Overview
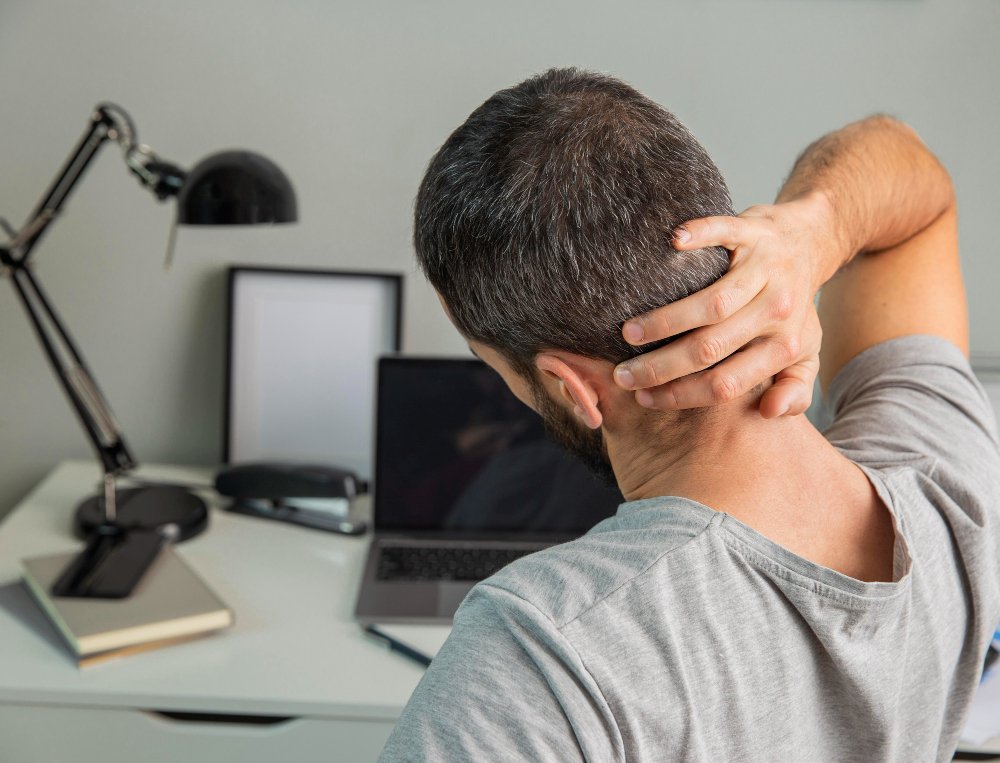
Whiplash, also known as neck strain or cervical acceleration–deceleration injury, is a soft tissue injury to the neck that occurs when the head is suddenly jerked backward and then forward. This motion overstretches and damages the muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the neck. Whiplash is most commonly associated with rear-end car accidents, but can also result from sports injuries, falls, or physical assault.
What is Whiplash (Neck Strain)?
Whiplash is a non-fracture injury to the neck caused by a sudden and forceful back-and-forth motion of the head. The condition primarily affects the cervical spine, including the muscles, discs, nerves, and soft tissues. It is considered a type of cervical sprain/strain. Symptoms may appear immediately or develop within days after the incident. While most cases resolve with conservative treatment, some individuals may experience chronic pain or long-term complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of whiplash can vary in intensity and may include:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Reduced range of motion in the neck
- Headaches, typically starting at the base of the skull
- Shoulder, upper back, or arm pain
- Tingling or numbness in the arms
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty concentrating or memory issues (in some cases)
- Sleep disturbances and irritability
Causes
Whiplash is caused by rapid acceleration and deceleration forces that snap the neck beyond its normal range of motion. Common causes include:
- Rear-end or side-impact car collisions
- Sports injuries (especially contact sports like football or boxing)
- Physical abuse or assault (e.g., shaking or punching)
- Falls or blows to the head or body
- Amusement park rides that involve sudden jolts
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase the likelihood or severity of whiplash:
- Previous neck injuries
- Poor posture or weak neck muscles
- Female gender (women may be more susceptible due to less neck muscle mass)
- Age – middle-aged individuals are often more affected
- Inadequate headrest positioning in vehicles
- Failure to wear seatbelts
Complications
While many people recover within a few weeks, whiplash can lead to long-term problems in some cases:
- Chronic neck pain or stiffness
- Persistent headaches
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) after serious accidents
- Cognitive difficulties such as memory loss or concentration issues
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction
- Reduced quality of life and work limitations
Prevention
Preventing whiplash involves improving safety and reducing risk during high-impact activities:
- Always wear a seatbelt when in a vehicle
- Adjust headrests properly – the top should be level with the top of your head
- Use proper neck support when sitting or sleeping
- Practice safe sports techniques, including use of protective gear
- Strengthen neck and upper back muscles with regular exercise
- Ensure workstations and driving positions are ergonomically sound
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive and advanced care for whiplash injuries through a combination of orthopedic, neurological, and physical therapy services. Treatment options include:
- Pain management with NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or local injections
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation – including stretching, strengthening, and posture correction
- Manual therapy or chiropractic care – under certified practitioners
- Trigger point injections or dry needling
- MRI or X-ray imaging – to rule out more serious injuries
- Acupuncture and traditional Korean medicine (TKM) – often integrated with conventional care
- Psychological counseling for trauma-related stress or chronic pain
- Care is widely available at orthopedic clinics and major hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Korea University Anam Hospital
With early intervention and multidisciplinary care, most whiplash patients in Korea recover fully without long-term effects.