces only the front layers of the cornea
- Endothelial keratoplasty (EK): Replaces the innermost corneal layer
- DALK (Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty): Preserves the patient’s endothelium
Indications for surgery:
- Keratoconus or corneal thinning
- Corneal scarring due to infection, trauma, or chemical burns
- Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy or other corneal endothelial disorders
- Corneal edema or opacity affecting vision
What are the Benefits?
Corneal transplant surgery provides significant visual and functional benefits:
✔ Restores vision impaired by corneal disease or injury.
✔ Reduces pain or discomfort associated with corneal disorders.
✔ Improves quality of life and ability to perform daily activities.
✔ Offers high success rates when performed in specialized centers.
✔ Minimally invasive options reduce recovery time and enhance outcomes.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Corneal Transplant Surgery?
- Medical assessment: Eye examination, corneal imaging, blood tests, and systemic health evaluation.
- Medication review: Certain eye drops or systemic medications may need adjustment.
- Preoperative counseling: Explanation of procedure type, risks, anesthesia, and post-operative care.
- Arrange support: Assistance for transportation and post-operative care, as vision may be temporarily impaired.
- Avoid contact lenses: Discontinue use for several days or weeks before surgery, as advised.
South Korean ophthalmology centers provide detailed preparation plans to ensure safety and surgical success.
2) What happens during the Corneal Transplant Surgery?
- Surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on age and health.
- The surgeon removes the damaged portion of the cornea.
- The donor cornea is carefully placed and secured with sutures or adhesive techniques.
- Modern techniques allow partial-thickness transplants to minimize complications.
- Surgery duration typically ranges from 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on complexity.
South Korean surgeons emphasize microsurgical precision, optimal graft alignment, and prevention of rejection.
3) What happens after a Corneal Transplant Surgery?
- Patients are monitored in the hospital or clinic for several hours post-surgery.
- Eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation are prescribed.
- Protective eyewear may be recommended for several weeks.
- Follow-up includes monitoring for graft rejection, infection, or suture-related issues.
- Full visual recovery may take several months, with gradual improvement in clarity and acuity.
Korean hospitals provide structured post-operative care, regular check-ups, and patient education for optimal outcomes.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Graft rejection or failure
- ➤ Infection or inflammation
- ➤ Increased intraocular pressure or glaucoma
- ➤ Astigmatism or irregular vision
- ➤ Complications related to anesthesia
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Restoration of vision impaired by corneal disease or injury
- ✔ Improved quality of life and daily functioning
- ✔ Minimally invasive options with high success rates
- ✔ Advanced post-operative care and monitoring
- ✔ Expertise of South Korean ophthalmologists ensures optimal outcomes
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate post-op: Eye protection, medication adherence, and rest.
- First weeks: Gradual improvement in vision; avoid rubbing the eye or heavy activity.
- Months: Full visual recovery may take 3–12 months, depending on graft type and individual healing.
- Long-term outlook: With proper care and follow-up, most patients achieve significant visual improvement and long-term graft survival.
South Korean hospitals provide comprehensive follow-up schedules, vision rehabilitation, and emergency support for post-operative care.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your ophthalmologist immediately if you notice:
- ➤ Sudden vision loss or blurring
- ➤ Severe eye pain
- ➤ Redness, swelling, or discharge
- ➤ Sensitivity to light or increased tearing
- ➤ Any signs of graft rejection, such as haze or swelling
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a leading destination for corneal transplant surgery due to:
- Expert ophthalmologists specializing in corneal surgery
- Advanced microsurgical and imaging technologies
- Minimally invasive techniques for partial-thickness transplants
- Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care
- International patient support, including translators, accommodation, and follow-up services
- Affordable costs with world-class quality
Top hospitals for corneal transplant in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System)