Overview
Amputation is a surgical procedure in which all or part of a limb (arm, leg, hand, or foot) is removed. It is generally performed to treat severe injuries, infections, circulation problems, or complications from diseases such as diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or cancer. Amputation can be life-saving in cases of trauma or uncontrolled infection and is also performed to improve overall quality of life when a limb is non-functional or causing chronic pain.
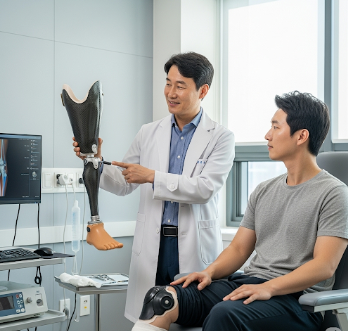
In Korea, amputation surgeries are performed in top hospitals with highly skilled orthopedic and vascular surgeons, modern operating theaters, and advanced prosthetic rehabilitation programs. Korean hospitals focus not only on surgical precision but also on post-amputation rehabilitation, including physical therapy, pain management, and prosthetic fitting, ensuring patients regain maximum independence.
What is Amputation?
Amputation involves the surgical removal of a limb or part of a limb. The level of amputation depends on the location and extent of damage, circulation, and overall health of the patient.
Types of amputation include:
- Partial amputation: Only a portion of a limb is removed (e.g., toes, fingers)
- Complete amputation: Entire limb (e.g., below or above the knee, below or above the elbow)
- Traumatic amputation: Resulting from an accident or injury
- Surgical amputation: Planned removal due to disease or medical necessity
The goal of amputation is to remove diseased or damaged tissue, prevent further complications, and optimize function and mobility with or without prosthetic support.
What are the benefits?
- Prevents the spread of infection or gangrene that could threaten life
- Relieves severe, chronic pain from non-functional limbs
- Improves mobility and independence with prosthetics
- Reduces complications from conditions like diabetes or peripheral artery disease
- ✅ In Korea, hospitals combine surgical expertise with advanced rehabilitation, ensuring patients adapt effectively to prosthetics
- ✅ Early amputation can prevent long-term disability and improve quality of life
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Amputation?
- ➤ Comprehensive medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging, and cardiovascular assessment
- ➤ Optimize underlying conditions, such as controlling blood sugar in diabetic patients or managing vascular disease
- ➤ Medication review; some drugs may need adjustment before surgery
- ➤ Preoperative counseling on post-surgery care, prosthetic options, and rehabilitation
- ➤ Emotional and psychological preparation, as amputation can significantly impact mental health
2) What happens during the procedure Amputation?
- ✅ Performed under general or regional anesthesia depending on patient condition
- ✅ The surgeon removes diseased tissue while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible
- ✅ Blood vessels, muscles, and nerves are carefully managed to prevent excessive bleeding and optimize residual limb function
- ✅ Bone is shaped to allow smooth healing and prosthetic fitting
- ✅ The wound is closed using sutures or staples, sometimes with drains to prevent fluid accumulation
- ✅ Bandages or compression wraps are applied to reduce swelling and support healing
3) What happens after an Amputation?
- ➤ Patients are monitored in the post-anesthesia care unit for vital signs and complications
- ➤ Pain management and medications for nerve-related pain (phantom limb pain) are provided
- ➤ Physical therapy begins as soon as medically feasible to maintain strength and mobility
- ➤ Wound care and residual limb shaping are essential for successful prosthetic fitting
- ➤ Patients receive emotional and psychological support to adjust to lifestyle changes
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Infection at the surgical site
- ➤ Bleeding or hematoma
- ➤ Poor wound healing or skin breakdown
- ➤ Phantom limb pain or neuroma formation
- ➤ Blood clots or cardiovascular complications
Benefits:
- ✅ Removes diseased or damaged tissue, preventing life-threatening complications
- ✅ Relieves chronic pain and discomfort
- ✅ Enables mobility with prosthetics
- ✅ Improves overall quality of life
- ✅ In Korea, comprehensive care and rehabilitation programs optimize functional outcomes
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery from amputation depends on the level and complexity of the surgery:
- Initial hospital stay: Typically 3–10 days, depending on health and type of amputation
- Wound healing: Residual limb heals within 4–8 weeks, sometimes longer for patients with diabetes or vascular disease
- Physical therapy: Begins early to maintain strength, prevent contractures, and prepare for prosthetic fitting
- Prosthetic fitting: Usually after residual limb is fully healed; modern prosthetics in Korea allow patients to regain mobility quickly
- Most patients regain independence and ability to perform daily activities, with continued improvements over months
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they experience:
- ➤ Redness, swelling, or discharge at the surgical site
- ➤ Persistent or worsening pain
- ➤ Fever or signs of infection
- ➤ Unusual bleeding or wound opening
- ➤ Difficulty adapting to prosthetic or residual limb pain
Best Korea Option / Process
- ✅ Korea is renowned for advanced orthopedic and vascular surgery, including amputation care
- ✅ Hospitals provide state-of-the-art surgical facilities, post-operative monitoring, and rehabilitation centers
- ✅ Expert surgeons ensure precise amputation and optimal residual limb care
- ✅ Comprehensive prosthetic services are available, with modern designs and functional customization
- ✅ International patients benefit from VIP services, including English-speaking coordinators, airport pickup, and rehabilitation planning
- ✅ Cost-effective treatment with high success rates and excellent functional outcomes