Overview
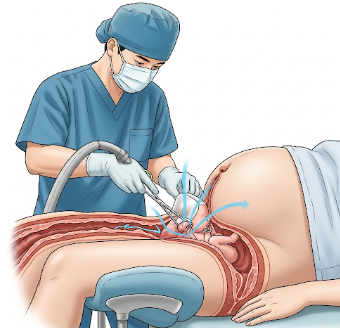
Assisted vaginal delivery is a medical procedure performed to aid the safe delivery of a baby when complications arise during the second stage of labor. This may involve the use of instruments such as forceps or a vacuum extractor to help guide the baby through the birth canal.
In Korea, assisted vaginal deliveries are performed in advanced maternity hospitals by skilled obstetricians, ensuring maternal and fetal safety. The procedure is performed under strict monitoring, with access to neonatal care units, to reduce risks and complications for both mother and baby.
What is Assisted Vaginal Delivery?
Assisted vaginal delivery refers to helping the baby’s passage during labor using instruments when natural delivery is prolonged or complicated.
Common indications include:
- Prolonged second stage of labor
- Fetal distress (low oxygen levels)
- Maternal exhaustion or medical conditions preventing effective pushing
- Abnormal fetal position
Types of Assisted Vaginal Delivery:
- Forceps Delivery:
- Metal instruments shaped to fit around the baby’s head
- Gently guide the baby through the birth canal
- Vacuum Extraction:
- A soft or rigid cup attached to a vacuum device is placed on the baby’s head
- Suction assists in guiding the baby out
Key points:
- Provides rapid resolution of complicated labor
- Reduces risk of cesarean section when appropriately indicated
- Ensures maternal and neonatal safety in high-risk situations
What are the benefits?
- ✅ Reduces maternal fatigue in prolonged labor
- ✅ Minimizes risk of fetal distress by expediting delivery
- ✅ Avoids or reduces the need for emergency cesarean section
- ✅ Performed under sterile conditions with continuous monitoring
- ✅ In Korea, obstetric teams are highly trained in both forceps and vacuum-assisted deliveries, ensuring optimal outcomes
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Assisted Vaginal Delivery?
- ➤ Prenatal assessment: Identify risk factors for assisted delivery during antenatal care
- ➤ Discuss delivery plan and potential need for intervention with obstetrician
- ➤ Hospital admission when in labor or approaching delivery
- ➤ Ensure hydration, empty bladder, and monitoring of fetal heart rate
- ➤ Anesthesia planning: Usually local epidural or spinal anesthesia is available to reduce discomfort
2) What happens during the procedure Assisted Vaginal Delivery?
- ✅ Maternal position is optimized, usually semi-recumbent or lithotomy
- ✅ Fetal heart rate and contractions are monitored continuously
- ✅ Forceps or vacuum device is applied to the baby’s head by the obstetrician
- ✅ Gentle traction is applied synchronized with maternal pushing efforts
- ✅ Baby is delivered safely, and immediate neonatal assessment is performed
- ✅ Duration: Usually a few minutes once instruments are applied
3) What happens after an Assisted Vaginal Delivery?
- ➤ Maternal monitoring for bleeding, perineal tears, or episiotomy
- ➤ Pain relief and wound care if needed
- ➤ Neonatal care including Apgar scoring, oxygen support if required, and observation for trauma
- ➤ Encourage early breastfeeding and skin-to-skin contact
- ➤ Postpartum follow-up to assess healing and recovery
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Maternal perineal or vaginal trauma
- ➤ Increased risk of episiotomy
- ➤ Postpartum bleeding or hematoma formation
- ➤ Neonatal injuries: bruising, minor scalp or facial trauma, rarely nerve injuries
- ➤ Infection at the maternal or neonatal site
Benefits:
- ✅ Resolves prolonged labor quickly and safely
- ✅ Reduces risk of fetal hypoxia and distress
- ✅ Avoids or reduces emergency cesarean section rate
- ✅ In Korea, advanced monitoring and trained obstetric teams minimize maternal and neonatal risks
Recovery and Outlook
- Maternal recovery: Usually within a few days for minor tears, longer if episiotomy or complications occur
- Neonatal recovery: Most injuries are minor and resolve quickly
- Activity: Gradual resumption of normal activity; perineal care advised
- Follow-up: Routine postnatal check-ups to monitor healing, breastfeeding, and maternal well-being
- Long-term outlook: Most mothers and babies recover fully without long-term complications
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Persistent bleeding or severe pain after delivery
- ➤ Signs of infection at the maternal or neonatal site
- ➤ Foul-smelling discharge or fever
- ➤ Neonatal feeding difficulties, jaundice, or unusual lethargy
- ➤ Any concerns regarding perineal or vaginal healing
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea provides specialized maternity hospitals and delivery units
- ✅ Skilled obstetricians perform forceps and vacuum-assisted deliveries with high success rates
- ✅ Advanced fetal monitoring and neonatal care units ensure safety for both mother and baby
- ✅ Post-delivery care includes pain management, perineal care, and breastfeeding support
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking staff, and coordinated maternal-neonatal care
- ✅ High safety standards make Korea a preferred destination for assisted vaginal deliveries