Overview
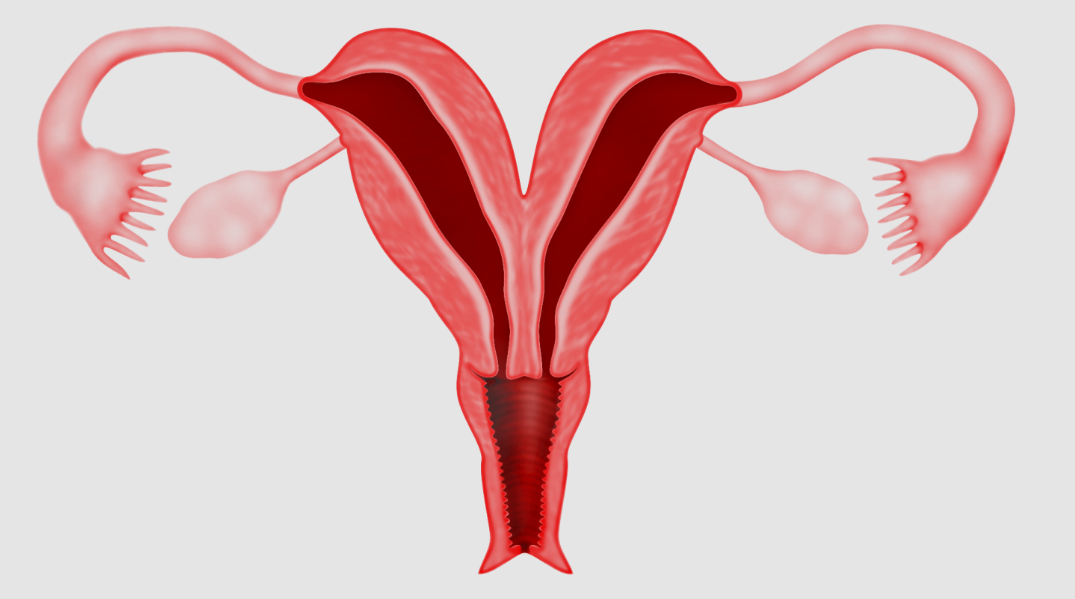
Unicornuate Uterus is a rare congenital uterine anomaly in which a woman is born with only one half of a uterus instead of a normal, pear-shaped organ. This malformation occurs during fetal development and may affect fertility, menstrual function, and pregnancy outcomes. Many women remain undiagnosed until they experience difficulty conceiving or maintaining a pregnancy.
What is Unicornuate Uterus
Unicornuate Uterus is a type of Müllerian duct anomaly where only one of the two embryologic uterine ducts (Müllerian ducts) fully develops. As a result, the uterus is smaller, asymmetrical, and may be connected to a small, underdeveloped remnant called a rudimentary horn. In some cases, this horn is non-communicating, meaning menstrual blood can become trapped, causing pain or complications. While some women with this condition may conceive, there is a higher risk of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or premature delivery.
Symptoms
- Irregular or painful menstruation (especially with a non-communicating horn)
- Recurrent pregnancy loss
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Preterm labor or abnormal fetal positioning
- Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation
- Often asymptomatic and only discovered during imaging for fertility evaluation
Causes
Unicornuate Uterus is caused by an abnormality in fetal development of the Müllerian ducts, which form the female reproductive tract:
- One duct fails to develop or only partially develops
- The other duct may develop normally or with a small rudimentary horn
- The condition arises spontaneously and is not linked to behavior or environmental factors during pregnancy
Risk Factors
- Congenital origin: Present from birth, not influenced by lifestyle
- Family history of uterine anomalies (rare but possible)
- Associated renal abnormalities: Kidney malformations often co-occur
- Women undergoing fertility treatment, where anomalies are more likely to be discovered
Complications
- Infertility or subfertility
- First-trimester miscarriage
- Second-trimester pregnancy loss
- Ectopic pregnancy, particularly in the rudimentary horn
- Preterm birth or intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
- Uterine rupture (especially during pregnancy in a rudimentary horn)
- Menstrual retention and hematometra (if horn is non-communicating)
Prevention
Unicornuate Uterus cannot be prevented, as it results from a developmental anomaly before birth. However, early diagnosis and careful monitoring can help manage reproductive risks:
- Early imaging (MRI, 3D ultrasound, or hysterosalpingography) for women with fertility problems
- Screening for kidney anomalies, as urinary tract defects often coexist
- Genetic counseling in rare familial cases
- Pre-pregnancy planning and high-risk obstetric care for affected women
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced diagnostic tools and specialized reproductive care for women with congenital uterine anomalies, including Unicornuate Uterus:
- Advanced imaging: MRI and 3D ultrasound to accurately diagnose uterine shape and associated structures
- Surgical removal of a rudimentary horn: If non-communicating and causing pain or risk of ectopic pregnancy
- Fertility support: Including ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF)
- High-risk pregnancy monitoring: Specialized care throughout pregnancy to manage risks of preterm labor, malpresentation, and miscarriage
- Cervical cerclage: May be used to prevent second-trimester loss in women with cervical insufficiency
- Psychological counseling: For women coping with infertility or pregnancy loss
With individualized treatment and access to cutting-edge reproductive medicine, many women with a Unicornuate Uterus in Korea successfully conceive and deliver healthy babies.