Overview
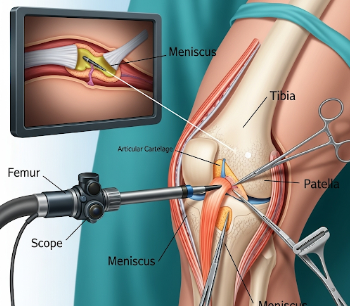
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems inside the knee joint. Using a small camera called an arthroscope, orthopedic surgeons can view the internal structures of the knee, remove damaged tissue, and repair cartilage or ligaments without large incisions.
In Korea, knee arthroscopy is performed in advanced orthopedic centers by highly skilled surgeons. Hospitals utilize state-of-the-art imaging equipment, precision surgical tools, and sterile operating rooms, ensuring minimal pain, faster recovery, and optimal joint function. Postoperative rehabilitation programs help patients regain mobility, strength, and flexibility efficiently.
What is Knee Arthroscopy?
Knee arthroscopy involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera (arthroscope) through small incisions (portals) around the knee. The camera projects images onto a monitor, allowing the surgeon to:
- Diagnose joint injuries such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries, cartilage damage, or loose bodies
- Remove or repair damaged cartilage or tissue
- Perform procedures like meniscus repair, ligament reconstruction, or synovial biopsy
- Treat chronic knee instability, impingement, or arthritis-related changes
Key points:
- Minimally invasive alternative to open knee surgery
- Can be used for diagnosis, treatment, or both
- Reduces pain, recovery time, and scarring
- Commonly performed for athletes and patients with traumatic or degenerative knee conditions
What are the benefits?
- Minimally invasive: smaller incisions reduce infection risk and scarring
- Faster recovery compared to open surgery
- Accurate diagnosis of knee joint conditions
- Pain relief and improved mobility
- ✅ Allows simultaneous treatment during the procedure
- ✅ Shorter hospital stay; often same-day discharge
- ✅ In Korea, high-precision arthroscopy ensures optimal restoration and rehabilitation
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Knee Arthroscopy?
- ➤ Preoperative evaluation: Blood tests, X-ray, MRI, and medical assessment
- ➤ Discuss current medications, especially blood thinners or anticoagulants
- ➤ Fasting instructions if general anesthesia is planned
- ➤ Preoperative counseling about procedure, risks, post-op care, and rehabilitation
- ➤ Arrange for transportation, as mobility may be limited post-surgery
2) What happens during the procedure Knee Arthroscopy?
- ✅ Performed under general or regional anesthesia
- ✅ Small incisions (portals) are made around the knee
- ✅ Arthroscope is inserted to visualize the joint on a monitor
- ✅ Surgical instruments are used to:
- Remove or repair damaged cartilage or ligaments
- Remove loose fragments
- Smooth rough surfaces
- Treat chronic instability or impingement
- ✅ Procedure duration typically 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on complexity
3) What happens after Knee Arthroscopy?
- ➤ Patients are monitored in recovery for a few hours
- ➤ Pain management with medications as needed
- ➤ Ice, elevation, and rest help reduce swelling
- ➤ Physical therapy begins shortly after surgery to restore mobility, strength, and balance
- ➤ Most patients resume daily activities within weeks, depending on procedure complexity
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Infection at the incision site
- ➤ Blood clots (rare)
- ➤ Stiffness or swelling in the knee joint
- ➤ Nerve or blood vessel injury (rare)
- ➤ Persistent pain or limited improvement
Benefits:
- ✅ Minimally invasive with smaller scars and faster recovery
- ✅ Accurate diagnosis and treatment of knee joint issues
- ✅ Reduces pain and improves joint function
- ✅ Early return to daily activities or sports
- ✅ In Korea, advanced arthroscopy minimizes complications and ensures optimal rehabilitation
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Often outpatient; some cases may require overnight observation
- Activity: Gradual resumption of daily activities, avoiding high-impact movement initially
- Physical therapy: Focuses on strength, flexibility, and range of motion
- Full recovery: Usually 4–6 weeks for minor repairs, up to 3–4 months for complex ligament reconstruction
- Lifestyle: Follow rehabilitation instructions, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid high-impact activity early
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Severe pain not relieved by prescribed medication
- ➤ Redness, swelling, or discharge from incision site
- ➤ Fever or signs of infection
- ➤ Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the leg
- ➤ Difficulty moving the knee despite rehabilitation
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea offers world-class orthopedic and sports medicine centers
- ✅ Hospitals provide minimally invasive knee arthroscopy with expert post-op care
- ✅ Advanced equipment ensures high precision, reduced complications, and optimal outcomes
- ✅ Post-operative care includes physical therapy, pain management, and monitoring for complications
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking staff, and coordinated care
- ✅ High success rates and short recovery times make Korea a preferred destination for knee arthroscopy