Overview
Wernicke’s Aphasia, also known as receptive aphasia, is a type of language disorder that affects the ability to understand spoken or written language. People with this condition can produce fluent speech, but it often lacks meaning or includes nonsensical words. It typically results from damage to Wernicke’s area, a part of the brain responsible for language comprehension, and is most often caused by a stroke or head injury.
What is Wernicke’s Aphasia?
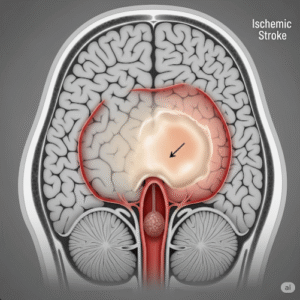
Wernicke’s Aphasia is a neurological language disorder that arises when the posterior part of the left superior temporal gyrus—known as Wernicke’s area—is damaged. Unlike other types of aphasia, individuals with Wernicke’s Aphasia speak with normal grammar, sentence length, and intonation. However, their speech may be nonsensical, contain made-up words, or lack relevance to the conversation. The hallmark symptom is impaired language comprehension. Reading and writing abilities are also often affected.
Symptoms
The primary signs and symptoms of Wernicke’s Aphasia include:
- Fluent but meaningless or jumbled speech
- Inability to understand spoken language
- Inappropriate or irrelevant word usage (semantic paraphasias)
- Neologisms – made-up words that sound like real words
- Unawareness of the language impairment (anosognosia)
- Difficulty reading and writing
- Impaired ability to follow conversations or instructions
Causes
Wernicke’s Aphasia is usually caused by damage to Wernicke’s area in the brain, most often due to:
- Ischemic stroke in the left middle cerebral artery territory
- Traumatic brain injury
- Brain tumors affecting the temporal lobe
- Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s or primary progressive aphasia
- Infections like encephalitis affecting the temporal lobe
Risk Factors
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing Wernicke’s Aphasia include:
- Advanced age
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
- Hypertension and cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Smoking
- Brain trauma or surgery
- Family history of neurological or vascular diseases
Complications
If not properly managed, Wernicke’s Aphasia can result in:
- Communication breakdown, affecting social and professional life
- Emotional and psychological distress, including depression or anxiety
- Frustration or isolation due to language barriers
- Dependence on caregivers for basic communication
- Misunderstanding of medical or safety instructions
- In rare cases, progression into global aphasia if brain damage expands
Prevention
While Wernicke’s Aphasia itself is not preventable, many of its underlying causes are. Preventive measures include:
- Stroke prevention through management of blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
- Healthy lifestyle choices – regular exercise, smoking cessation, and balanced diet
- Prompt treatment of brain injuries or infections
- Regular medical checkups for at-risk individuals
- Stroke awareness education, recognizing early signs (FAST: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call emergency services)
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is globally recognized for its advanced neurology and rehabilitation care. For patients with Wernicke’s Aphasia, available treatments include:
- Speech and language therapy – the cornerstone of recovery, focusing on comprehension and communication strategies
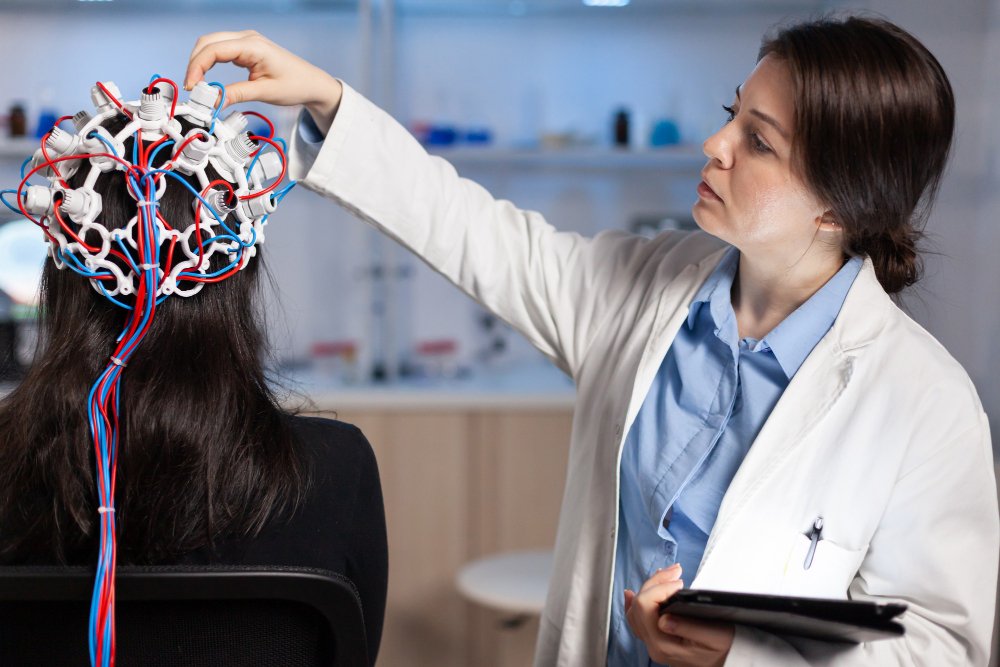
- Neurological evaluation and imaging – including MRI and CT scans for accurate diagnosis
- Pharmacological support – in selected cases, medications to improve neuroplasticity and mood
- Cognitive-linguistic therapy – using computer-assisted or manual exercises to stimulate brain recovery
- Multidisciplinary rehabilitation – involving neurologists, speech therapists, occupational therapists, and psychologists
- Family and caregiver education – to support communication at home
- Innovative treatments – such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) offered at some tertiary hospitals
- Leading centers such as Seoul National University Hospital, Yonsei Severance Hospital, and Asan Medical Center provide specialized aphasia clinics
With intensive therapy and support, many patients in Korea make significant progress in communication and regain independence.