Overview
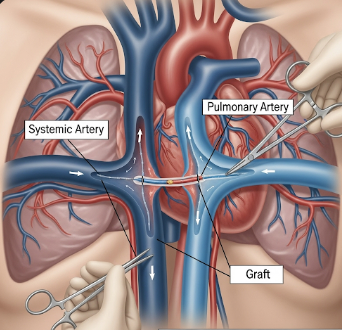
The Blalock-Taussig-Thomas (BTT) Shunt is a palliative surgical procedure performed in children with congenital heart defects that limit blood flow to the lungs, such as Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) or pulmonary atresia. The shunt creates a connection between a systemic artery (usually the subclavian artery) and the pulmonary artery, increasing blood flow to the lungs and improving oxygenation.
In Korea, BTT shunt procedures are performed in advanced pediatric cardiology and cardiothoracic centers with high success rates, providing critical stabilization before definitive corrective heart surgery.
What is BTT Shunt?
The BTT shunt is a surgically created conduit that redirects blood from the systemic circulation to the pulmonary circulation, bypassing obstructed or underdeveloped pulmonary arteries.
Key points:
- Primarily performed in infants and children with cyanotic congenital heart defects
- Increases oxygen-rich blood flow to the lungs, improving blood oxygen levels
- Acts as a temporary or palliative procedure before corrective heart surgery
- Can be created using synthetic grafts or directly connecting vessels
What are the benefits?
- ✅ Improves oxygenation in cyanotic heart disease
- ✅ Stabilizes the child until definitive corrective surgery can be performed
- ✅ Reduces symptoms such as cyanosis, fatigue, and poor growth
- ✅ Minimally invasive compared to full heart surgery in neonates
- ✅ In Korea, performed in highly specialized pediatric cardiac centers with expert surgical teams
- ✅ Helps prevent complications related to chronic low oxygen levels, including stroke or delayed development
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for BTT Shunt?
- ➤ Comprehensive cardiac evaluation: Echocardiography, cardiac catheterization, and imaging studies
- ➤ Review medical history, medications, and allergies
- ➤ Discuss anesthesia risks and post-operative care with the surgical team
- ➤ Ensure optimal hydration and nutrition before surgery
- ➤ Preoperative counseling for parents about procedure, risks, and recovery expectations
2) What happens during the procedure BTT Shunt?
- ✅ Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered
- ✅ Surgical approach: Small incision near the chest or clavicle
- ✅ Shunt creation:
- Connects subclavian artery to pulmonary artery using a synthetic graft or direct vessel anastomosis
- Ensures controlled blood flow to the lungs
- ✅ Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation, heart rate, and blood pressure
- ✅ Duration: Typically 2–4 hours depending on patient size and complexity
- ✅ Immediate stabilization: Postoperative care ensures adequate oxygenation and circulation
3) What happens after BTT Shunt?
- ➤ Intensive care unit (ICU) monitoring for 24–72 hours
- ➤ Oxygen levels, heart function, and shunt patency continuously monitored
- ➤ Pain and infection prevention managed with medications
- ➤ Gradual feeding and activity as tolerated
- ➤ Follow-up includes echocardiography, oxygen assessment, and planning for definitive corrective surgery
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Shunt blockage or thrombosis, potentially requiring intervention
- ➤ Bleeding or infection at the surgical site
- ➤ Temporary heart rhythm disturbances
- ➤ Rare complications: stroke, pulmonary overcirculation, or heart failure
- ➤ Anesthesia-related risks
Benefits:
- ✅ Improves oxygenation and quality of life in cyanotic infants
- ✅ Stabilizes the child for future corrective cardiac surgery
- ✅ Reduces cyanosis-related complications
- ✅ High success rates in Korea due to advanced pediatric cardiac care and surgical expertise
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Typically 7–14 days depending on age and complexity
- Activity: Gradual, with restrictions on strenuous activity until cleared
- Follow-up: Regular cardiology visits, echocardiograms, and oxygen monitoring
- Outcome: Most children experience improved oxygen saturation, growth, and overall health
- Long-term outlook: BTT shunt is palliative, so definitive repair (e.g., complete TOF correction) is usually performed later in childhood
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Sudden cyanosis or shortness of breath
- ➤ Signs of shunt blockage: lethargy, poor feeding, or sudden drop in oxygen saturation
- ➤ Fever, swelling, or redness at surgical site
- ➤ Unusual bleeding or bruising
- ➤ Persistent arrhythmias or changes in heart rate
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea provides specialized pediatric cardiac surgery centers with experience in BTT shunt procedures
- ✅ Advanced surgical techniques, ICU care, and imaging guidance ensure precision and safety
- ✅ Multidisciplinary teams of pediatric cardiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, and anesthesiologists
- ✅ Postoperative care includes monitoring, medication management, and long-term follow-up
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking staff, and coordinated care planning
- ✅ High survival and success rates due to cutting-edge technology and experienced clinicians