Overview
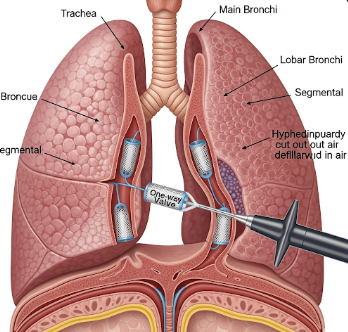
Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to treat patients with severe emphysema, a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The procedure involves reducing overinflated areas of the lungs using a bronchoscope, allowing the healthier lung tissue to function more efficiently and improving breathing.
In Korea, BLVR is offered in advanced pulmonary and thoracic centers using state-of-the-art bronchoscopic techniques and endobronchial devices. It is particularly suitable for patients who cannot undergo conventional lung surgery due to poor lung function or comorbidities.
What is Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction (BLVR)?
BLVR involves placement of specialized devices through a bronchoscope to reduce the volume of diseased lung areas. This improves lung mechanics, airflow, and gas exchange.
Common methods include:
- Endobronchial Valves (EBVs): One-way valves block airflow to diseased areas, allowing healthy tissue to expand
- Lung Coils: Nitinol coils compress diseased lung tissue to improve elasticity
- Bronchoscopic Thermal Vapor Ablation: Heat-induced shrinkage of diseased tissue
- Biologic Sealants: Collapse emphysematous regions by inducing fibrosis
Key points:
- Minimally invasive, performed via bronchoscopy under sedation or general anesthesia
- Targets overinflated, poorly functioning areas of the lung
- Improves breathing, exercise tolerance, and quality of life
What are the benefits?
- ✅ Reduces lung hyperinflation and improves breathing efficiency
- ✅ Minimally invasive compared to surgical lung volume reduction
- ✅ Shorter recovery time and lower risk of complications
- ✅ Enhances exercise capacity and daily functioning
- ✅ Improves oxygenation and quality of life for advanced COPD patients
- ✅ In Korea, advanced imaging and bronchoscopic guidance ensure precise placement and optimal outcomes
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for BLVR?
- ➤ Pulmonary evaluation: Lung function tests (spirometry), CT scan, blood oxygen levels
- ➤ Discuss current medications, oxygen therapy, and comorbidities
- ➤ Stop blood thinners or anticoagulants as instructed
- ➤ Fasting required if sedation or anesthesia is used
- ➤ Pre-procedure counseling about procedure steps, expectations, and possible side effects
2) What happens during Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction?
- ✅ Anesthesia: Sedation or general anesthesia administered
- ✅ Bronchoscope insertion: Through the mouth or nose into the airways
- ✅ Targeting diseased lung regions: Using CT imaging and endoscopic navigation
- ✅ Device placement:
- Endobronchial valves are inserted to block airflow to damaged areas
- Coils or thermal ablation may be deployed depending on the method
- ✅ Duration: Typically 30–90 minutes depending on the method and number of lobes treated
- ✅ Immediate monitoring for vital signs, oxygen levels, and procedural complications
3) What happens after BLVR?
- ➤ Observation in hospital for 1–2 days to monitor breathing and oxygen levels
- ➤ Mild cough, shortness of breath, or chest discomfort may occur
- ➤ Follow-up imaging to confirm device placement and lung collapse or volume reduction
- ➤ Pulmonary rehabilitation recommended to maximize functional improvement
- ➤ Patients usually notice improved breathing and exercise tolerance within weeks
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Pneumothorax (collapsed lung) requiring chest tube placement
- ➤ Mild cough, sputum, or chest discomfort
- ➤ Rare infection or pneumonia
- ➤ Rare migration of valves or devices
- ➤ Temporary shortness of breath after the procedure
Benefits:
- ✅ Improves lung function and breathing efficiency
- ✅ Minimally invasive, avoiding thoracic surgery
- ✅ Enhances exercise capacity and daily living activities
- ✅ Reduces symptoms of severe emphysema
- ✅ Advanced Korean centers provide expert bronchoscopic guidance and follow-up care
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Usually 1–2 days, outpatient follow-up thereafter
- Activity: Gradual return to daily activities; avoid strenuous activity for 1–2 weeks
- Follow-up: Pulmonary function tests, imaging, and oxygen level assessment
- Outcome: Many patients experience improved dyspnea, exercise tolerance, and quality of life
- Long-term outlook: BLVR may delay or reduce the need for lung transplantation or more invasive surgery
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Sudden shortness of breath or chest pain
- ➤ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- ➤ Severe cough or coughing up blood
- ➤ Device migration or unusual chest discomfort
- ➤ Any sudden worsening of breathing or oxygen levels
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea provides specialized pulmonary and thoracic centers for BLVR
- ✅ Use of advanced bronchoscopic devices, 3D imaging, and endoscopic navigation
- ✅ Multidisciplinary teams including pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, and respiratory therapists
- ✅ Post-procedure care includes pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy adjustment, and follow-up imaging
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking staff, and comprehensive care coordination
- ✅ High success rates due to precision device placement, expert monitoring, and advanced technology