Overview
Vaginal problems refer to a wide range of conditions that can affect the structure, function, and overall health of the vagina. These may include infections, inflammation, hormonal changes, injuries, and structural abnormalities. While some vaginal issues are temporary and easily treatable, others may indicate underlying medical conditions that require prompt attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications and maintain reproductive and sexual health.
What is Vaginal Problems?
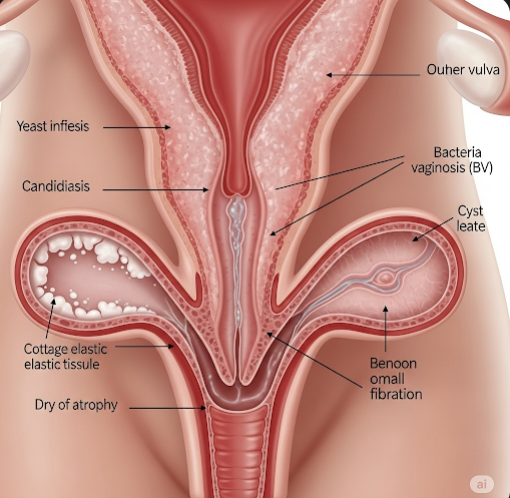
Vaginal problems are disorders or conditions that cause discomfort, abnormal discharge, itching, pain, swelling, bleeding, or other changes in the vaginal area. They can be caused by infections (bacterial, fungal, or viral), hormonal imbalances, allergic reactions, or trauma. Common examples include bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, vaginal dryness, vaginitis, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and injuries due to childbirth or sexual activity.
Symptoms
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (unusual color, odor, or consistency)
- Itching, burning, or irritation in the vaginal area
- Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Vaginal dryness
- Swelling or redness around the vagina
- Unusual vaginal bleeding (outside of menstruation)
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Painful urination
Causes
- Infections – Bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, STIs
- Hormonal changes – Menopause, pregnancy, birth control use
- Poor hygiene – Improper cleaning, prolonged use of wet clothing
- Allergic reactions – Soaps, detergents, sanitary products
- Trauma – Childbirth injuries, sexual trauma
- Medical conditions – Endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease
Risk Factors
- Unprotected sexual activity
- Multiple sexual partners
- Use of irritating feminine products
- Weakened immune system
- Hormonal fluctuations (menopause, pregnancy)
- Poor genital hygiene
- Diabetes or other chronic health conditions
Complications
If left untreated, vaginal problems can lead to:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Infertility
- Spread of infections to the reproductive tract (e.g., pelvic inflammatory disease)
- Increased risk of acquiring or transmitting STIs
- Emotional distress and reduced sexual satisfaction
Prevention
- Practice safe sex using condoms
- Maintain good genital hygiene (gentle cleaning, breathable underwear)
- Avoid scented soaps, douches, or harsh feminine products
- Change wet clothing promptly after swimming or exercise
- Maintain a healthy diet and immune system
- Get regular gynecological check-ups
Treatment Options in Korea
In South Korea, treatment for vaginal problems is advanced and tailored to the cause. Common approaches include:
- Medications – Antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungals for yeast infections, antivirals for herpes or HPV-related issues
- Hormonal therapy – Estrogen creams or tablets for vaginal dryness due to menopause
- Laser therapy – Vaginal rejuvenation lasers for dryness and tissue repair
- Minimally invasive surgery – For structural problems or severe trauma
- Specialized clinics – Women’s health centers in Korea offer state-of-the-art diagnostics (PCR tests, vaginal pH testing) and personalized treatment plans
- Counseling & education – Support for sexual health and hygiene practices