Overview
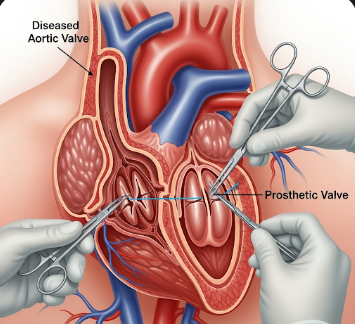
Aortic valve replacement (AVR) is a cardiac surgical procedure to replace a damaged or diseased aortic valve in the heart. The aortic valve regulates blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta and the rest of the body. When the valve is stenotic (narrowed) or regurgitant (leaky), it can lead to heart failure, chest pain, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
In Korea, AVR is performed in state-of-the-art cardiac centers by highly experienced cardiothoracic surgeons. Hospitals use advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), and robotic-assisted surgery, ensuring optimal outcomes, reduced complications, and faster recovery.
What is Aortic Valve Replacement?
Aortic valve replacement involves removing the diseased valve and replacing it with a mechanical or tissue (bioprosthetic) valve.
Types of Replacement Valves:
- Mechanical Valves:
- Made from durable materials like titanium or carbon
- Long-lasting, often lifelong
- Require lifelong anticoagulation to prevent blood clots
- Bioprosthetic (Tissue) Valves:
- Made from pig, cow, or human donor tissue
- Do not usually require long-term anticoagulation
- May need replacement after 10–20 years
Key points:
- Corrects aortic stenosis or regurgitation
- Improves heart function, blood flow, and quality of life
- Can be performed using traditional open-heart surgery or transcatheter minimally invasive approaches
What are the benefits?
- ✅ Restores normal blood flow and reduces heart strain
- ✅ Relieves symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath
- ✅ Prevents heart failure and other complications of valve disease
- ✅ Long-term survival benefit, especially for severe valve disease
- ✅ Minimally invasive or transcatheter options reduce recovery time and hospital stay
- ✅ In Korea, advanced surgical techniques maximize safety and success rates
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Aortic Valve Replacement?
- ➤ Comprehensive cardiac evaluation: Echocardiography, CT scan, angiography, and blood tests
- ➤ Review of current medications, including anticoagulants
- ➤ Preoperative counseling about procedure type, risks, recovery, and lifestyle adjustments
- ➤ Fasting and hospital preparation as instructed by the surgical team
- ➤ Arrange for postoperative care and rehabilitation support
2) What happens during the procedure Aortic Valve Replacement?
Open-heart AVR:
- ✅ Performed under general anesthesia
- ✅ Median sternotomy (chest incision) to access the heart
- ✅ Patient connected to cardiopulmonary bypass machine
- ✅ Diseased aortic valve is removed and replaced with mechanical or tissue valve
- ✅ Heart restarted, chest closed, and patient transferred to ICU
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR):
- ✅ Performed under local or general anesthesia
- ✅ Valve delivered via catheter through femoral artery or other access
- ✅ Diseased valve is expanded and secured in place
- ✅ Minimally invasive with no large chest incision
- ✅ Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery
3) What happens after Aortic Valve Replacement?
- ➤ Monitored in ICU for 1–2 days
- ➤ Pain management and anticoagulation therapy if mechanical valve used
- ➤ Gradual mobilization and breathing exercises
- ➤ Cardiac rehabilitation program to restore strength and endurance
- ➤ Hospital discharge typically 5–10 days for open surgery, 2–4 days for TAVR
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Infection or endocarditis
- ➤ Bleeding or blood clots
- ➤ Stroke or heart attack
- ➤ Valve malfunction or structural failure
- ➤ Arrhythmias or conduction abnormalities requiring pacemaker
- ➤ Rare complications related to anesthesia
Benefits:
- ✅ Corrects valve dysfunction and restores heart efficiency
- ✅ Relieves symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain
- ✅ Prevents heart failure and other long-term complications
- ✅ Long-term survival and quality of life improvement
- ✅ In Korea, advanced ICU care, monitoring, and minimally invasive options reduce risk
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: 5–10 days for open-heart AVR; 2–4 days for TAVR
- Activity: Gradual return to light activity; avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exertion initially
- Cardiac rehabilitation: Structured program to restore endurance, strength, and heart function
- Full recovery: Open-heart surgery 6–12 weeks; TAVR typically 2–4 weeks
- Lifestyle: Follow heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication adherence
When To Call the Doctor
- ➤ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- ➤ Chest pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath
- ➤ Swelling of legs or sudden weight gain (possible heart failure signs)
- ➤ Excessive bleeding or bruising (especially on anticoagulation)
- ➤ Any unusual symptoms after discharge
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea offers top-tier cardiac centers with world-class cardiothoracic surgeons
- ✅ Both traditional AVR and TAVR procedures are performed with high precision and low complication rates
- ✅ Comprehensive care includes preoperative evaluation, ICU monitoring, cardiac rehabilitation, and follow-up
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, English-speaking staff, and coordinated care
- ✅ Advanced surgical techniques and state-of-the-art facilities make Korea a preferred destination for aortic valve replacement