Overview
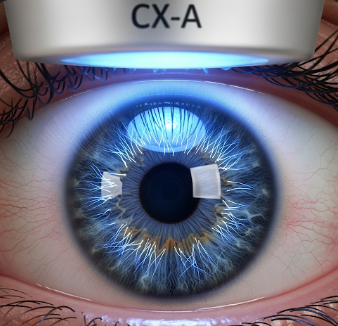
Corneal cross-linking (CXL) is a minimally invasive ophthalmic procedure used to strengthen the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. It is primarily used to treat progressive keratoconus, a condition where the cornea thins and bulges into a cone-like shape, leading to distorted vision.
In South Korea, corneal cross-linking is performed in advanced eye hospitals and specialized ophthalmology centers, using state-of-the-art UV light devices and riboflavin solutions to ensure safety, efficacy, and precise outcomes. The procedure can halt the progression of keratoconus, reducing the need for corneal transplantation in many patients.
What is Corneal Cross-Linking?
Corneal cross-linking is a procedure that uses riboflavin (vitamin B2) drops activated by ultraviolet-A (UV-A) light to create new bonds between collagen fibers in the cornea. This increases corneal stiffness and stability, preventing further bulging and vision deterioration.
Indications include:
- Progressive keratoconus
- Post-LASIK ectasia (corneal weakening after laser eye surgery)
- Pellucid marginal degeneration
- High-risk patients for corneal thinning and vision loss
Purpose:
- Halt progression of corneal deformation
- Stabilize vision and improve contact lens tolerance
- Reduce the need for corneal transplantation in progressive cases
Types of CXL:
- Epi-off (standard): Epithelium removed to allow better riboflavin penetration
- Epi-on (transepithelial): Epithelium remains intact for faster recovery
- Accelerated CXL: Shorter treatment time using higher UV intensity
What are the Benefits?
Corneal cross-linking provides several therapeutic and visual benefits:
✔ Stops or slows progression of keratoconus and corneal thinning.
✔ Stabilizes vision, improving quality of life.
✔ May reduce dependency on rigid contact lenses.
✔ Minimally invasive with no tissue removal.
✔ Reduces the likelihood of future corneal transplantation.
✔ Can be combined with other procedures like photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) for visual correction.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Corneal Cross-Linking?
- Medical evaluation: Comprehensive eye examination, corneal topography, pachymetry (corneal thickness), and visual acuity testing.
- Medication adjustments: Avoid contact lenses for a few days prior; discontinue eye drops as instructed.
- Preoperative counseling: Discussion of procedure, benefits, risks, and post-procedure care.
- Consent: Understanding the process, expected outcomes, and recovery plan.
- Lifestyle preparation: Arrange transportation as vision may be blurred immediately after the procedure.
South Korean ophthalmology centers provide thorough pre-procedure assessment to ensure patient safety and procedural success.
2) What happens during Corneal Cross-Linking?
- Anesthesia: Topical eye drops are used to numb the cornea.
- Epithelium management: Depending on technique, the corneal epithelium may be removed (epi-off) or left intact (epi-on).
- Riboflavin application: Riboflavin drops applied to cornea for 20–30 minutes to saturate corneal tissue.
- UV-A irradiation: Ultraviolet-A light is applied to activate riboflavin, creating cross-links between collagen fibers.
- Protection: A sterile shield or bandage contact lens is placed for comfort and protection post-procedure.
- Duration: Typically 30–60 minutes, depending on the protocol used.
South Korean surgeons emphasize precision, corneal safety, and individualized treatment based on corneal thickness and keratoconus severity.
3) What happens after Corneal Cross-Linking?
- Immediate post-op: Mild burning, irritation, or blurred vision may occur.
- Eye protection: Bandage contact lens worn for 3–5 days if epithelium removed.
- Medication: Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops prescribed to prevent infection and reduce discomfort.
- Activity restrictions: Avoid eye rubbing, swimming, or strenuous activity for several weeks.
- Follow-up: Regular corneal topography and visual assessment to monitor corneal stability and healing.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Temporary blurred vision or light sensitivity
- ➤ Corneal haze or scarring
- ➤ Infection (rare)
- ➤ Eye irritation or pain
- ➤ Delayed epithelial healing in epi-off technique
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Halts progression of keratoconus effectively
- ✔ Improves corneal stability and visual outcomes
- ✔ Minimally invasive with a short recovery period
- ✔ Reduces future need for corneal transplantation
- ✔ Safe and widely performed in advanced South Korean eye centers
Recovery and Outlook
- First week: Mild discomfort, light sensitivity, and blurred vision; protective contact lens used if epi-off.
- 2–4 weeks: Vision gradually improves; corneal surface heals completely.
- 1–3 months: Corneal stability achieved; regular monitoring continues to ensure long-term success.
- Long-term: Most patients experience halted keratoconus progression and improved contact lens tolerance or visual stability.
Korean ophthalmology centers provide comprehensive post-operative care, including eye drop management, activity guidance, and follow-up corneal imaging.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your ophthalmologist if you notice:
- ➤ Severe eye pain or sudden decrease in vision
- ➤ Redness, discharge, or signs of infection
- ➤ Persistent corneal haze or scarring
- ➤ Excessive tearing or light sensitivity beyond expected recovery
- ➤ Any unusual eye symptoms post-procedure
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class corneal cross-linking services due to:
- Advanced ophthalmology centers with specialized corneal surgeons
- State-of-the-art UV-A and riboflavin technology
- Personalized treatment protocols based on corneal thickness and keratoconus severity
- Comprehensive pre- and post-procedure care and follow-up
- International patient support including consultation, scheduling, and post-treatment monitoring
- High success rates and patient satisfaction
Top hospitals for corneal cross-linking in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System)