Overview
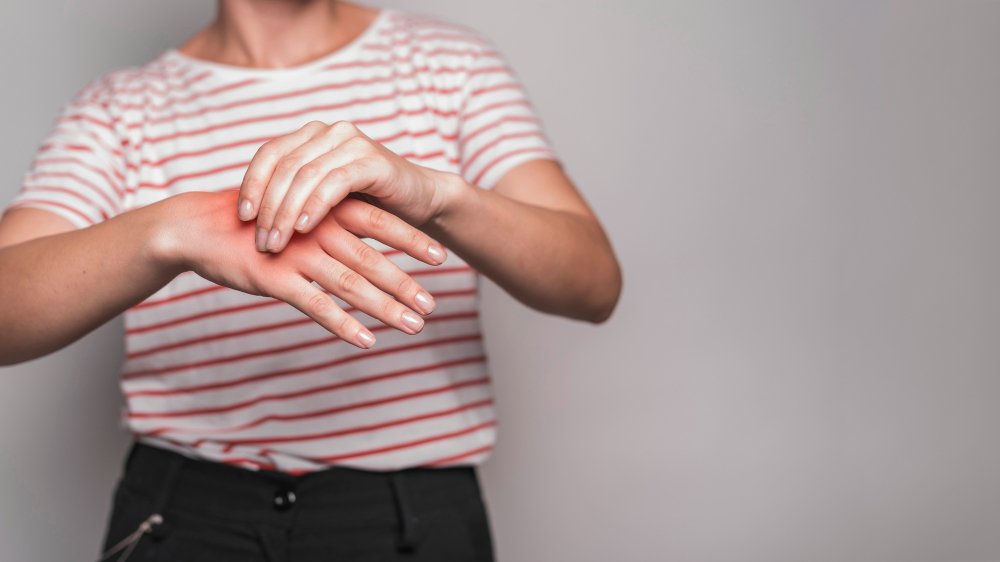
Wrist tendonitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the tendons in the wrist, often resulting in pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. It commonly occurs due to repetitive wrist movements, overuse, or strain, especially in individuals who perform manual tasks, type extensively, or engage in sports. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent progression to chronic tendon damage or long-term discomfort.
What is Wrist Tendonitis?
Wrist tendonitis (also called tenosynovitis when the sheath surrounding the tendon is involved) occurs when one or more tendons around the wrist become inflamed or irritated. Tendons are tough cords that connect muscles to bones, and in the wrist, they pass through tight tunnels. When these tendons are overused or injured, pain and inflammation develop, limiting wrist function.
Common types of wrist tendonitis include:
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis (thumb side of the wrist)
- Extensor or flexor tendonitis (back or palm side of the wrist)
Symptoms
Symptoms of wrist tendonitis may develop gradually or suddenly and include:
- Pain in the wrist that worsens with movement
- Swelling around the wrist joint
- Tenderness or warmth over the affected tendon
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- A grinding or creaking sensation during wrist movement
- Weak grip strength or discomfort when holding objects
Symptoms typically worsen during activities involving wrist movement or gripping.
Causes
Wrist tendonitis is most often caused by repetitive stress or overuse of the wrist, but other contributing factors include:
- Repetitive motions (typing, texting, writing, lifting)
- Manual labor or construction work
- Racquet or throwing sports (e.g., tennis, golf, baseball)
- Poor ergonomics or posture at a desk or workstation
- Sudden trauma or strain to the wrist
- Underlying inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at higher risk of developing wrist tendonitis, including:
- People with physically demanding jobs (e.g., factory workers, typists, hairdressers)
- Athletes involved in repetitive wrist activities
- Older adults, due to tendon degeneration
- People with poor wrist ergonomics or posture
- Individuals with diabetes, arthritis, or previous wrist injuries
- Pregnant women, particularly for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
Complications
If not properly treated, wrist tendonitis can lead to:
- Chronic pain or inflammation
- Tendon degeneration (tendinosis)
- Tendon rupture (in severe, neglected cases)
- Permanent stiffness or reduced mobility
- Difficulty performing everyday tasks like writing or lifting
- Development of compensatory pain in the elbow or shoulder due to overuse
Prevention
You can prevent wrist tendonitis with a combination of ergonomic care and healthy movement practices:
- Take frequent breaks during repetitive tasks
- Use ergonomic tools or workstations (e.g., wrist rests, adjustable keyboards)
- Warm up and stretch before and after activities involving the wrist
- Avoid prolonged pressure or extreme bending of the wrist
- Maintain proper form in sports or physical labor
- Strengthen wrist and forearm muscles through exercises
- Wear protective braces if engaging in repetitive or risky wrist activities
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers high-quality orthopedic and rehabilitation care for wrist tendonitis, with a variety of treatment options:
Conservative (non-surgical) treatments:
- Rest and activity modification
- Cold packs and anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs)
- Wrist splints or braces to immobilize the area
- Physical therapy to improve flexibility, strength, and posture
- Ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation in rehabilitation centers
- Corticosteroid injections for persistent inflammation
Surgical treatment:
- Reserved for severe or chronic cases where conservative measures fail
- Tendon release or repair surgery may be performed
- Minimally invasive techniques are often used in top Korean hospitals
Top centers such as Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Yonsei Severance Hospital provide expert care through orthopedic surgeons, rehabilitation specialists, and sports medicine experts. Patients also have access to cutting-edge therapy devices and personalized recovery programs.