Overview
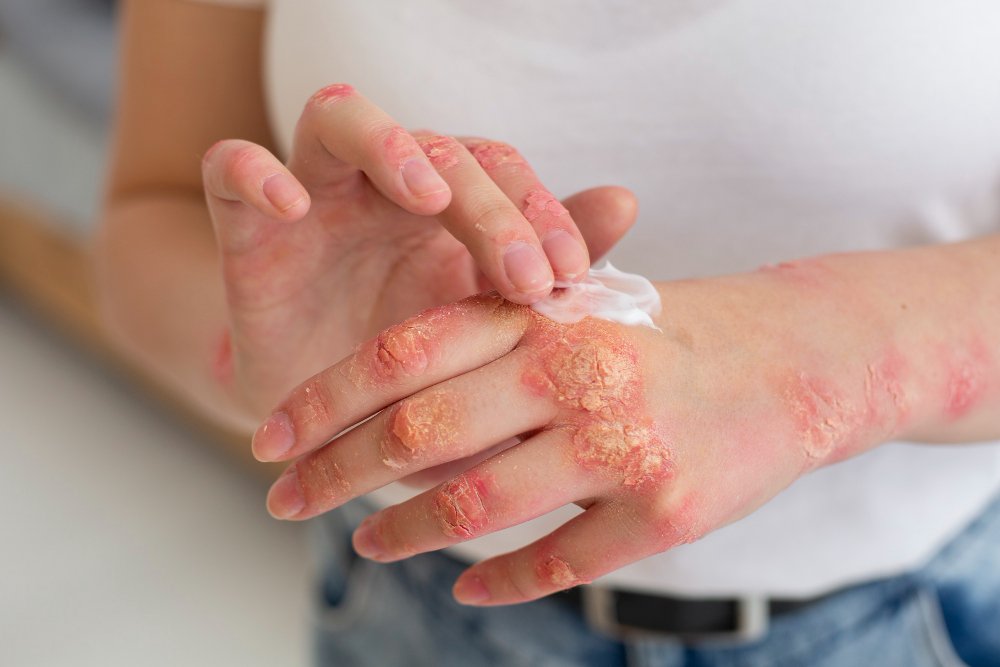
Weeping eczema is a severe and inflamed form of eczema where the skin becomes so irritated and damaged that it oozes clear or yellow fluid. This fluid is usually a sign of inflammation or infection. Also known as exudative eczema, this condition can be painful and distressing, often requiring medical treatment to control flare-ups and prevent complications.
What is Weeping Eczema?
Weeping eczema is not a distinct type of eczema but a stage or complication of various eczema types, such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, or nummular eczema. It occurs when the skin becomes so inflamed that fluid leaks from broken or blistered skin. In many cases, this fluid build-up is a sign of secondary bacterial infection, especially by Staphylococcus aureus. If left untreated, the condition can worsen rapidly.
Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of weeping eczema include:
- Oozing or crusting skin lesions
- Yellow, clear, or honey-colored fluid drainage
- Intense redness and inflammation
- Swelling and warmth in affected areas
- Cracked, blistered, or broken skin
- Pain or burning sensation
- Itching and discomfort
- Possible fever or malaise in cases of systemic infection
Causes
Weeping eczema results from severe inflammation or infection of previously irritated skin. Common causes include:
- Underlying eczema (e.g., atopic or allergic dermatitis)
- Skin barrier damage due to scratching or harsh irritants
- Bacterial infection, especially Staphylococcus aureus
- Fungal or viral infections (less common)
- Allergic reactions to soaps, chemicals, or fabrics
- Excessive sweating or heat, exacerbating skin inflammation
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing weeping eczema include:
- Pre-existing eczema or dermatitis
- Weakened immune system
- Poor hygiene or over-washing of skin
- Living in hot, humid climates
- Contact with allergens or irritants
- Use of harsh soaps or topical products
- Secondary infection from scratching
- Wearing non-breathable or irritating clothing
Complications
If not treated promptly, weeping eczema can lead to serious complications such as:
- Widespread skin infection (impetiginization)
- Cellulitis, a deep bacterial skin infection
- Scarring or skin thickening from chronic scratching
- Sepsis in extreme cases if infection spreads systemically
- Emotional and psychological distress due to appearance and discomfort
- Chronic or recurring flare-ups
Prevention
Preventing weeping eczema involves good skin care practices and prompt management of eczema flare-ups:
- Moisturize regularly with hypoallergenic creams
- Avoid scratching and use antihistamines to reduce itch
- Identify and avoid triggers, such as allergens or harsh soaps
- Use gentle, fragrance-free products
- Keep fingernails short to avoid skin damage
- Treat eczema early to prevent infection
- Maintain good hygiene, but avoid over-washing or drying the skin
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers world-class dermatology services with both conventional and advanced therapies for weeping eczema. Treatment options include:
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Antibiotic creams or oral antibiotics for infected eczema
- Wet dressings and bandaging to soothe and protect oozing areas
- Calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus) as steroid-sparing agents
- Moisturizing therapy using medical-grade emollients
- Phototherapy (narrowband UVB) in chronic or severe cases
- Allergy testing and immunotherapy for recurring flare-ups
- Custom treatment plans from top clinics like Seoul National University Hospital, Yonsei Severance Dermatology, and private skin centers
South Korean dermatologists provide personalized care for both children and adults, using a combination of modern techniques and holistic approaches to manage weeping eczema effectively.