Overview
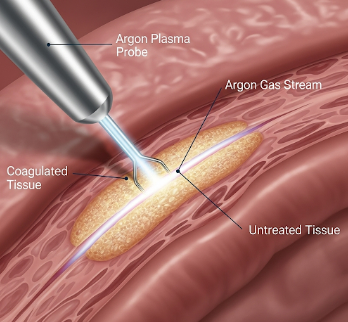
Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC) is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure used to control bleeding, remove abnormal tissue, and treat lesions in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. APC utilizes argon gas and electrical current to coagulate tissue without direct contact, making it a safe and precise method for stopping bleeding or ablating lesions.
In Korea, APC is widely performed in advanced gastroenterology centers equipped with state-of-the-art endoscopy suites. Expert gastroenterologists and surgeons perform APC for bleeding ulcers, polyps, vascular malformations, and other GI conditions, ensuring high precision, safety, and rapid recovery.
What is Argon Plasma Coagulation?
Argon Plasma Coagulation is an endoscopic technique in which an argon gas stream conducts electrical energy to coagulate tissue without direct contact. It is primarily used in the digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon.
Key points:
- Non-contact method reduces risk of tissue perforation
- Can be used for hemostasis, tissue ablation, or treating vascular lesions
- Suitable for patients who cannot undergo surgery or require minimally invasive therapy
- Often used in combination with other endoscopic procedures for optimal results
What are the benefits?
- Effective control of GI bleeding from ulcers, tumors, or vascular lesions
- Minimally invasive, reducing risk compared to open surgery
- Precise tissue coagulation with minimal damage to surrounding areas
- ✅ Performed as outpatient or short hospital stay
- ✅ Can be repeated if necessary, without significant cumulative risk
- ✅ In Korea, hospitals use high-definition endoscopy and advanced APC devices for optimal outcomes
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Argon Plasma Coagulation?
- ➤ Medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging, and endoscopic assessment
- ➤ Fasting for 6–8 hours before the procedure
- ➤ Medication review, especially anticoagulants or blood-thinning medications
- ➤ Consent and counseling about procedure steps, risks, and recovery
- ➤ Arrange post-procedure monitoring, especially for patients with comorbid conditions
2) What happens during the procedure Argon Plasma Coagulation?
- ✅ Performed under conscious sedation or general anesthesia, depending on patient condition
- ✅ A flexible endoscope is inserted through the mouth or rectum to reach the target area
- ✅ Argon gas is delivered through a catheter to conduct electrical energy to the tissue
- ✅ Targeted tissue is coagulated or ablated while preserving surrounding tissue
- ✅ The procedure usually lasts 15–60 minutes, depending on lesion size and location
- ✅ Patients are monitored for vital signs and oxygen levels throughout
3) What happens after an Argon Plasma Coagulation?
- ➤ Patients are observed for a few hours in recovery area
- ➤ Mild sore throat, bloating, or discomfort may occur after upper GI APC
- ➤ Diet is gradually resumed, starting with liquids
- ➤ Follow-up endoscopy may be scheduled to assess treatment efficacy
- ➤ Most patients resume normal activities within 24 hours
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Mild abdominal discomfort or bloating
- ➤ Rare perforation of the GI tract
- ➤ Rare bleeding after procedure
- ➤ Reaction to sedation
- ➤ Incomplete ablation requiring repeat procedures
Benefits:
- ✅ Minimally invasive and safe for high-risk patients
- ✅ Effective hemostasis and tissue ablation
- ✅ Precise targeting of vascular lesions or abnormal tissue
- ✅ Outpatient procedure with rapid recovery
- ✅ In Korea, modern APC devices and expert gastroenterologists ensure high success rates
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Usually outpatient; some patients may stay for observation if medically indicated
- Activity: Most patients resume normal activities within 24 hours
- Diet: Liquids first, gradually returning to normal diet
- Follow-up: Endoscopic review may be required to monitor lesion resolution or recurrence
- Long-term outcomes are generally excellent, with high success rates in controlling GI bleeding or abnormal tissue growth
- Repeat procedures are safe and effective if required
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Severe abdominal pain or persistent bloating
- ➤ Vomiting, especially with blood
- ➤ Signs of GI bleeding (dark stools, bright red blood)
- ➤ Fever or signs of infection
- ➤ Chest discomfort or difficulty swallowing after upper GI APC
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea provides state-of-the-art endoscopy centers performing APC for upper and lower GI conditions
- ✅ Hospitals use high-definition imaging and advanced APC devices for precision and safety
- ✅ Experienced gastroenterologists provide preoperative assessment, procedure, and post-procedure care
- ✅ Outpatient procedure allows rapid recovery, minimal hospital stay, and reduced complications
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking coordinators, and comprehensive follow-up
- ✅ APC in Korea ensures high success rates, safety, and effective GI bleeding or lesion management