Overview
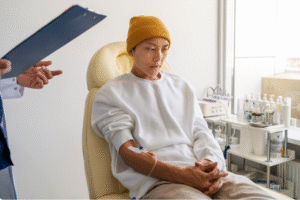
A biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of tissue, fluid, or cells is removed from the body for laboratory testing. It is one of the most important diagnostic tools used by doctors to detect cancer, infections, autoimmune diseases, or inflammatory conditions. Biopsies help confirm or rule out diseases and guide treatment decisions.
In South Korea, biopsies are performed with cutting-edge medical technology such as ultrasound-guided, CT-guided, and robotic-assisted systems, ensuring accuracy and safety. Korean hospitals are internationally recognized for their fast pathology processing, meaning patients get results quickly to begin treatment without delay.
What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy is a procedure in which doctors extract a small portion of tissue or cells from an organ or suspected area of disease. Unlike imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs, which show structural changes, a biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis under a microscope.
Types of biopsies include:
- Needle biopsy: Uses a fine or core needle to collect tissue (commonly for breast, liver, or lymph nodes).
- Surgical biopsy: Removes a larger sample or entire lump for examination.
- Endoscopic biopsy: Performed with a camera and tools inserted into the digestive tract, lungs, or bladder.
- Skin biopsy: Removes small sections of skin to test for dermatological or autoimmune conditions.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Checks for blood cancers or bone marrow disorders.
What are the Benefits?
Biopsies provide crucial health information:
✔ Accurate diagnosis of cancer, infections, and chronic diseases
✔ Helps doctors choose the most effective treatment plan
✔ Minimally invasive methods available in Korea reduce pain and scarring
✔ Quick results with advanced pathology labs
✔ Early detection improves survival rates and long-term health outcomes
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Biopsy?
Preparation depends on the type of biopsy:
- Medical history review including allergies, medications, and bleeding disorders.
- Stop blood thinners (aspirin, warfarin) before the procedure if advised.
- Fasting may be required for abdominal or surgical biopsies.
- Local anesthesia or sedation may be planned, so patients should arrange transport home.
- In Korea, hospitals provide pre-biopsy counseling and imaging scans to plan the most accurate approach.
2) What happens during the procedure Biopsy?
The method depends on biopsy type:
- Needle biopsy: A fine or core needle is inserted into the suspected tissue under imaging guidance (ultrasound or CT).
- Surgical biopsy: An incision is made to remove part or all of the suspicious tissue.
- Endoscopic biopsy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the body, and a small tool collects tissue.
- Skin biopsy: Local anesthesia is applied, and a punch tool removes a small sample.
- Bone marrow biopsy: A special needle is inserted into the hip bone to collect marrow.
Most biopsies take 15–45 minutes, are done under local anesthesia, and patients go home the same day.
3) What happens after a Biopsy?
- Patients may feel mild soreness or bruising at the biopsy site.
- Bandages or stitches may be applied depending on the procedure.
- Normal activities can usually resume within 24–48 hours.
- Tissue samples are analyzed in the lab, and results are usually available within a few days in Korea due to advanced pathology services.
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled to discuss the findings and treatment options.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
- ➤ Minor bleeding or bruising at the biopsy site
- ➤ Infection (rare, usually preventable with proper care)
- ➤ Pain or discomfort at the incision or needle site
- ➤ Organ injury (very rare, when biopsying deep structures like liver or lungs)
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Gold-standard diagnostic tool for many conditions
- ✔ Helps detect cancer at an early stage
- ✔ Guides treatment options with precise information
- ✔ Usually safe, quick, and minimally invasive
Recovery and Outlook
Most patients recover quickly after a biopsy:
- Minor pain or tenderness may last a day or two.
- Stitches (if used) heal within a week.
- Biopsy results often determine the next steps of treatment—such as surgery, chemotherapy, or medication adjustments.
In South Korea, patients benefit from rapid test results and multidisciplinary case reviews, where different specialists collaborate to ensure the best treatment plan.
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should seek immediate medical help if they experience:
- ➤ Severe or increasing pain at the biopsy site
- ➤ Heavy bleeding that does not stop
- ➤ Signs of infection (fever, redness, pus, or swelling)
- ➤ Difficulty breathing (after chest biopsy)
- ➤ Dizziness or fainting
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is one of the best destinations for biopsy procedures due to:
- Advanced imaging-guided and robotic-assisted biopsy systems for precision.
- World-class hospitals like Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital.
- Fast pathology turnaround times, providing results within days.
- Multidisciplinary medical teams (oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, surgeons) collaborating on diagnosis.
- Affordable costs compared to Western countries, with equal or superior quality.
Korea’s combination of technology, expertise, and efficiency ensures patients receive accurate diagnoses quickly, allowing them to begin treatment as early as possible.