Overview
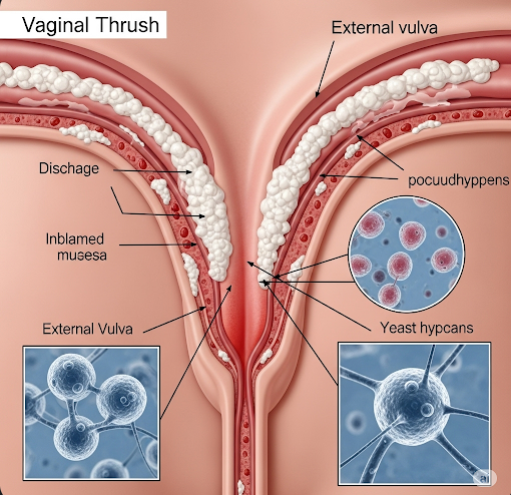
Vaginal thrush, also known as vaginal yeast infection or candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida species, usually Candida albicans. It affects many women at some point in their lives, causing itching, irritation, and abnormal discharge. Although not considered a sexually transmitted infection, sexual activity can sometimes trigger symptoms. Vaginal thrush is usually harmless if treated promptly but can cause discomfort and may recur if underlying causes are not addressed.
What is Vaginal Thrush?
Vaginal thrush occurs when the natural balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina is disrupted, allowing Candida to multiply excessively. This imbalance can result from hormonal changes, antibiotic use, immune suppression, or other lifestyle factors. The infection is generally mild to moderate but can become chronic or severe in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms
- Intense itching and irritation in the vaginal area
- Thick, white, cottage cheese-like vaginal discharge (usually odorless)
- Redness and swelling of the vulva
- Burning sensation during urination
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Vaginal soreness
Causes
- Overgrowth of Candida albicans due to imbalance in vaginal flora
- Antibiotic use, which reduces protective bacteria (Lactobacillus)
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause
- Weakened immune system from illness or medication
- High-sugar diet, which encourages fungal growth
- Wearing tight, non-breathable underwear
- Prolonged moisture in the genital area
Risk Factors
- Frequent antibiotic use
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes (especially if poorly controlled)
- Immunosuppressive medications or conditions
- Hormonal contraceptives
- High carbohydrate or sugar intake
- Wearing synthetic or tight-fitting underwear
Complications
If untreated or recurrent, vaginal thrush may lead to:
- Chronic yeast infections
- Increased discomfort during sex
- Spread to other areas such as the skin folds
- Emotional distress and reduced quality of life
- Difficulty in distinguishing symptoms from other infections, leading to delayed proper treatment
Prevention
- Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight clothing
- Keep the genital area dry and clean
- Avoid using scented soaps, bubble baths, or vaginal douches
- Limit sugar intake
- Take probiotics or eat yogurt to maintain healthy vaginal flora
- Change out of wet clothing (swimwear, workout clothes) promptly
- Use antibiotics only when prescribed and necessary
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers effective, advanced treatment options for vaginal thrush, including:
- Antifungal medications – Oral (fluconazole) or topical (clotrimazole, miconazole) treatments are commonly prescribed.
- Prescription creams and suppositories – Direct application inside the vagina for targeted relief.
- Probiotic therapy – Restoring healthy vaginal flora through supplements or probiotic-rich foods.
- Advanced diagnostic testing – Korean clinics use PCR and culture tests to confirm Candida type and tailor treatment.
- Laser therapy – In chronic or recurrent cases, non-invasive vaginal laser treatment may improve tissue health and resistance to infection.
- Integrated care – Combination of medication, diet counseling, and hygiene education to prevent recurrence.