Overview
Vitamin K deficiency is a condition characterized by inadequate levels of vitamin K, a crucial nutrient required for proper blood clotting and bone health. Deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding and impaired bone metabolism. It can affect people of all ages, but newborns and individuals with certain medical conditions are particularly at risk. South Korea offers advanced diagnostic tools and effective treatments to manage vitamin K deficiency and prevent complications.
What is Vitamin K Deficiency?
Vitamin K deficiency occurs when the body lacks sufficient vitamin K to produce clotting factors needed for blood coagulation. Without enough vitamin K, blood clotting is impaired, leading to a higher risk of bleeding and bruising. Vitamin K also plays an important role in maintaining healthy bones by activating proteins involved in bone mineralization.
Symptoms
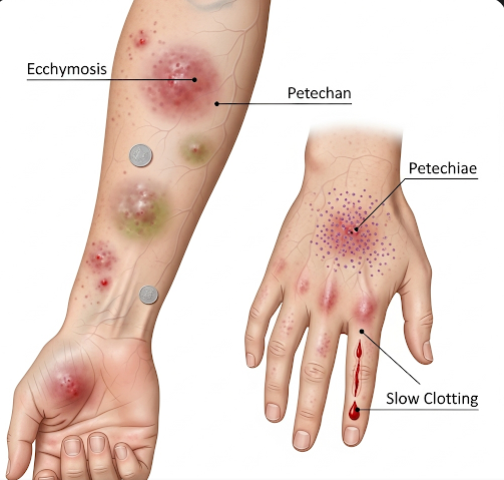
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries
- Nosebleeds or bleeding gums
- Blood in urine or stool
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- In severe cases, internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening
- In infants, vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB) can cause serious brain hemorrhages
Causes
- Poor dietary intake of vitamin K-rich foods such as leafy green vegetables
- Malabsorption disorders like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or cystic fibrosis
- Use of antibiotics that disrupt gut bacteria which produce vitamin K
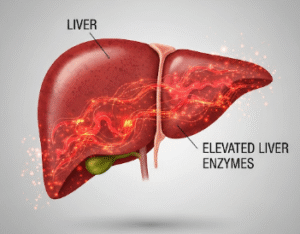
- Liver diseases impairing vitamin K metabolism
- Newborns with low vitamin K stores at birth
- Use of blood-thinning medications like warfarin (if not properly monitored)
Risk Factors
- Newborn infants, especially if not given vitamin K prophylaxis at birth
- People with chronic gastrointestinal diseases
- Individuals on long-term antibiotics or anticoagulant therapy
- Malnourished individuals
- People with liver disease or bile duct obstruction
Complications
- Severe bleeding episodes, including internal bleeding
- Hemorrhagic disease of the newborn (a serious condition causing brain bleeds)
- Increased risk of fractures due to poor bone mineralization
- Excessive bleeding during surgery or trauma
Prevention
- Routine vitamin K injections for newborns shortly after birth
- Consuming a diet rich in vitamin K (leafy greens, broccoli, cabbage)
- Monitoring and managing anticoagulant medication carefully
- Treating underlying malabsorption or liver conditions
- Regular screening in at-risk patients
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides effective treatment strategies for vitamin K deficiency:
- Vitamin K supplementation – Oral or injectable vitamin K to quickly restore levels
- Dietary advice – Encouraging intake of vitamin K-rich foods
- Management of underlying disorders – Addressing malabsorption or liver dysfunction
- Careful monitoring – For patients on anticoagulants to balance bleeding risks
- Newborn care programs – Routine vitamin K prophylaxis to prevent hemorrhagic disease
- Laboratory diagnostics – Blood clotting tests (PT/INR) to assess vitamin K status