Overview
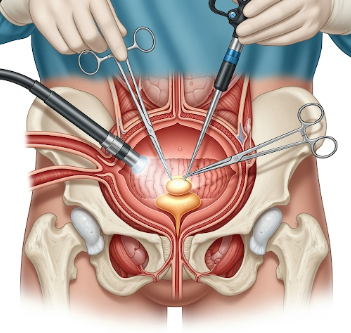
Bladder surgery refers to a range of surgical procedures performed on the bladder to treat conditions such as bladder cancer, urinary incontinence, bladder stones, neurogenic bladder, or congenital abnormalities. The type of surgery depends on the underlying condition, severity, and overall patient health.
In Korea, bladder surgeries are performed in advanced urology centers with minimally invasive techniques, robotic-assisted surgery, and open surgical options, providing high precision, shorter recovery times, and improved patient outcomes.
What is Bladder Surgery?
Bladder surgery encompasses procedures that remove diseased tissue, reconstruct the bladder, or improve bladder function.
Common types include:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): Removal of bladder tumors via the urethra
- Partial Cystectomy: Removal of part of the bladder affected by disease
- Radical Cystectomy: Complete removal of the bladder, often with urinary diversion
- Bladder Augmentation or Reconstruction: Expands bladder capacity using intestine segments
- Bladder Stone Removal: Extraction of calculi causing obstruction or infection
- Sling or Suspension Procedures: Correct urinary incontinence
Key points:
- Can be performed via open surgery, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted methods
- May involve urinary diversion techniques if bladder is partially or fully removed
- Requires preoperative assessment of kidney function, infection status, and overall health
What are the benefits?
- ✅ Removes or reduces tumors or diseased tissue
- ✅ Improves urinary function and quality of life
- ✅ Prevents recurrent infections or obstruction
- ✅ In Korea, advanced techniques allow minimally invasive procedures with quicker recovery
- ✅ Supports long-term bladder health and cancer control
- ✅ Can correct congenital abnormalities or improve continence
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Bladder Surgery?
- ➤ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, urine tests, imaging (CT, MRI, ultrasound)
- ➤ Discuss medications, allergies, and prior surgeries with your doctor
- ➤ Bowel preparation may be needed for some bladder reconstruction surgeries
- ➤ Fasting before surgery as advised by the surgical team
- ➤ Preoperative counseling to understand procedure, risks, and recovery
2) What happens during the procedure Bladder Surgery?
- ✅ Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia administered
- ✅ Surgical approach:
- Transurethral for tumors or stones
- Open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted for partial or radical cystectomy
- ✅ Tumor or diseased tissue removal; reconstruction or urinary diversion if needed
- ✅ Urinary catheter placement to ensure proper drainage during recovery
- ✅ Duration: 1–6 hours, depending on complexity
3) What happens after Bladder Surgery?
- ➤ Patient monitored in post-anesthesia care unit
- ➤ Catheter management and urine output monitoring
- ➤ Pain controlled with analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications
- ➤ Gradual resumption of diet and activity as tolerated
- ➤ Follow-up visits to assess healing, infection prevention, and bladder function
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Bleeding, infection, or blood clots
- ➤ Urinary leakage or fistula formation
- ➤ Temporary difficulty urinating or incontinence
- ➤ Rare complications: damage to nearby organs or nerves
- ➤ Anesthesia-related risks
Benefits:
- ✅ Treats cancer, stones, incontinence, and structural abnormalities
- ✅ Restores urinary function and quality of life
- ✅ Minimally invasive options in Korea reduce hospital stay and recovery time
- ✅ Long-term outcomes include disease control, continence, and improved bladder capacity
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Typically 3–10 days, longer for radical procedures
- Activity: Gradual return to daily activities; avoid heavy lifting until cleared
- Follow-up: Imaging, cystoscopy, and lab tests to monitor healing and detect recurrence
- Catheter care: Temporary urinary catheters may remain 1–3 weeks depending on surgery type
- Outcome: Most patients experience improved urinary function, reduced infections, and effective disease control
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Fever, chills, or signs of urinary tract infection
- ➤ Persistent blood in urine or severe pain
- ➤ Difficulty urinating or urine leakage
- ➤ Catheter-related complications or blockage
- ➤ Any unusual swelling, redness, or discharge from the surgical site
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea offers highly specialized urology centers with robotic-assisted and minimally invasive bladder surgery
- ✅ Experienced surgeons provide tailored procedures based on diagnosis, age, and health condition
- ✅ Advanced imaging and intraoperative guidance ensure precision and safety
- ✅ Postoperative care includes catheter management, infection prevention, and rehabilitation
- ✅ International patients receive VIP care, English-speaking staff, and coordinated follow-up
- ✅ High success rates with shorter recovery, minimal complications, and improved quality of life